|
Contax
Contax (stylised as CONTAX in the Yashica/Kyocera era) began as a German camera model in the Zeiss Ikon line in 1932, and later became a brand name. The early cameras were among the finest in the world, typically featuring high quality Carl Zeiss AG, Zeiss interchangeable Photographic lens, lenses. The final products under the Contax name were a line of 135 film, 35 mm, medium format, and digital cameras engineered and manufactured by Japanese multinational Kyocera, and featuring modern Zeiss optics. In 2005, Kyocera announced that it would no longer produce Contax cameras. The rights to the brand are currently part of Carl Zeiss AG, but no Contax cameras are currently in production, and the brand is considered dormant. Historical overview While the firm of Ernst Leitz of Wetzlar established the 24 mm × 36 mm negative format on perforated 35 mm movie film as a viable photographic system, Zeiss Ikon of Dresden decided to produce a competitor designed to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeiss Ikon
Zeiss ( ; ) is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany, in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe (joined 1866) and Otto Schott (joined 1884) he laid the foundation for today's multinational company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue (Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology) in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide. Carl Zeiss AG is the holding of all subsidiaries within Zeiss Group, of which Carl Zeiss Meditec AG is the only one that is traded at the stock market. Carl Zeiss AG is owned by the foundation Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung. The Zeiss Group has its headquarters in southern Germany, in the small town of Oberkochen, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Zeiss AG
Zeiss ( ; ) is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany, in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe (joined 1866) and Otto Schott (joined 1884) he laid the foundation for today's multinational company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue (Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology) in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide. Carl Zeiss AG is the holding of all subsidiaries within Zeiss Group, of which Carl Zeiss Meditec AG is the only one that is traded at the stock market. Carl Zeiss AG is owned by the foundation Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung. The Zeiss Group has its headquarters in southern Germany, in the small town of Oberkochen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yashica
was a Japanese manufacturer of cameras, lenses, and film editing equipment active from 1949 until 2005 when its then-owner, Kyocera, ceased production. It acquired the lens manufacturer Tomioka (Tomioka Optical Co., Ltd). In 2008, the Yashica name reappeared on cameras produced by the Hong Kong–based MF Jebsen Group. In 2015, trademark rights were transferred to Yashica International Company Limited and appointed 100 Enterprises International Group Co. Limited as Yashica Global Sole Agent. History The company began in December 1949 in Nagano Prefecture, Nagano, Japan, when the Yashima Seiki Company was founded with an initial investment of $566.Heiberg, Milton, ''The Yashica Guide, A Modern Camera Guide Series Book'', New York: Amphoto Press, , p. 10 Its eight employees originally manufactured components for electric clocks.Heiberg, p. 10 Later, they began making camera components, and by June 1953 had introduced their first complete camera, the Yashimaflex, a Twin lens refl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
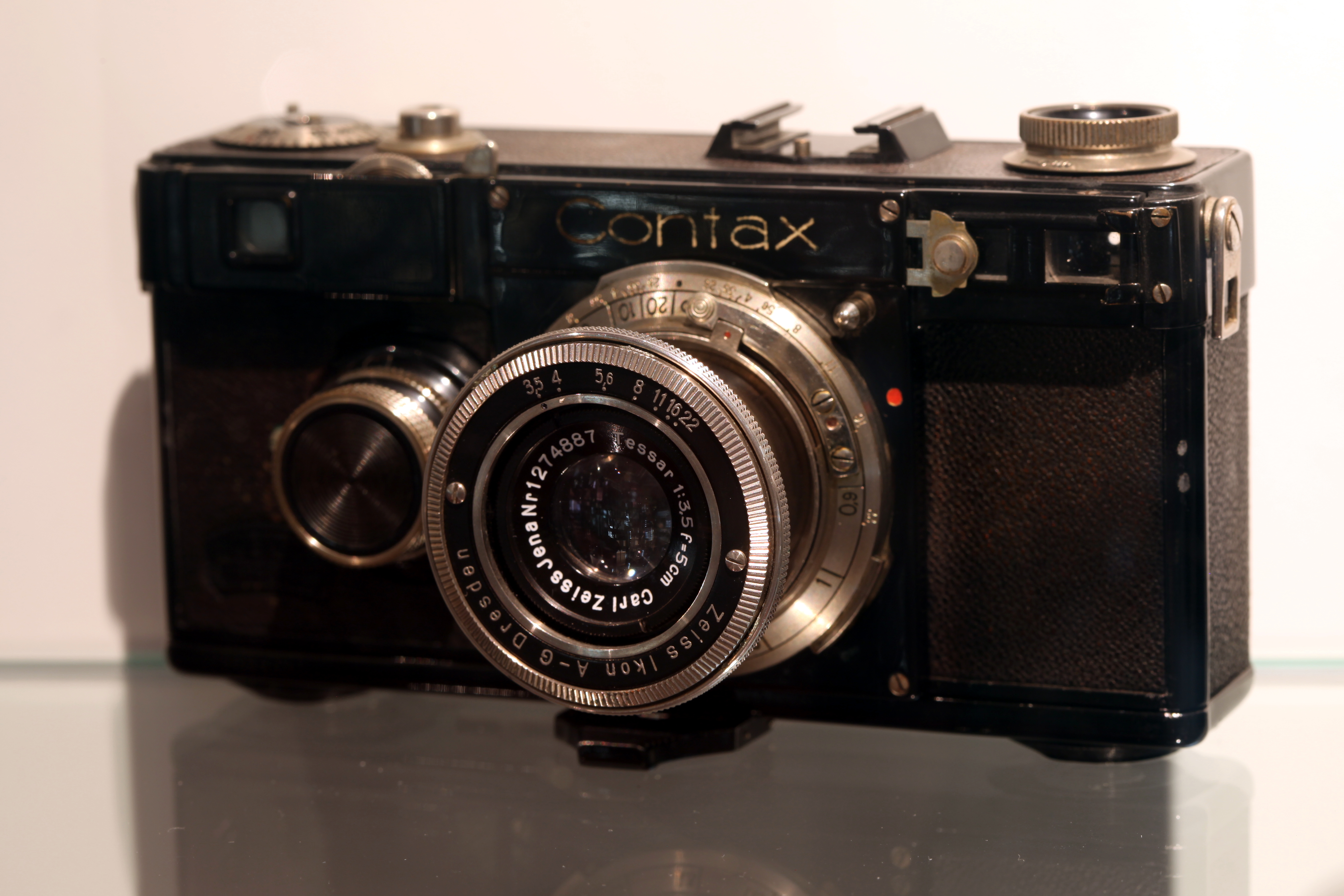
Contax II
The Contax II is a 35 mm rangefinder camera. It was released in 1936 and was the successor of the original Contax later called the Contax I. It was the first camera with a rangefinder and viewfinder combined in a single window. Its chief designer was Hubert Nerwin. The Nettax was meant to be a cheaper alternative, it was a derivative of the Super Nettel with a rigid body and interchangeable lenses with a specific bayonet and a very limited range of lenses. The Contax ll was the impressive Zeiss response to the popularity and demand for the Leica 35mm camera. This demand for high quality 35mm picture making tools was based on portability and the increasing availability of 35mm motion picture film, packaged into spools and marketed to amateur as well as professional photographers. The Contax became the 'first choice' among the professional community while the Leica was considered more the choice for well heeled amateurs and practitioners of a more artistic leaning. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contax I
The Contax I, or Original Contax, is a 35 mm rangefinder camera made between 1932 and 1936 by Zeiss Ikon. The Contax I had six identifiable variants, but fundamentally identical; every aspect was designed to outperform the Leica. For instance, the removable back was for faster loading and reloading, the bayonet lens mount was designed for rapid lens interchangeability, the long-base rangefinder allowed more accurate focusing, and the vertical metal shutter not only gave a faster maximum speed but also banished the problem of shutter blinds burning. History In 1932, Zeiss Ikon of Dresden decided to produce a competitor to the Leica II, designed to be superior in every way. The name Contax was chosen after a poll among its employees. Dr. Ing. Heinz Kuppenbender was listed On patents as the inventor of this camera. But, in fact, Dr. Emanuel Goldberg was the designer of the Contax. Goldberg continued to work on this camera design until he was forced to leave Dresden in 1933 for Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-lens Reflex Camera
In photography, a single-lens reflex camera (SLR) is a type of camera that uses a mirror and prism system to allow photographers to view through the lens and see exactly what will be captured. SLRs became the dominant design for professional and consumer-level cameras throughout the late 20th century, offering interchangeable lenses, through-the-lens (TTL) metering, and precise framing. Originating in the 1930s and popularized in the 1960s and 70s, SLR technology played a crucial role in the evolution of modern photography. Although digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) cameras succeeded film-based models, the rise of Mirrorless camera, mirrorless cameras in the 2010s has led to a decline in SLR use and production. With twin lens reflex and rangefinder cameras, the viewed image could be significantly different from the final image. When the shutter button is pressed on most SLRs, the mirror flips out of the light path and allows light to pass through to the light receptor and the im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeiss Sonnar
The Zeiss Sonnar is a photographic lens originally designed by Dr. Ludwig Bertele in 1929 and patented by Zeiss Ikon. It was notable for its relatively light weight, simple design and fast aperture. Naming The name "Sonnar" is derived from the German word " Sonne", meaning sun. It was originally a tradename owned by in for a Tessar-like lens. Sontheim's coat of arms includes a symbol of the sun. Nettel merged with August Nagel's in 1919. The resulting AG in Stuttgart was one of the companies that merged to form the Zeiss Ikon AG in 1926. When the modern Zeiss lens was designed by Bertele, Zeiss re-used the old Nettel tradename in order to build on the sun association to emphasize on the lens' large aperture (), which was much greater than many other lenses available at the time. History File:Taylor US568052A (Cooke Triplet, 1893 Fig 11).svg, '' Cooke triplet'' ( Taylor, 1893, per US 568,052) File:Minor US1360667A (Ultrastigmat, 1916).svg, ''Ultrastigmat'' (Minor, 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal-plane Shutter
In camera design, a focal-plane shutter (FPS) is a type of photographic shutter that is positioned immediately in front of the focal plane of the camera, that is, right in front of the photographic film or image sensor. Two-curtain shutters The traditional type of focal-plane shutter in 35 mm cameras, pioneered by Leitz for use in its Leica cameras, uses two shutter curtains, made of opaque rubberised fabric, that run horizontally across the film plane. For slower shutter speeds, the first curtain opens (usually) from right to left, and after the required time with the shutter open, the second curtain closes the aperture in the same direction. When the shutter is cocked again the shutter curtains are moved back to their starting positions, ready to be released. Focal-plane shutter at low speed ''Figure 1:'' The black rectangle represents the frame aperture through which the exposure is made. It is currently covered by the first shutter curtain, shown in red. The se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camera
A camera is an instrument used to capture and store images and videos, either digitally via an electronic image sensor, or chemically via a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. As a pivotal technology in the fields of photography and videography, cameras have played a significant role in the progression of visual arts, media, entertainment, surveillance, and scientific research. The invention of the camera dates back to the 19th century and has since evolved with advancements in technology, leading to a vast array of types and models in the 21st century. Cameras function through a combination of multiple mechanical components and principles. These include exposure control, which regulates the amount of light reaching the sensor or film; the lens, which focuses the light; the viewfinder, which allows the user to preview the scene; and the film or sensor, which captures the image. Several types of camera exist, each suited to specific uses and offering unique cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
135 Film
file:135film.jpg, 135 film. The film is wide. Each image is 24×36 mm in the most common "small film" format (sometimes called "double-frame" for its relationship to the "single-frame" 35 mm movie format or full frame after the introduction of 135 sized digital sensors; confusingly, "full frame" was also used to describe the Full frame (cinematography), full gate of the movie format half the size). file:LEI0060 186 Leica I Sn.5193 1927 Originalzustand Front-2 FS-15.jpg, Leica I, 1927, the first successful camera worldwide for 35 cine film 135 film, more popularly referred to as 35 mm film or 35 mm, is a format of photographic film with a film gauge of loaded into a standardized type of magazine (also referred to as a cassette or cartridge) for use in 135 film cameras. The term 135 was introduced by Kodak in 1934 as a designation for 35 mm film specifically for still photography, perforated with Kodak Standard perforations. It quickly grew in populari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
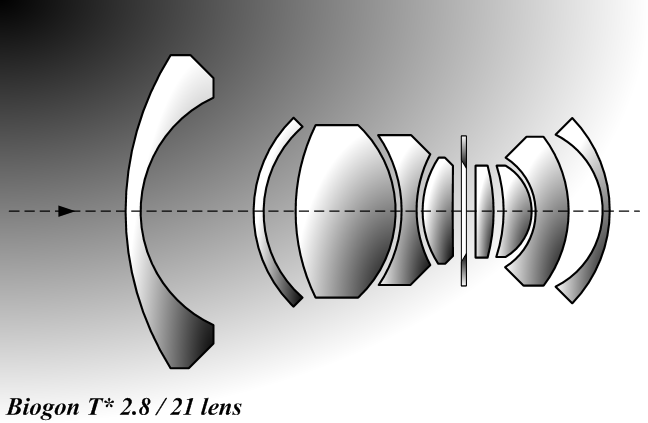
Zeiss Biogon
Biogon is the brand name of Carl Zeiss for a series of photographic camera lenses, first introduced in 1934. Biogons are typically wide-angle lenses. History ''Biogon'' (I), 1934 File:Bertele-Zeiss Biogon (1934).svg, Zeiss ''Biogon'' by Bertele (1934), from US 2,084,309 File:Bertele US2549159A (Aviotar, 1947).svg, Wild ''Aviotar'' by Bertele (1947), from US 2,549,159 File:Jupiter-12 (Contax-Kiev lens mount).JPG, KMZ ''Jupiter-12'' lens The first ''Biogon'' lens (2.8 / 3.5 cm, an asymmetric design featuring seven elements in four groups) was designed in 1934 by Ludwig Bertele while he was working for Zeiss, as a modification of his earlier '' Sonnar'' design (1929). The ''Biogon'' was assigned to Zeiss Ikon Dresden and marketed with the Contax rangefinder camera. It was produced by Carl Zeiss starting in approximately 1937, first in Jena, then a redesigned version was built in Oberkochen. Bertele would go on to reuse the design for the Wild ''Aviotar''. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentaprism
A pentaprism is a five-sided reflecting prism (optics), prism used to deviate a beam of light by a constant 90°, even if the entry beam is not at 90° to the prism. The beam reflects inside the prism ''twice'', allowing the transmission of an image through a right angle without inverting it (that is, without changing the image's Chirality (electromagnetism), handedness) as an ordinary right-angle prism or mirror would. The reflections inside the prism are not caused by total internal reflection, since the beams are incident at an angle less than the critical angle (optics), critical angle (the minimum angle for total internal reflection). Instead, the two faces are coated to provide mirror surfaces. The two opposite transmitting faces are often coated with an anti-reflective coating, antireflection coating to reduce spurious reflections. The fifth face of the prism is not used optically but truncates what would otherwise be an awkward angle joining the two mirrored faces. In c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |