|
Consensus CDS Project
The Consensus Coding Sequence (CCDS) Project is a collaborative effort to maintain a dataset of protein-coding regions that are identically annotated on the human and mouse reference genome assemblies. The CCDS project tracks identical protein annotations on the reference mouse and human genomes with a stable identifier (CCDS ID), and ensures that they are consistently represented by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), Ensembl, and UCSC Genome Browser. The integrity of the CCDS dataset is maintained through stringent quality assurance testing and on-going manual curation. Motivation and background Biological and biomedical research has come to rely on accurate and consistent annotation of genes and their products on genome assemblies. Reference annotations of genomes are available from various sources, each with their own independent goals and policies, which results in some annotation variation. The CCDS project was established to identify a gold sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Center For Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland, and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by US Congressman Claude Pepper. The NCBI houses a series of databases relevant to biotechnology and biomedicine and is an important resource for bioinformatics tools and services. Major databases include GenBank for DNA sequences and PubMed, a bibliographic database for biomedical literature. Other databases include the NCBI Epigenomics database. All these databases are available online through the Entrez search engine. NCBI was directed by David Lipman, one of the original authors of the BLAST sequence alignment program and a widely respected figure in bioinformatics. GenBank NCBI had responsibility for making available the GenBan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
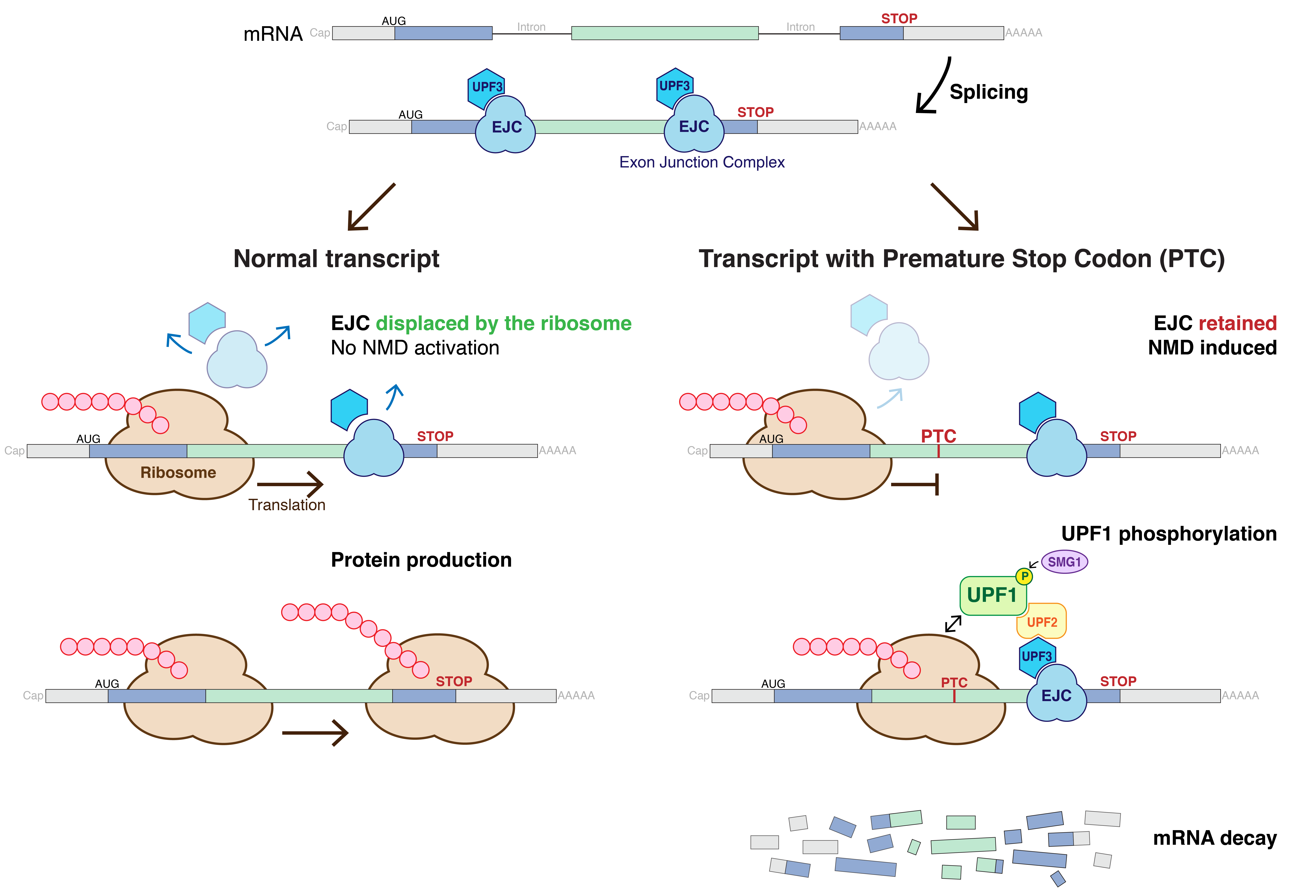
Nonsense-mediated Decay
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a surveillance pathway that exists in all eukaryotes. Its main function is to reduce errors in gene expression by eliminating mRNA transcripts that contain premature stop codons. Translation of these aberrant mRNAs could, in some cases, lead to deleterious gain-of-function or dominant-negative activity of the resulting proteins. NMD was first described in human cells and in yeast almost simultaneously in 1979. This suggested broad phylogenetic conservation and an important biological role of this intriguing mechanism. NMD was discovered when it was realized that cells often contain unexpectedly low concentrations of mRNAs that are transcribed from alleles carrying nonsense mutations. Nonsense mutations code for a premature stop codon which causes the protein to be shortened. The truncated protein may or may not be functional, depending on the severity of what is not translated. In human genetics, NMD has the possibility to not only limit the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GENCODE
GENCODE is a scientific project in genome research and part of the ENCODE (ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements) scale-up project. The GENCODE consortium was initially formed as part of the pilot phase of the ENCODE project to identify and map all protein-coding genes within the ENCODE regions (approx. 1% of Human genome). Given the initial success of the project, GENCODE now aims to build an “Encyclopedia of genes and genes variants”. The result will be a set of annotations including all protein-coding loci with alternatively transcribed variants, non-coding loci with transcript evidence, and pseudogenes. Current progress GENCODE is currently progressing towards its goals in Phase 2 of the project. The most recent release of the Human geneset annotations is Gencode 36, with a freeze date of December 2020. This release utilises the latest GRCh38 human reference genome assembly. The latest release for the mouse geneset annotations is Gencode M25, also with a freeze date Dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itm2a Report
ITM may stand for: Education * ITM Global School, an English medium co-educational day school in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, India * ITM Law School, one of the professional graduate schools of ITM University * ITM-IFM, Mumbai, India * Institut Teknologi Mara, a public university in Shah Alam, Selangor, Malaysia * Institute for Information, Telecommunication and Media Law Institute for Information, Telecommunication and Media Law or ITM (german: Institut für Informations-, Telekommunikations- und Medienrecht) is a research & educational organisation located in Münster, North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. All ma ..., educational organization in Münster, Germany * Institute of Tropical Medicine Antwerp, research and training in tropical medicine, Belgium * Information technology management * International Tourism Management Music * In This Moment, a female-led metalcore band * Irish traditional music * In the Meantime (Alessia Cara album), ''In the Meantime'' (Alessia Cara album) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate And Genome Annotation Project
The Vertebrate Genome Annotation (VEGA) database is a biological database dedicated to assisting researchers in locating specific areas of the genome and annotating genes or regions of vertebrate genomes. The VEGA browser is based on Ensembl web code and infrastructure and provides a public curation of known vertebrate genes for the scientific community. The VEGA website is updated frequently to maintain the most current information about vertebrate genomes and attempts to present consistently high-quality annotation of all its published vertebrate genomes or genome regions. VEGA was developed by the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute and is in close association with other annotation databases, such as ZFIN (The Zebrafish Information Network), the Havana Group and GenBank. Manual annotation is currently more accurate at identifying splice variants, pseudogenes, polyadenylation features, non-coding regions and complex gene arrangements than automated methods. History The Vertebrate Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entrez
The Entrez (pronounced ''ɒnˈtreɪ'') Global Query Cross-Database Search System is a federated search engine, or web portal that allows users to search many discrete health sciences databases at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) website. The NCBI is a part of the National Library of Medicine (NLM), which is itself a department of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which in turn is a part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The name "Entrez" (a greeting meaning "Come in" in French) was chosen to reflect the spirit of welcoming the public to search the content available from the NLM. Entrez Global Query is an integrated search and retrieval system that provides access to all databases simultaneously with a single query string and user interface. Entrez can efficiently retrieve related sequences, structures, and references. The Entrez system can provide views of gene and protein sequences and chromosome maps. Some textbooks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by DNA duplication or indirectly by reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences needed for transcription or translation, or whose coding sequences are obviously defective due to frameshifts or premature stop codons. Most non-bacterial genomes contain many pseudogenes, often as many as functional genes. This is not surprising, since various biological processes are expected to accidentally create pseudogenes, and there are no specialized mechanisms to remove them from genomes. Eventually pseudogenes may be deleted from their genomes by chance DNA replication or DNA repair errors, or they may accumulate so many mutational changes that they are no longer recognizable as former genes. Analysis of these degeneration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
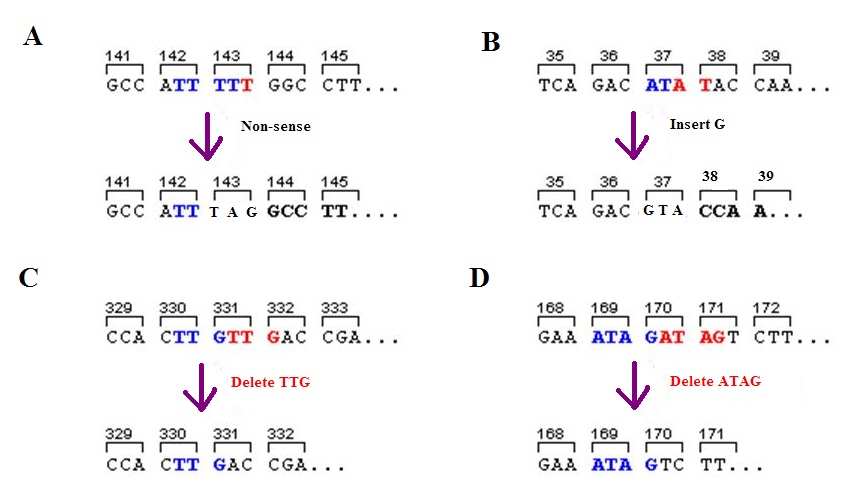
Frameshift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels (gene insertion, insertions or genetic deletion, deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different Translation (genetics), translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stop Codon
In molecular biology (specifically protein biosynthesis), a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon ( nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in messenger RNA correspond to the addition of an amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain, which may ultimately become a protein; stop codons signal the termination of this process by binding release factors, which cause the ribosomal subunits to disassociate, releasing the amino acid chain. While start codons need nearby sequences or initiation factors to start translation, a stop codon alone is sufficient to initiate termination. Properties Standard codons In the standard genetic code, there are three different termination codons: Alternative stop codons There are variations on the standard genetic code, and alternative stop codons have been found in the mitochondrial genomes of vertebrates, '' Scenedesmus obliquus'', and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overlapping Genes
An overlapping gene (or OLG) is a gene whose expressible nucleotide sequence partially overlaps with the expressible nucleotide sequence of another gene. In this way, a nucleotide sequence may make a contribution to the function of one or more gene products. Overlapping genes are present and a fundamental feature of both cellular and viral genomes. The current definition of an overlapping gene varies significantly between eukaryotes, prokaryotes, and viruses. In prokaryotes and viruses overlap must be between coding sequences but not mRNA transcripts, and is defined when these coding sequences share a nucleotide on either the same or opposite strands. In eukaryotes, gene overlap is almost always defined as mRNA transcript overlap. Specifically, a gene overlap in eukaryotes is defined when at least one nucleotide is shared between the boundaries of the primary mRNA transcripts of two or more genes, such that a DNA base mutation at any point of the overlapping region would affect t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjoined Gene
A conjoined gene (CG) is defined as a gene, which gives rise to transcripts by combining at least part of one exon from each of two or more distinct known (parent) genes which lie on the same chromosome, are in the same orientation, and often (95%) translate independently into different proteins. In some cases, the transcripts formed by CGs are translated to form chimeric or completely novel proteins. Several alternative names are used to address conjoined genes, including combined gene and complex gene, fusion gene, fusion protein, read-through transcript, co-transcribed genes, bridged genes, spanning genes, hybrid genes, locus-spanning transcripts, etc. At present, 800 CGs have been identified in the entire human genome by different research groups across the world including Prakash et al., Akiva et al., Parra et al., Kim et al., and in the 1% of the human genome in the ENCODE pilot project. 36% of all these CGs could be validated experimentally using RT-PCR and sequencing te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid ''residues'' form the second-largest component ( water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |