|
Conon (other)
Conon () (before 443 BC – ) was an Athenian general at the end of the Peloponnesian War, who led the Athenian naval forces when they were defeated by a Peloponnesian fleet in the crucial Battle of Aegospotami; later he contributed significantly to the restoration of Athens' political and military power. Commanding the Athenian fleet Shortly after the Battle of Notium, Conon took over command of the Athenian fleet from Alcibiades, who had fled to Thrace. When the new Spartan navarch (commander-in-chief of the fleet) Callicratidas took over command from Lysander, he started an aggressive campaign against the Athenians in the Aegean. After taking Methymna in Lesbos, he sent a message to Conon, declaring that he would put an end to Conon's command of the sea. Soon thereafter, Callicratidas caught Conon's fleet of seventy ships at sea and pursued him towards Mytilene Harbor on Lesbos, where in the ensuing battle, Conon lost thirty ships. Conon drew the remaining forty ships up on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conon
Conon ( el, Κόνων) (before 443 BC – c. 389 BC) was an Athenian general at the end of the Peloponnesian War, who led the Athenian naval forces when they were defeated by a Peloponnesian fleet in the crucial Battle of Aegospotami; later he contributed significantly to the restoration of Athens' political and military power. Defeat at Aegospotami Conon had been sent out to lead the Athenian forces following the recall of Alcibiades in 406 BC, and in 405 BC pursued the Peloponnesian fleet under Lysander to the Hellespont. Once there, the Peloponnesian took up a strong defensive position at Lampsacus and as they could not lure them out, the Athenians retreated to Aegospotami. Alcibiades came to warn them of the danger of their position, as they were based on an open beach without harbours, and advised them to move to Sestos about two miles away from where they were retrieving supplies. It seems that Alcibiades' advice was ignored and perhaps ridiculed. On the fifth day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lampsacus
Lampsacus (; grc, Λάμψακος, translit=Lampsakos) was an ancient Greek city strategically located on the eastern side of the Hellespont in the northern Troad. An inhabitant of Lampsacus was called a Lampsacene. The name has been transmitted in the nearby modern town of Lapseki. Ancient history Originally known as Pityusa or Pityussa ( grc, Πιτυούσ(σ)α), it was colonized from Phocaea and Miletus. In the 6th century BC Lampsacus was attacked by Miltiades the Elder and Stesagoras, the Athenian tyrants of the nearby Thracian Chersonese. During the 6th and 5th centuries BC, Lampsacus was successively dominated by Lydia, Persia, Athens, and Sparta. The Greek tyrants Hippoclus and later his son Acantides ruled under Darius I. Artaxerxes I assigned it to Themistocles with the expectation that the city supply the Persian king with its famous wine. When Lampsacus joined the Delian League after the battle of Mycale (479 BC), it paid a tribute of twelve talents, a testimony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peisander (general)
Peisander (; el, Πείσανδρος) was a Spartan admiral during the Corinthian War. In 395 BC, he was placed in command of the Spartan fleet in the Aegean by his brother-in-law, the king Agesilaus II. Peisander was a relatively inexperienced general, and in its very first action his Spartan fleet was decisively defeated at the Battle of Cnidus The Battle of Cnidus ( gr, Ναυμαχία της Κνίδου) was a military operation conducted in 394 BC by the Achaemenid Empire against the Spartan naval fleet during the Corinthian War. A fleet under the joint command of Pharnabazus and .... Peisander died fighting aboard his ship. References *Fine, John V.A. ''The Ancient Greeks: A critical history'' (Harvard University Press, 1983). * Ancient Spartan admirals 4th-century BC Spartans Ancient Greeks killed in battle 394 BC deaths Spartans of the Corinthian War Year of birth unknown {{AncientGreece-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the South Aegean administrative region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Rhodes. The city of Rhodes had 50,636 inhabitants in 2011. In 2022 the island has population of 124,851 people. It is located northeast of Crete, southeast of Athens. Rhodes has several nicknames, such as "Island of the Sun" due to its patron sun god Helios, "The Pearl Island", and "The Island of the Knights", named after the Knights of Saint John of Jerusalem, who ruled the island from 1310 to 1522. Historically, Rhodes was famous for the Colossus of Rhodes, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The Medieval Old Town of the City of Rhodes has been declared a World Heritage Site. Today, it is one of the most popular tourist dest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. Carians were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan descent,''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. while he reports that the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns in classical Greece is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and geomorphic features, such as bays and headlands, reveal an ethnic layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artaxerxes II Of Persia
Arses ( grc-gre, Ἄρσης; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and successor of Darius II () and his mother was Parysatis. Soon after his accession, Artaxerxes II faced opposition from his younger brother Cyrus the Younger, who assembled an army composing of troops from his Lydian and Ionian satrapies as well as Greek mercenaries in his bid for the throne. The forces of the brothers clashed at Cunaxa in 401 BC, which resulted in the defeat and death of Cyrus. Following this, Artaxerxes II had to contend with several other revolts; a revolt by Evagoras I () in Cyprus between 391–380 BC, by the Phoenicians in , and most importantly, the revolts by the western satraps (known as the Great Satraps' Revolt) in the 360s and 350s BC, led by distinguished figures such as Datames, Ariobarzanes, and Autophradates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissaphernes
Tissaphernes ( peo, *Ciçafarnāʰ; grc-gre, Τισσαφέρνης; xlc, 𐊋𐊆𐊈𐊈𐊀𐊓𐊕𐊑𐊏𐊀 , ; 445395 BC) was a Persian soldier and statesman, Satrap of Lydia and Ionia. His life is mostly known from the works of Thucydides and Xenophon. According to Ctesias, he was the son of Hidarnes III and therefore the great grandson of Hydarnes, one of the six conspirators who had supported the rise of Darius the Great. Etymology ''Čiçafarnah'' (''čiça'' + ''farnah'') "with shining splendor": ''čiça'' is from the Proto-Indo-European adjective ''(s)koitrós'' 'bright'; ''farnah'' is equivalent to Avestan '' xvarənah'' 'fortune', 'glory', which appears as 'luminous'. ''čiθra'' means nature, specifically the animate nature. ''Čiça-'' is the Old Persian form of the Old Iranian term ''Čiθra-'', which is reflected in the Median form of the name, ''*Čiθrafarnah-'' ( grc, Τετραφέρνης). Family and early life Tissaphernes was born in 445 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
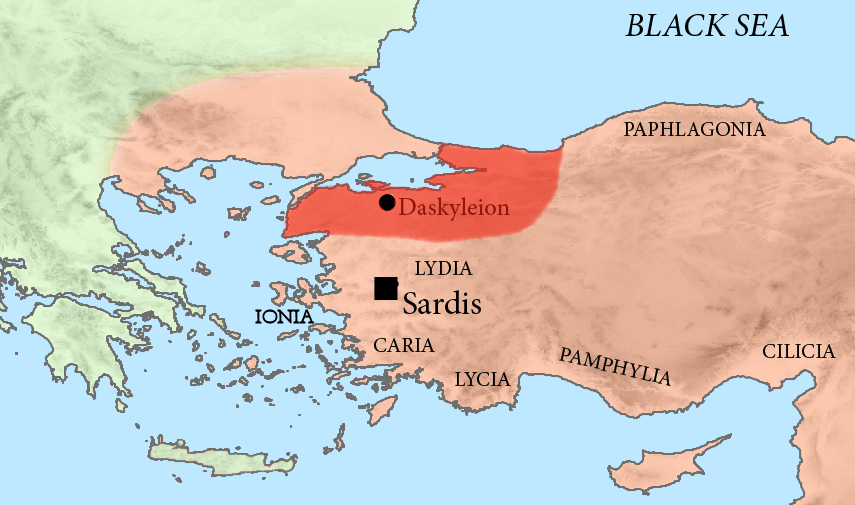
Pharnabazus (5th Century BC)
Pharnabazus II ( Old Iranian: ''Farnabāzu'', grc-gre, Φαρνάβαζος ; ruled 413-374 BC) was a Persian soldier and statesman, and Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of Pharnaces II of Phrygia and grandson of Pharnabazus I, and great-grandson of Artabazus I. He and his male ancestors, forming the Pharnacid dynasty, had governed the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia from its headquarters at Dascylium since 478 BC. He married Apama, daughter of Artaxerxes II of Persia, and their son Artabazus also became a satrap of Phrygia. According to some accounts, his granddaughter Barsine may have become Alexander the Great's concubine. According to research by Theodor Nöldeke, he was descended from Otanes, one of the associates of Darius in the murder of Smerdis. Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia War with Sparta against Athens (c.413-404 BC) Athens was the dominant power in the Aegean in the 5th century BC, following the Greeks' victories over the Achaem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages acro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta (Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city neverthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geographically in Western Asia, its cultural ties and geopolitics are overwhelmingly Southern European. Cyprus is the third-largest and third-most populous island in the Mediterranean. It is located north of Egypt, east of Greece, south of Turkey, and west of Lebanon and Syria. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. The northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which was established after the 1974 invasion and which is recognised as a country only by Turkey. The earliest known human activity on the island dates to around the 10th millennium BC. Archaeological remains include the well-preserved ruins from the Hellenistic period such as Salamis, Cyprus, Salam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evagoras I
Evagoras or Euagoras ( grc, Εὐαγόρας) was the king of Salamis (411–374 BC) in Cyprus, known especially from the work of Isocrates, who presents him as a model ruler. History He claimed descent from Teucer, the son of Telamon and half-brother of Ajax, and his family had long been rulers of Salamis, although during his childhood Salamis came under Phoenician control, which resulted in his exile. While in Cilicia, Evagoras gathered the support of 50 followers and returned secretly in 410, to gain possession of the throne. Expecting an eventual Persian response to recapture Cyprus, he cultivated the friendship of the Athenians, and after Conon's defeat at the Battle of Aegospotami he provided him with a refuge. For a time he also maintained friendly relations with Persia, and secured the aid of Artaxerxes II for Athens against Sparta. He took part in the Battle of Cnidus of 394 BC which he provided most of the resources for and in which the Spartan fleet was defeated thanks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |