|
Constantine Pavlovich
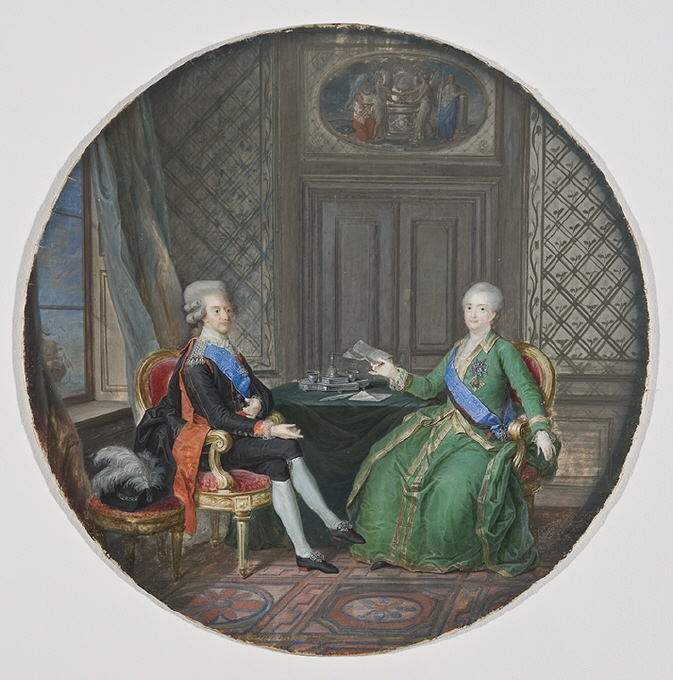
Konstantin Pavlovich (; ) was a grand duke of Russia and the second son of Emperor Paul I and Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg. He was the heir-presumptive for most of his elder brother Alexander I's reign, but had secretly renounced his claim to the throne in 1823. For 25 days after the death of Alexander I, from 19 November (O.S.)/1 December 1825 to 14 December (O.S.)/26 December 1825 he was known as ''His Imperial Majesty Konstantin I Emperor and Sovereign of Russia'', although he never reigned and never acceded to the throne. His younger brother Nicholas became tsar in 1825. The succession controversy became the pretext of the Decembrist revolt. Konstantin was known to eschew court etiquette and to take frequent stands against the wishes of his brother Alexander I, for which he is remembered fondly in Russia, but in his capacity as the governor of Poland he is remembered as a hated ruler. Early life Konstantin was born in Tsarskoye Selo on 27 April 1779, the second son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Dawe
George Dawe (6 February 1781 – 15 October 1829) was an English portraitist who painted 329 portraits of Russian generals active during Napoleon's invasion of Russia for the Military Gallery of the Winter Palace. He relocated to Saint Petersburg in 1819, where he won acclaim for his work from the artistic establishment and complimentary verses by Pushkin. He was the son of Philip Dawe, a successful mezzotint engraver who also produced political cartoons relating to the events of the Boston Tea Party. One of his brothers was Henry Edward Dawe, also a portraitist. He died on 15 October 1829 in Kentish Town, United Kingdom. Life and career Early life and studies George Dawe was born on 6 February 1781 to Philip Dawe and Jane in Brewer Street, in the parish of St James's in Westminster. Philip was an artist and engraver in mezzotint who had worked with Hogarth and Joseph Mallord William Turner and who also produced satirical political cartoons about life in America w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decembrist Revolt
The Decembrist revolt () was a failed coup d'état led by liberal military and political dissidents against the Russian Empire. It took place in Saint Petersburg on , following the death of Emperor Alexander I. Alexander's brother and heir-presumptive Grand Duke Konstantin Pavlovich privately renounced his claim to the throne two years prior to Alexander's sudden death on 1 December Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 19 November1825. The next in the line of succession therefore was younger brother Nicholas, who would ascend to the throne as Emperor Nicholas I. Neither the Russian government nor the general public were initially aware of Konstantin's renunciation, and as a result, parts of the military took a premature oath of loyalty to Konstantin. A general swearing of loyalty to the true emperor Nicholas was scheduled for in Senate Square, Saint Petersburg. In the midst of this Northern Society, a secret society" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Fedorovna By Unknown
Anna may refer to: People Surname and given name * Anna (name) Mononym * Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke * Anna of East Anglia, King (died c.654) * Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773) * Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century) * Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 1221) * Anna of Poland, Countess of Celje (1366–1425) * Anna of Cilli (1386–1416) * Anna, Grand Duchess of Lithuania (died 1418) * Anne of Austria, Landgravine of Thuringia (1432–1462) * Anna of Nassau-Dillenburg (died 1514) * Anna, Duchess of Prussia (1576–1625) * Anna of Russia (1693–1740) * Anna, Lady Miller (1741–1781) * Anna Russell, Duchess of Bedford (1783–1857) * Anna, Lady Barlow (1873–1965) * Anna (feral child) (1932–1942) * Anna (rapper) (born 2003) * Anna (singer) (born 1987) * C. N. Annadurai (1909–1969), Indian politician, known as Anna (elder brother) * Sunil Shetty (born 1961), Indian actor, known by his nickname Anna Places Australia * Hundred of Anna, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Pavlovich By P
Constantine most often refers to: * Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I * Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria Constantine may also refer to: People * Constantine (name), a masculine given name and surname Roman/Byzantine emperors * Constantine II (emperor) * Constantine III (Western Roman emperor) * Constantine III (Byzantine emperor) * Constantine IV * Constantine V * Constantine VI * Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus * Constantine VIII * Constantine IX Monomachos * Constantine X Doukas * Constantine XI Palaiologos Emperors not enumerated * Tiberius II, reigned officially as "Constantine" * Constans II, reigned officially as "Constantine" * Constantine (son of Leo V) * Constantine (son of Theophilos) * Constantine (son of Basil I) * Constantine Lekapenos * Constantine Doukas (co-emperor) * Constantine Laskaris (?) Other rulers * Constantine I, Prince of Armenia * Constantine II, Prince of Armenia * Constantine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsarskoe Selo
Tsarskoye Selo (, , ) was the town containing a former residence of the Russian imperial family and visiting nobility, located south from the center of Saint Petersburg. The residence now forms part of the town of Pushkin. Tsarskoye Selo forms one of the World Heritage Site Saint Petersburg and Related Groups of Monuments. The town bore the name Tsarskoye Selo until 1918. The new Bolshevik government of Soviet Russia renamed it as Detskoye Selo (), which it held from 1918–1937. At that time, it was renamed under Stalin's government as Pushkin () after the famous Russian poet and writer. It is still known by that name. History The area of Tsarskoye Selo, once part of Swedish Ingria, first became a Russian royal/imperial residence in the early 18th century as an estate of the Empress-consort Catherine (later Empress-regnant as Catherine I, ), for whom the Catherine Palace is named. When Peter the Great took possession of the mouth of the Neva, a Finnish village, Saari-mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Potemkin
Prince Grigory Aleksandrovich Potemkin-Tauricheski (A number of dates as late as 1742 have been found on record; the veracity of any one is unlikely to be proved. This is his "official" birth-date as given on his tombstone.) was a Russian military leader, statesman, nobleman, and favourite of Catherine the Great. He died during negotiations over the Treaty of Jassy, which ended a war with the Ottoman Empire that he had overseen. Potemkin was born into a family of middle-income landowners of Russian nobility. He first attracted Catherine's favor for helping in her 1762 coup, then distinguished himself as a military commander in the Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774). He became Catherine's lover, favorite and possibly her consort. After their passion cooled, he remained her lifelong friend and favored statesman. Catherine obtained for him the title of Prince of the Holy Roman Empire and gave him the title of Prince of the Russian Empire among many others: he was both a Grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Harris, 1st Earl Of Malmesbury
James Harris, 1st Earl of Malmesbury (21 April 1746 – 21 November 1820), was an English diplomat. Early life (1746–1768) Born at Salisbury, the son of James Harris, an MP and the author of ''Hermes'', and Elizabeth Clarke of Sandford, Somerset.H. M. Scott, �Harris, James, first earl of Malmesbury (1746–1820)��, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, May 2009, accessed 7 August 2011. He was educated at Winchester, at Merton College, Oxford and did Law and History at the University of Leiden (1765-1767). Early diplomatic career: Spain (1768–1771) Harris arrived in Spain in December 1768 and became secretary to the British embassy at Madrid, and was left as ''chargé d'affaires'' at that court on the departure of Sir James Grey in August 1769 until the arrival of George Pitt, afterwards Lord Rivers. This interval gave him his opportunity; he discovered the intention of Spain to attack the Falkland Islands, and was instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Plan
The Greek Plan or Greek Project (), an early proposed solution to the Eastern question, was advanced by the Russian empress Catherine the Great in the early 1780s. It envisaged the partition of the Ottoman Empire between the Russian and Habsburg Empires followed by the restoration of the Eastern Roman Empire centered in Constantinople. Outline Like her predecessors, Catherine concerned herself with the Orthodox Christians under Ottoman rule; she sponsored the Orlov Revolt in the Morea during the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774, and invited many Greeks like Ioannis Varvakis to settle in Russia, mainly in Crimea and New Russia. She conceived that one of her grandsons, born in 1779 and appropriately named Constantine, would become the first emperor of the restored Byzantium. Another important consideration was Russia's goal of free access (especially for the Imperial Russian Navy's Black Sea Fleet, founded in 1783) to the Mediterranean Sea through the Bosphorus, which th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, experienced recurring cycles of decline and recovery. It reached its greatest extent un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine The Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal role in elevating the status of Christianity in Rome, Edict of Milan, decriminalising Christian practice and ceasing Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, Christian persecution. This was a turning point in the Historiography of the Christianization of the Roman Empire, Christianisation of the Roman Empire. He founded the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and made it the capital of the Empire, which it remained for over a millennium. Born in Naissus, a city located in the Roman province, province of Moesia Superior (now Niš, Serbia), Constantine was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer from Moesia Superior, who would become one of the four emperors of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine The Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter III. Under her long reign, inspired by the ideas of the Enlightenment, Russia experienced a renaissance of culture and sciences, which led to the founding of many new cities, universities, and theatres, along with large-scale immigration from the rest of Europe and the recognition of Russia as one of the great powers of Europe. In her accession to power and her rule of the empire, Catherine often relied on her noble favourites, most notably Count Grigory Orlov and Grigory Potemkin. Assisted by highly successful generals such as Alexander Suvorov and Pyotr Rumyantsev, and admirals such as Samuel Greig and Fyodor Ushakov, she governed at a time when the Russian Empire was expanding rapidly by conquest and diplomacy. In the south, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Württemberg
The Duchy of Württemberg () was a duchy located in the south-western part of the Holy Roman Empire. It was a Imperial Estate, state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1495 to 1803. The dukedom's long survival for over three centuries was mainly due to its size, being larger than its immediate neighbors. During the Protestant Reformation, Württemberg faced great pressure from the Catholic emperors to remain loyal. Württemberg resisted repeated French invasions in the 17th and 18th centuries, the duchy being directly in the path of French and Austrian armies who were engaged in the French–Habsburg rivalry, long rivalry between the House of Bourbon and the House of Habsburg. In 1803, Napoleon raised the duchy to be the Electorate of Württemberg. On 1 January 1806, the last elector assumed the title of King of Württemberg. Later that year, on 6 August 1806, the last Emperor, Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis II, abolished (de facto) the Holy Roman Empire. Geography Much of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |