|
Confederate Ireland
Confederate Ireland, also referred to as the Irish Catholic Confederation, was a period of Irish Catholic Church, Catholic self-government between 1642 and 1652, during the Irish Confederate Wars, Eleven Years' War. Formed by Catholic aristocrats, landed gentry, clergy and military leaders after the Irish Rebellion of 1641, the Confederates controlled up to two-thirds of Ireland from their base in Kilkenny; hence it is sometimes called the Confederation of Kilkenny. The Confederates included Catholics of Gaels, Gaelic and Normans in Ireland, Anglo-Norman descent. They wanted an end to anti-Catholic discrimination within the Kingdom of Ireland and greater Irish self-governance; many also wanted to roll back the plantations of Ireland. Most Confederates professed loyalty to Charles I of England in the belief they could reach a lasting settlement in return for helping defeat his opponents in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Confederate Wars
The Irish Confederate Wars, took place from 1641 to 1653. It was the Irish theatre of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, a series of civil wars in Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, all then ruled by Charles I of England, Charles I. The conflict caused an estimated 200,000 deaths from fighting, as well as war-related famine and disease. It began with the Irish Rebellion of 1641, when local Catholics tried to seize control of the Dublin Castle administration. They wanted an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, to increase Irish self-governance, and to roll back the Plantations of Ireland. They also wanted to prevent an invasion by anti-Catholic Roundhead, English Parliamentarians and Covenanter, Scottish Covenanters, who were defying the king. Rebel leader Felim O'Neill of Kinard, Felim O'Neill claimed to be Proclamation of Dungannon, doing the king's bidding, but Charles condemned the rebellion after it broke out. The rebellio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland (; , ) was a dependent territory of Kingdom of England, England and then of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1542 to the end of 1800. It was ruled by the monarchs of England and then List of British monarchs, of Great Britain, and was Dublin Castle administration, administered from Dublin Castle by a viceroy appointed by the English king: the lord deputy of Ireland. Aside from brief periods, the state was dominated by the Protestant English (or Anglo-Irish people, Anglo-Irish) minority, known as the Protestant Ascendancy. The Protestant Church of Ireland was the state church. The Parliament of Ireland was composed of Anglo-Irish nobles. From 1661, the administration controlled an Irish Army (1661–1801), Irish army. Although ''de jure'' styled as a kingdom, for most of its history it was ''de facto'' an English Dependent territory, dependency (specifically a viceroyalty). This status was enshrined in the Declaratory Act 1719, also known as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Expedition To Scotland
The Irish Confederate expedition to Scotland took place in 1644–1645 during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. A force of about 2,000 Irish Confederate troops, under the command of Alasdair Mac Colla, sailed to Scotland in June 1644, where they joined with Royalist forces fighting Montrose's Highland campaign against the Covenanters. The expedition was the result of an effort by King Charles I to enlist help from Irish Catholics in fighting Parliamentarian forces. Troop request In September 1643, a truce was made between James Butler, Marquis of Ormonde, who was leader of the Royalist regime based in Dublin, Ireland, and the Confederate Catholics of Ireland. The truce permitted Butler to send Royalist forces previously engaged against the Irish Confederates in Ireland to fight for King Charles I in Britain, while allowing the Confederate Catholics to concentrate their forces against the Scots and Parliamentarian forces in Ireland. King Charles also hoped for additional tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork (city)
Cork ( ; from , meaning 'marsh') is the second-largest city in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, the county town of County Cork, the largest city in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, third largest on the island of Ireland. At the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, it had a population of 224,004. The city centre is an island between two channels of the River Lee (Ireland), River Lee which meet downstream at its eastern end, where the quays and Dock (maritime), docks along the river lead outwards towards Lough Mahon and Cork Harbour, one of the largest natural harbours in the world. Cork was founded in the 6th century as a monastic settlement, and was expanded by Vikings, Viking invaders around 915. Its charter was granted by John, King of England, Prince John in 1185 in Ireland, 1185. Cork city was once fully walled, and the remnants of the old medieval town centre can be found around South and North M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); the remaining three are in the Republic of Ireland. It is the second-largest (after Munster) and second-most populous (after Leinster) of Ireland's four traditional provinces, with Belfast being its biggest city. Unlike the other provinces, Ulster has a high percentage of Protestantism in Ireland, Protestants, making up almost half of its population. English is the main language and Ulster English the main dialect. A minority also speak Irish, and there are (Irish-speaking regions) in County Donegal which is home to a quarter of the total Gaeltacht population of the Republic of Ireland. There are also large Irish-speaking networks in southern County Londonderry and in the Gaeltacht Quarter, Belfast. Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Pale
The Pale ( Irish: ''An Pháil'') or the English Pale (' or ') was the part of Ireland directly under the control of the English government in the Late Middle Ages. It had been reduced by the late 15th century to an area along the east coast stretching north from Dalkey, which is just south of Dublin, to the garrison town of Dundalk. The inland boundary went to Naas and Leixlip around the Earldom of Kildare, towards Trim and north towards Kells. In this district, many townlands have English or Norman-French names, the latter associated with Anglo-Norman influence in England. Etymology The word ''pale'', meaning a fence, is derived from the Latin word ', meaning "stake", specifically a stake used to support a fence. A paling fence is made of pales ganged side by side, and the word ''palisade'' is derived from the same root. From this came the figurative meaning of "boundary". The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' is dubious about the popular notion that the phrase '' beyond the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covenanter
Covenanters were members of a 17th-century Scottish religious and political movement, who supported a Presbyterian Church of Scotland and the primacy of its leaders in religious affairs. It originated in disputes with James VI and his son Charles I over church organisation and doctrine, but expanded into political conflict over the limits of royal authority. In 1638, thousands of Scots signed the National Covenant, pledging to resist changes in religious practice imposed by Charles. This led to the 1639 and 1640 Bishops' Wars, which ended with the Covenanters in control of the Scottish government. In response to the Irish Rebellion of 1641, Covenanter troops were sent to Ireland, and the 1643 Solemn League and Covenant brought them into the First English Civil War on the side of Parliament. As the Wars of the Three Kingdoms progressed, many Covenanters came to view English religious Independents like Oliver Cromwell as a greater threat than the Royalists, particularl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laggan Army
The Laggan Army, sometimes referred to as the Lagan Army, was a militia formed by Protestant settlers in the fertile Laggan district in the east of County Donegal in Ulster, during the time of the Irish Rebellion of 1641. Background Following the defeat of Gaelic Ireland after the Nine Years War and the Flight of the Earls in 1607, the colonization of Ulster began in 1609. English and Scottish settlers, supported by the Crown, started to colonize the north-east province of Ulster. The settlers largely settled on land which was confiscated from Gaelic chiefs in Ulster, many of whom had fled from Ireland following the Irish defeat in the Nine Years' War. In 1641, the Irish rose up in a rebellion led by Felim O'Neill. This coup's purposes included putting an end to anti-Catholic discrimination, greater Irish self-governance, and to partially or fully reverse the plantations of Ireland. Although it was intended to be bloodless, the rebellion was characterized by rebel at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundhead
Roundheads were the supporters of the Parliament of England during the English Civil War (1642–1651). Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I of England and his supporters, known as the Cavaliers or Royalists, who claimed rule by absolute monarchy and the principle of the divine right of kings. The goal of the Roundheads was to give to Parliament the supreme control over executive branch, executive administration of England. Beliefs Most Roundheads sought constitutional monarchy in place of the absolute monarchy sought by Charles; however, at the end of the English Civil War in 1649, public antipathy towards the king was high enough to allow republican leaders such as Oliver Cromwell to abolish the monarchy completely and establish the Commonwealth of England. The Roundhead commander-in-chief of the first Civil War, Thomas Fairfax, remained a supporter of constitutional monarchy, as did many other Roundhead leaders such as Edward Montagu, 2nd Earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalier
The term ''Cavalier'' () was first used by Roundheads as a term of abuse for the wealthier royalist supporters of Charles I of England and his son Charles II of England, Charles II during the English Civil War, the Interregnum (England), Interregnum, and the Restoration (England), Restoration (1642 – ). It was later adopted by the Royalists themselves. Although it referred originally to political and social attitudes and behaviour, of which clothing was a very small part, it has subsequently become strongly identified with the fashionable clothing of the court at the time. Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Prince Rupert, commander of much of Charles I's cavalry, is often considered to be an archetypal Cavalier. Etymology ''Cavalier'' derives from the same Latin root as the Italian word , the French word , and the Spanish word , the Vulgar Latin word ''wikt:caballarius, caballarius'', meaning 'horseman'. Shakespeare used the word ''cavaleros'' to describe an overbearing swashbuckl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th century until the unification of Italy, which took place between 1859 and 1870, culminated in their demise. The state was legally established in the 8th century when Pepin the Short, king of the Franks, gave Pope Stephen II, as a temporal sovereign, lands formerly held by Arian Christian Lombards, adding them to lands and other real estate formerly acquired and held by the bishops of Rome as landlords from the time of Constantine onward. This donation came about as part of a process whereby the popes began to turn away from the Byzantine emperors as their foremost temporal guardians for reasons such as increased imperial taxes, disagreement with respect to iconoclasm, and failure of the emperors, or their exarchs in Italy, to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
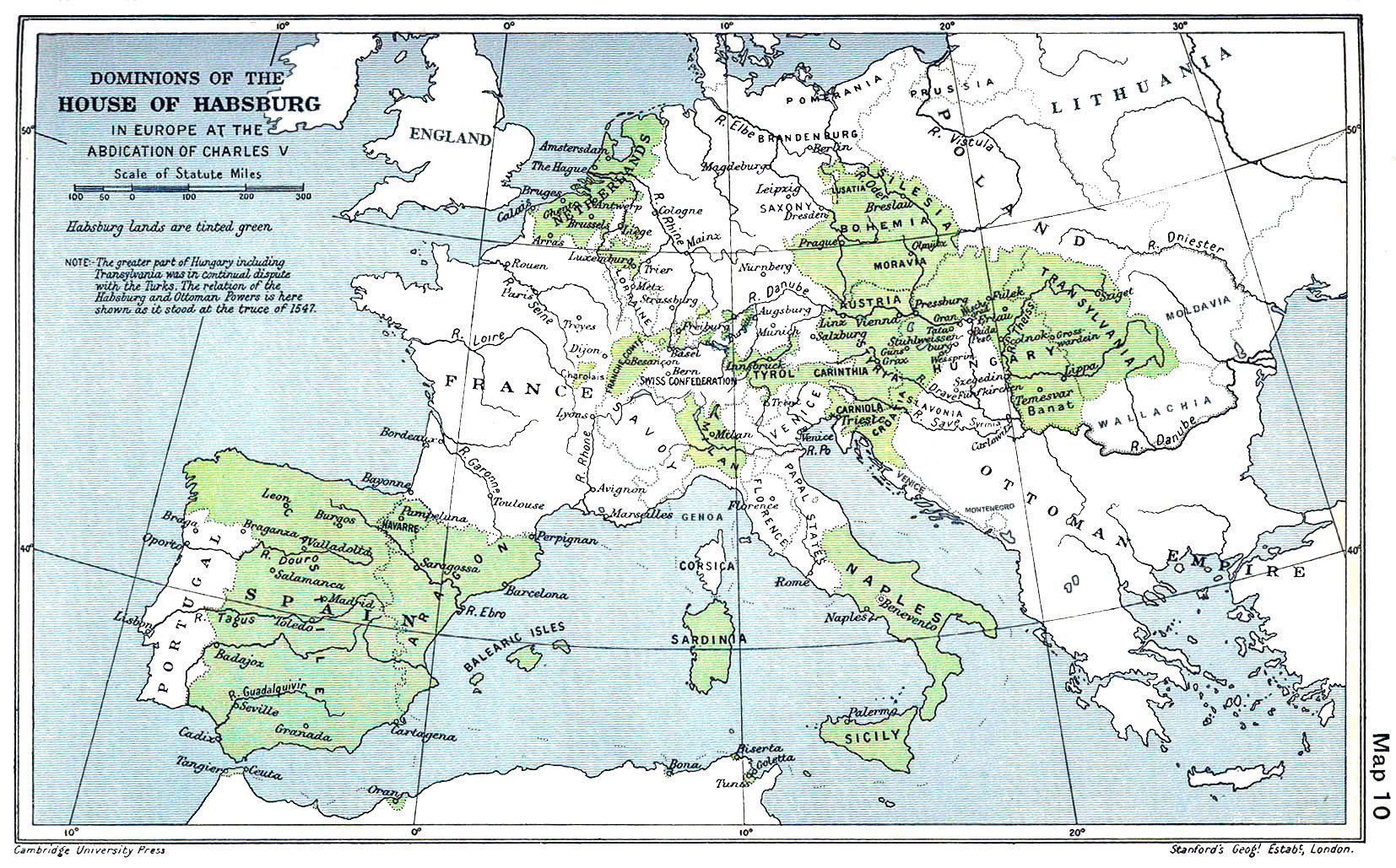
Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain refers to Spain and the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy, also known as the Rex Catholicissimus, Catholic Monarchy, in the period from 1516 to 1700 when it was ruled by kings from the House of Habsburg. In this period the Spanish Empire was at the zenith of its influence and power. During this period, Spain held many territories, including American continental holdings and the Spanish West Indies, West Indies; European territories like the Habsburg Netherlands, Low Countries, Council of Italy, Italian territories, Iberian Union, Portugal and parts of County of Burgundy, France; and the Captaincy General of the Philippines, Philippines and other possessions in Southeast Asia. The period of Spanish history has also been referred to as the "Age of Discovery, Age of Expansion". The Habsburg name was not always used by the family members, who often emphasized their more prestigious princely titles. The dynasty was long known as the "House of Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |