|
Continuum (theory)
Continuum (: continua or continuums) theories or models explain variation as involving gradual quantitative transitions without abrupt changes or discontinuities. In contrast, categorical theories or models explain variation using qualitatively different states. In physics In physics, for example, the space-time continuum model describes space and time as part of the same continuum rather than as separate entities. A spectrum in physics, such as the electromagnetic spectrum, is often termed as either continuous (with energy at all wavelengths) or discrete (energy at only certain wavelengths). In contrast, quantum mechanics uses quanta, certain defined amounts (i.e. categorical amounts) which are distinguished from continuous amounts. In mathematics and philosophy A good introduction to the philosophical issues involved is John Lane Bell's essay in the ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy''. A significant divide is provided by the law of excluded middle. It determ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level Of Measurement
Level of measurement or scale of measure is a classification that describes the nature of information within the values assigned to variables. Psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens developed the best-known classification with four levels, or scales, of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. This framework of distinguishing levels of measurement originated in psychology and has since had a complex history, being adopted and extended in some disciplines and by some scholars, and criticized or rejected by others. Other classifications include those by Mosteller and Tukey, and by Chrisman. Stevens's typology Overview Stevens proposed his typology in a 1946 ''Science'' article titled "On the theory of scales of measurement". In that article, Stevens claimed that all measurement in science was conducted using four different types of scales that he called "nominal", "ordinal", "interval", and "ratio", unifying both " qualitative" (which are described by his "nominal" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (or Leibnitz; – 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat who is credited, alongside Sir Isaac Newton, with the creation of calculus in addition to many other branches of mathematics, such as binary arithmetic and statistics. Leibniz has been called the "last universal genius" due to his vast expertise across fields, which became a rarity after his lifetime with the coming of the Industrial Revolution and the spread of specialized labor. He is a prominent figure in both the history of philosophy and the history of mathematics. He wrote works on philosophy, theology, ethics, politics, law, history, philology, games, music, and other studies. Leibniz also made major contributions to physics and technology, and anticipated notions that surfaced much later in probability theory, biology, medicine, geology, psychology, linguistics and computer science. Leibniz contributed to the field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
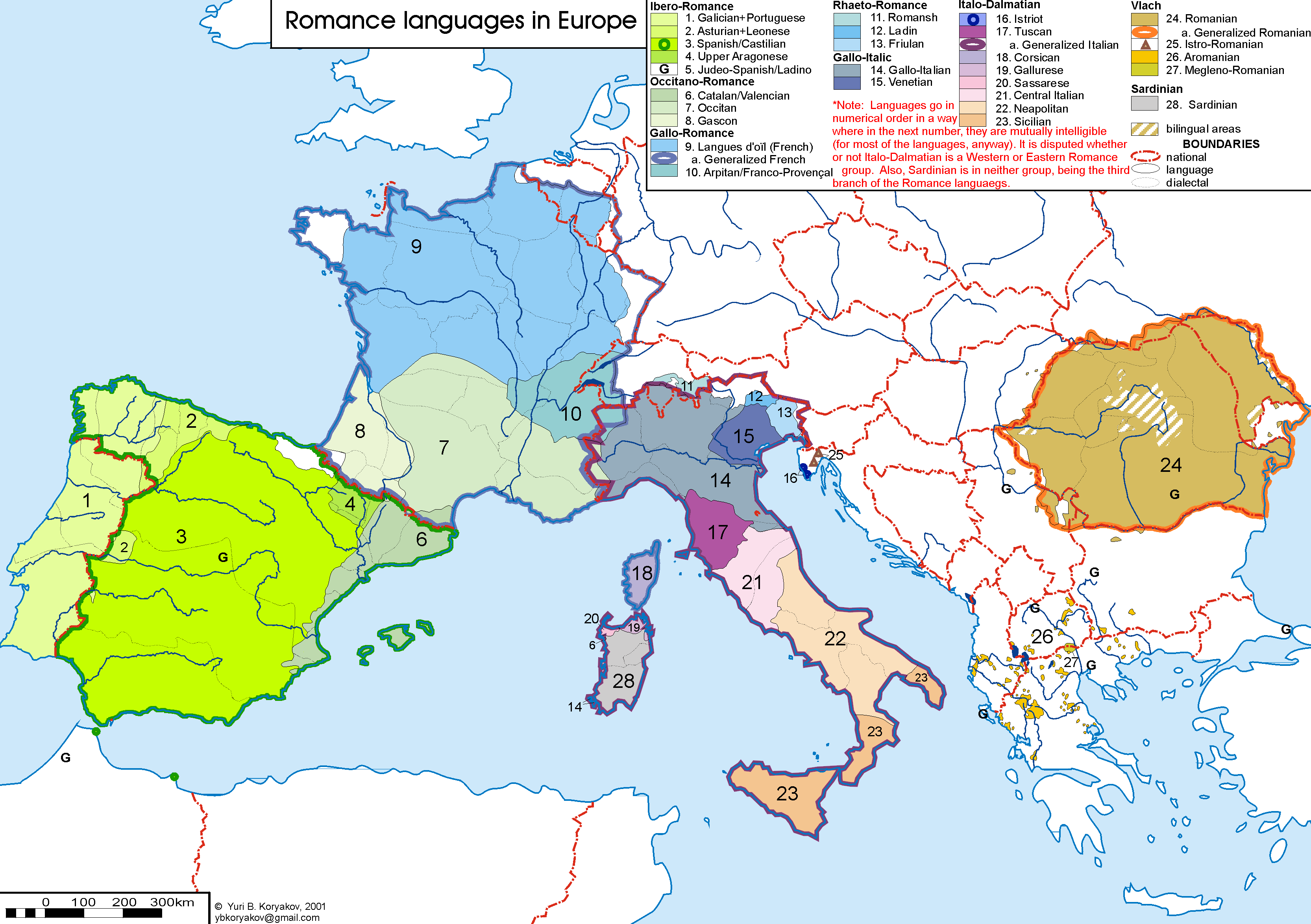
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect Continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of Variety (linguistics), language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated varieties may not be. This is a typical occurrence with widely spread languages and language families around the world, when these languages did not spread recently. Some prominent examples include the Indo-Aryan languages across large parts of India, varieties of Arabic across north Africa and southwest Asia, the Turkic languages, the varieties of Chinese, and parts of the Romance languages, Romance, Germanic languages, Germanic and Slavic languages, Slavic families in Europe. Terms used in older literature include dialect area (Leonard Bloomfield) and L-complex (Charles F. Hockett). Dialect continua typically occur in long-settled agrarian populations, as innovations spread from their various poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardized varieties, such as those used in developing countries or isolated areas. The non-standard dialects of a language with a writing system will operate at different degrees of distance from the standardized written form. Standard and nonstandard dialects A ''standard dialect'', also known as a "standardized language", is supported by institutions. Such institutional support may include any or all of the following: government recognition or designation; formal presentation in schooling as the "correct" form of a language; informal monitoring of everyday Usage (language), usage; published grammars, dictionaries, and textbooks that set forth a normative spoken and written form; and an extensive formal literature (be it prose, poetry, non-ficti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethics
Ethics is the philosophy, philosophical study of Morality, moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates Normativity, normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches include normative ethics, applied ethics, and metaethics. Normative ethics aims to find general principles that govern how people should act. Applied ethics examines concrete ethical problems in real-life situations, such as abortion, treatment of animals, and Business ethics, business practices. Metaethics explores the underlying assumptions and concepts of ethics. It asks whether there are objective moral facts, how moral knowledge is possible, and how moral judgments motivate people. Influential normative theories are consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics. According to consequentialists, an act is right if it leads to the best consequences. Deontologists focus on acts themselves, saying that they must adhere to Duty, duties, like t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociology
Sociology is the scientific study of human society that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of Interpersonal ties, social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. The term sociology was coined in the late 18th century to describe the scientific study of society. Regarded as a part of both the social sciences and humanities, sociology uses various methods of Empirical research, empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge about social order and social change. Sociological subject matter ranges from Microsociology, micro-level analyses of individual interaction and agency (sociology), agency to Macrosociology, macro-level analyses of social systems and social structure. Applied sociological research may be applied directly to social policy and welfare, whereas Theory, theoretical approaches may focus on the understanding of social processes and phenomenology (sociology), phenomenologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichotomy
A dichotomy () is a partition of a set, partition of a whole (or a set) into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be * jointly exhaustive: everything must belong to one part or the other, and * mutually exclusive: nothing can belong simultaneously to both parts. If there is a concept A, and it is split into parts B and not-B, then the parts form a dichotomy: they are mutually exclusive, since no part of B is contained in not-B and vice versa, and they are jointly exhaustive, since they cover all of A, and together again give A. Such a partition is also frequently called a bipartition. The two parts thus formed are Complement (set theory), complements. In logic, the partitions are dual (category theory), opposites if there exists a proposition such that it holds over one and not the other. Treating continuous variables or multicategorical variables as binary variables is called discretization, dichotomization. The discretization error inherent in dichoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levels Of Measurement
Level of measurement or scale of measure is a classification that describes the nature of information within the values assigned to dependent and independent variables, variables. Psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens developed the best-known classification with four levels, or scales, of measurement: #Nominal level, nominal, #Ordinal scale, ordinal, #Interval scale, interval, and #Ratio scale, ratio. This framework of distinguishing levels of measurement originated in psychology and has since had a complex history, being adopted and extended in some disciplines and by some scholars, and criticized or rejected by others. Other classifications include those by Mosteller and John Tukey, Tukey, and by Chrisman. Stevens's typology Overview Stevens proposed his typology in a 1946 ''Science (journal), Science'' article titled "On the theory of scales of measurement". In that article, Stevens claimed that all measurement in science was conducted using four different types of scales tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of society", established in the 18th century. It now encompasses a wide array of additional academic disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, economics, geography, history, linguistics, management, communication studies, psychology, culturology, and political science. The majority of positivist social scientists use methods resembling those used in the natural sciences as tools for understanding societies, and so define science in its stricter modern sense. Speculative social scientists, otherwise known as interpretivist scientists, by contrast, may use social critique or symbolic interpretation rather than constructing empirically falsifiable theories, and thus treat science in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonstandard Analysis
The history of calculus is fraught with philosophical debates about the meaning and logical validity of fluxions or infinitesimal numbers. The standard way to resolve these debates is to define the operations of calculus using (ε, δ)-definition of limit, limits rather than infinitesimals. Nonstandard analysis instead reformulates the calculus using a logically rigorous notion of infinitesimal numbers. Nonstandard analysis originated in the early 1960s by the mathematician Abraham Robinson. He wrote: ... the idea of infinitely small or ''infinitesimal'' quantities seems to appeal naturally to our intuition. At any rate, the use of infinitesimals was widespread during the formative stages of the Differential and Integral Calculus. As for the objection ... that the distance between two distinct real numbers cannot be infinitely small, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz argued that the theory of infinitesimals implies the introduction of ideal numbers which might be infinitely small or inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |