|
Conservative Party (Romania, 1880–1918)
The Conservative Party () was between 1880 and 1918 one of Romania's two most important parties, the other one being the Liberal Party.Scurtu 1982, p.41''n''; for the founding of the party, this source gives February 1880, does not specify day of month. The party was the party of government for a total of 14 years, more than a third of its existence. It was founded on 3 February 1880 in Bucharest, although the doctrines and various groups of conservatives had already existed for some time. Precursors to the party had included the political grouping "Juna Dreaptă" (November 1868) and the newspaper '' Timpul'' (founded March 1876). The party relied on the support of the great landowners, the bourgeoisie, and some intellectuals. Their economic policy encouraged light industry and crafts but did not oppose investments in heavy industry. The 1907 Romanian Peasants' Revolt showed that some reforms needed to be made in the Romanian social and political scene. As a result, in 1913, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manolache Costache Epureanu
Manolache Costache Epureanu (; 1823–1880) was twice the Prime Minister of Romania both as a representative of the Conservative Party and of the National Liberal Party, more specifically for the first time in 1870 (20 April–14 December) and for the second time in 1876 (6 May–5 August). Biography Born in Bârlad, Moldavia, he studied in Heidelberg, Germany and returned to Moldavia to participate in the 1848 revolutionary movement, being part of the ad hoc committee. In 1866, he was the president of the council which decided to invite a foreign dynasty to rule Romania. In 1871, during the Lascăr Catargiu conservative government, Epureanu was the Minister of Justice between October 1872 and March 1873. He then switched to the opposition and in 1876, he was a national liberal Prime Minister, but later he switched again to the Conservative Party. He published ''Chestia locuitorilor privită din punctul de vedere al Regulamentului organic'' (1866) and ''Despre pretinsa rescu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Suffrage
Universal suffrage or universal franchise ensures the right to vote for as many people bound by a government's laws as possible, as supported by the " one person, one vote" principle. For many, the term universal suffrage assumes the exclusion of the young and non-citizens (among others). At the same time, some insist that more inclusion is needed before suffrage can be truly universal. Democratic theorists, especially those hoping to achieve more universal suffrage, support presumptive inclusion, where the legal system would protect the voting rights of all subjects unless the government can clearly prove that disenfranchisement is necessary. Universal full suffrage includes both the right to vote, also called active suffrage, and the right to be elected, also called passive suffrage. History In the first modern democracies, governments restricted the vote to those with property and wealth, which almost always meant a minority of the male population. In some jurisdiction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Rosetti
Prince Theodor Rosetti (; 5 May 1837 – 17 July 1923) was a Romanian writer, journalist and politician who served as Prime Minister of Romania between 23 March 1888 and 22 March 1889, with two cabinets formed. Over his life, he also served several other roles within the judicial and government. He is an aristocrat and member of the House of Rosetti. He was born in Iași or Solești, Moldavia. He was brother-in-law of Prince Alexandru Ioan Cuza, the former ruler of Romania and was considered to be on the conservative pro-monarchy side of the government. Rosetti was one of the most important members of the Junimea literary society and was elected honorary member of the Romanian Academy in 1891. He died in Bucharest at age 86 and was buried in the city's Bellu Cemetery. Streets in Bârlad Bârlad () is a city in Vaslui County, Romania. It lies on the banks of the river Bârlad (river), Bârlad, which waters the high plains of Western Moldavia. At Bârlad the railway from I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantin Garoflid
Constantin is an Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian and Romanian male given name. It can also be a surname. For a list of notable people called Constantin, see Constantine (name). See also * Constantine (name) * Konstantin The first name Konstantin () is a derivation from the Latin name '' Constantinus'' ( Constantine) in some European languages, such as Bulgarian, Russian, Estonian and German. As a Christian given name, it refers to the memory of the Roman empe ... References {{Reflist Aromanian masculine given names Megleno-Romanian masculine given names Romanian masculine given names Masculine given names Romanian-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimitrie A
Dimitrie is the Romanian form of a Slavic given name. Notable persons with that name include: ;First name * Dimitrie Alexandresco (1850–1925), Romanian encyclopedist * Dimitrie Anghel (1872–1914), Romanian poet * Dimitri Atanasescu (1836–1907), Aromanian teacher commonly referred to as Dimitrie Atanasescu * Dimitrie Bogos (1889–1946), Romanian politician * Dimitrie Bolintineanu (1819–1872), Romanian poet, diplomat, politician, and revolutionary * Dimitrie Brândză (1846–1895), Romanian botanist * Dimitrie Brătianu (1818–1892), Romanian politician, Prime Minister of Romania in 1881 * Dimitrie Cantemir (1673–1723), Prince of Moldavia * Dimitrie Călugăreanu (1868-1937), Romanian physician and naturalist * Dimitrie Cărăuş (born 1892), a Bessarabian politician, member of the Moldovan Parliament (1917–1918) * Dimitrie Comșa (1846-1931), Romanian agronomer and activist * Dimitrie Cornea (1816–1884), Romanian politician, and diplomat * Dimitrie Cozacovici (179 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimitrie S
Dimitrie is the Romanian form of a Slavic given name. Notable persons with that name include: ;First name * Dimitrie Alexandresco (1850–1925), Romanian encyclopedist * Dimitrie Anghel (1872–1914), Romanian poet * Dimitri Atanasescu (1836–1907), Aromanian teacher commonly referred to as Dimitrie Atanasescu * Dimitrie Bogos (1889–1946), Romanian politician * Dimitrie Bolintineanu (1819–1872), Romanian poet, diplomat, politician, and revolutionary * Dimitrie Brândză (1846–1895), Romanian botanist * Dimitrie Brătianu (1818–1892), Romanian politician, Prime Minister of Romania in 1881 * Dimitrie Cantemir (1673–1723), Prince of Moldavia * Dimitrie Călugăreanu (1868-1937), Romanian physician and naturalist * Dimitrie Cărăuş (born 1892), a Bessarabian politician, member of the Moldovan Parliament (1917–1918) * Dimitrie Comșa (1846-1931), Romanian agronomer and activist * Dimitrie Cornea (1816–1884), Romanian politician, and diplomat * Dimitrie Cozacovici (179 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandru Lahovari
Alexandru Lahovary (; August 16, 1841 – March 4, 1897) was a member of the Romanian aristocracy, a politician and diplomat who served as the Minister of Justice, Minister of Agriculture, Industry, Trade and Property, Minister of Public Works and Minister of Foreign Affairs of Kingdom of Romania. Life and political career Alexandru Lahovary was the brother of Ioan Lahovary, who served as foreign minister within the Royal government, and General Iacob Lahovary, who also served as Minister of Foreign Affairs and later Minister of War. He was born as a member of the Lahovary family, an old noble Boyar family to Nicolae Lahovary (1816–1883), who served as Senator and his wife, Eufrosina Iacovache (1825–1884) from Râmnicu Vâlcea (maybe related to the House of Lackovic). After being tutored by private teachers, he moved to Paris to teach. In Paris, he also completed his doctoral studies in 1865. In July 1867, he entered foreign service and from July 30 until October 11, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Bucharest
The University of Bucharest (UB) () is a public university, public research university in Bucharest, Romania. It was founded in its current form on by a decree of Prince Alexandru Ioan Cuza to convert the former Princely Academy of Bucharest, Princely Academy into the current University of Bucharest, making it one of the oldest Romanian universities. It is one of the five members of the ''Universitaria Consortium'' (a group of elite Romanian universities). The University of Bucharest offers study programmes in Romanian and English and is classified as an ''advanced research and education university'' by the Ministry of Education and Scientific Research (Romania), Ministry of Education. History The University of Bucharest was founded by the Decree no. 765 of 4 July 1864 by Alexandru Ioan Cuza and is a leading academic centre and a significant point of reference in society. The University of Bucharest is rich in history and has been actively contributing to the development a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
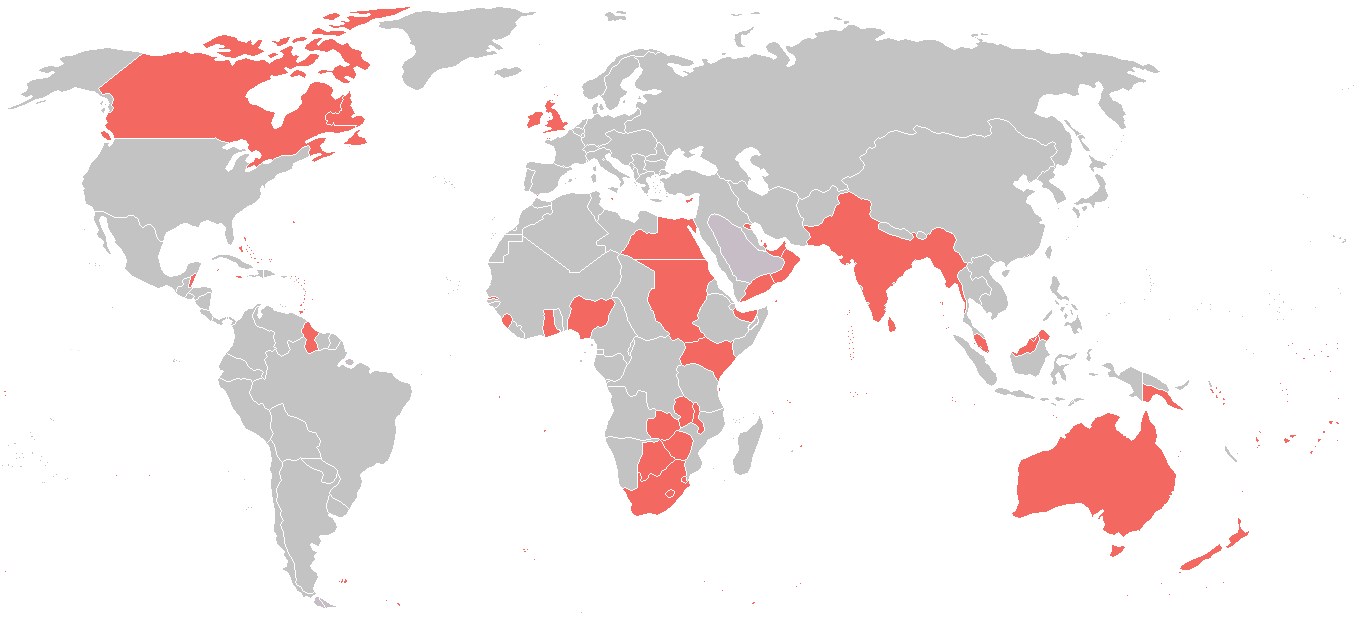
Allies Of World War I
The Allies or the Entente (, ) was an international military coalition of countries led by the French Republic, the United Kingdom, the Russian Empire, the United States, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan against the Central Powers of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria in World War I (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of the United Kingdom, France, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and, despite proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although the United Kingdom, Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolae Filipescu
Nicolae Filipescu (December 5, 1862 – September 30, 1916) was a Romanian politician. Filipescu was the Mayor of Bucharest between February 1893 and October 1895. It was during his term the first electric tramways circulated in Bucharest. Between December 29, 1910, and March 27, 1912, he was the Minister of War of Romania, in the Cabinet led by Petre P. Carp. Biography He attended primary school in Bucharest, after which he completed graduated from the high school in Geneva and law school in Paris. Coming back to his home country, he started to work politically and joined the young conservatives grouped around the newspaper "Epoca". In 1885 he became a Member of the Chamber of Deputies for the first time in the Brăila constituency. On February 9, 1893, he was elected the mayor of Bucharest, a position that he held for almost two years, until 1895, when he became the mayor of Brăila. In 1899 the Conservatives returned to power and Filipescu was re-elected as Deputy. When th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Take Ionescu
Take or Tache Ionescu (; born Dumitru Ghiță Ioan and also known as Demetriu G. Ionnescu; – 21 June 1922) was a Romanian Centrism, centrist politician, journalist, lawyer and diplomat, who also enjoyed reputation as a short story author. Starting his political career as a Liberalism and radicalism in Romania, radical member of the National Liberal Party (Romania, 1875), National Liberal Party (PNL), he joined the Conservative Party (Romania, 1880–1918), Conservative Party in 1891, and became noted as a Social conservatism, social conservative expressing support for several Progressivism, progressive and Nationalism, nationalist tenets. Ionescu is generally viewed as embodying the rise of middle-class politics inside the early 20th century Kingdom of Romania (occasionally described as ''Takism''), and, throughout the period, promoted a project of Balkans, Balkan alliances while calling for measures to incorporate the Romanian-inhabited Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |