|
Companiganj Upazila, Sylhet
Companiganj ( bn, কোম্পানীগঞ্জ) is an upazila of Sylhet District in the Division of Sylhet, Bangladesh. History In 1779, the Khasi people attacked merchants in the village of Pandua in Bholaganj, who were going towards Calcutta after they experienced abuse from Europeans. Many merchants pleaded Robert Lindsay, the Collector of Sylhet, to build a small brick fort to protect them from further attacks from the Khasi. In 1789, the Collector of Sylhet, John Willes, stationed many sepoys in Pandua. The Khasi however, continued their attacks, killing the thanadar and many sepoys. Two European merchants managed to escape and inform Willes of the incident, who passed it on to the Government at Calcutta. A force was then sent from there to the village of Pandua, although it led to a bloodless end. Willes also told the government that he really had little control over northern Sylhet as the Khasi chiefs refused every order, would behead the messenger and then conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
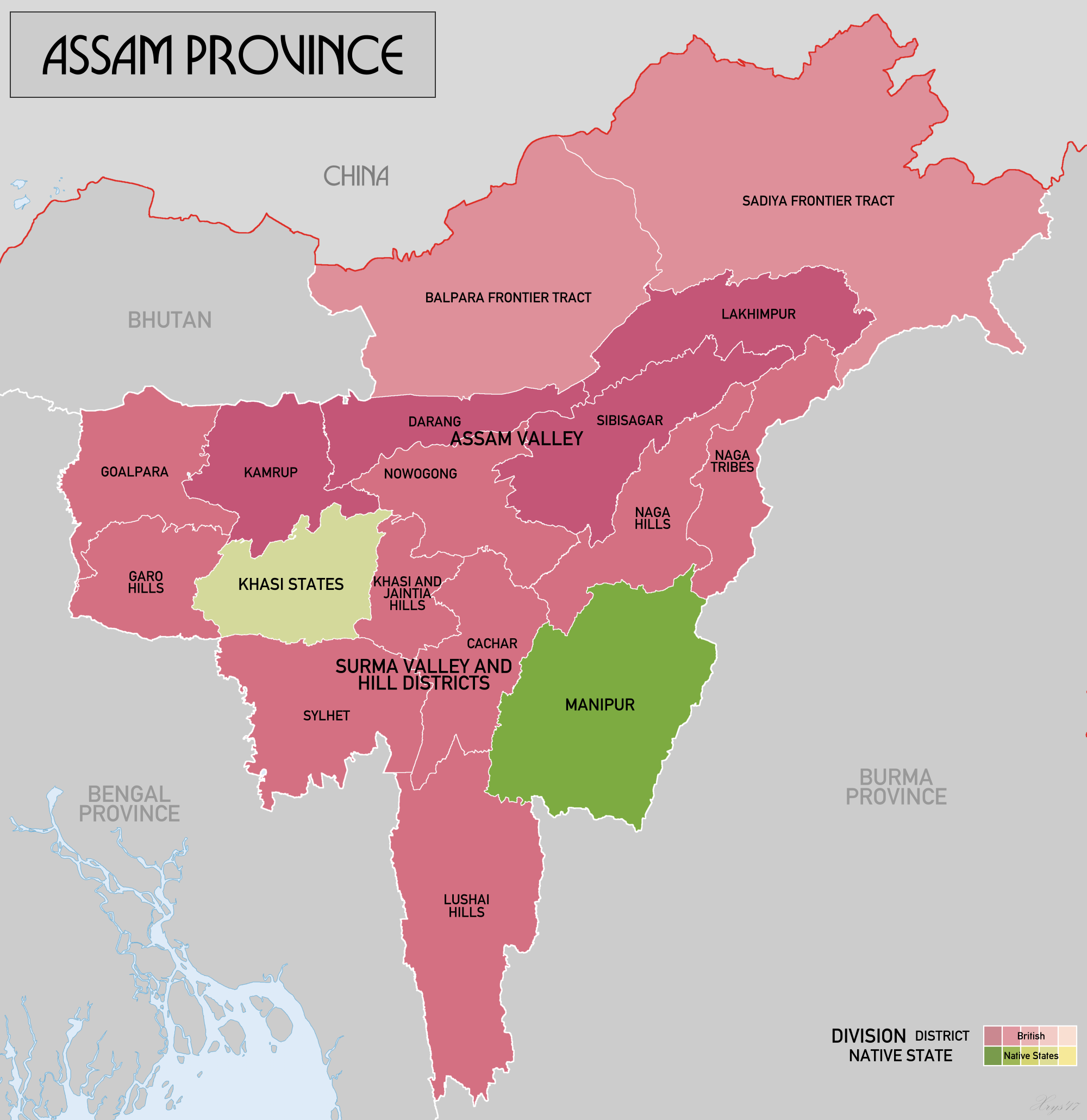
Sylhet Division
Sylhet Division ( bn, সিলেট বিভাগ) is the northeastern division of Bangladesh. It is bordered by the Indian states of Meghalaya, Assam and Tripura to the north, east and south respectively, and by the Bangladeshi divisions of Chittagong to the southwest and Dhaka and Mymensingh to the west. Prior to 1947, it included the subdivision of Karimganj (presently in Barak Valley, India). However, Karimganj (including the thanas of Badarpur, Patharkandi and Ratabari) was inexplicably severed from Sylhet by the Radcliffe Boundary Commission. According to Niharranjan Ray, it was partly due to a plea from a delegation led by Abdul Matlib Mazumdar. Etymology and names The name ''Sylhet'' is an anglicisation of ''Shilhot'' (শিলহট). Its origins seem to come from the Sanskrit words শিলা ''śilā'' (meaning 'stone') and হট্ট ''haṭṭa'' (meaning 'marketplace'). These words match the landscape and topography of the hilly region. The shila st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhatak Upazila
Chhatak ( bn, ছাতক) is an upazila of the Sunamganj District in Sylhet Division, Bangladesh. It is named after its headquarters, the town of Chhatak. Etymology According to the majority of researchers including Dewan Mohammad Azraf, the area got its name from ''chhātā'', the Bengali word for umbrella. It is said that upon the founding of a haat bazaar in such a rain-prone area, shopkeepers and shoppers would arrive with umbrellas and use umbrellas to prevent rain from falling on their fruits and crops. The area would be filled with umbrellas which later caused the market to be known as ''Chhātār Bazār'' (Umbrella's Market). Over time, it became corrupted into ''Chhātak Bazār''. On the other hand, Monir Uddin Chowdhury asserted that ''Chhātak'' was actually corrupted from ''Chhatrāk'', the word for an umbrella holder. He added that the area was first settled by a group of ''Chhatrāk''s who used to serve the local ruler. History After the Conquest of Srihatta in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upazilas Of Bangladesh
An ''upazila'' ( bn, উপজেলা, upôzela, lit=sub-district pronounced: ), formerly called ''thana'', is an administrative region in Bangladesh, functioning as a sub-unit of a district. It can be seen as an analogous to a county or a borough of Western countries. Rural upazilas are further administratively divided into union council areas (union parishads). Bangladesh ha495 upazilas(as of 20 Oct 2022). The upazilas are the second lowest tier of regional administration in Bangladesh. The administrative structure consists of divisions (8), districts (64), upazilas (495) and union parishads (UPs). This system of devolution was introduced by the former military ruler and president of Bangladesh, Lieutenant General Hossain Mohammad Ershad, in an attempt to strengthen local government. Below UPs, villages (''gram'') and ''para'' exist, but these have no administrative power and elected members. The Local Government Ordinance of 1982 was amended a year later, redesignati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Parishad
Union council ( bn, ইউনিয়ন পরিষদ, translit=iūniyan pariṣad, translit-std=IAST), also known as union parishad, rural council, rural union and simply union, is the smallest rural administrative and local government unit in Bangladesh. Each union council is made up of nine wards. Usually one village is designated as a ward. There are 4,562 unions in Bangladesh. A union council consists of a chairman and twelve members including three members exclusively reserved for women. Union councils are formed under the ''Local Government (Union Parishads) Act, 2009''. The boundary of each union council is demarcated by the Deputy Commissioner of the District. A union council is the body primarily responsible for agricultural, industrial and community development within the local limits of the union. History The term ''union'' dates back to the 1870 British legislation titled the ''Village Chowkidari Act'' which established union ''panchayats'' for collecting tax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shada Pathor
Shada or SHADA may refer to: * ''Shada'' (''Doctor Who''), an unaired serial of ''Doctor Who'' * USS ''Shada'' (SP-580), a United States Navy patrol vessel *Sexual Health and Disability Alliance * Société Haitiano-Américaine de Développement Agricole, a Haiti–United States agricultural venture *Jada Shada Hudson Jada Shada Hudson is the stage name of Dwight Giraud, a Barbadian-Canadian drag performer who competed on season 3 of ''Canada's Drag Race''. Career Jada Shada Hudson is a drag performer. She has performed at drag shows in Toronto. Jada Shad ..., Haitian-Canadian drag queen See also * Shadda, an emphasis symbol in the Arabic alphabet * Şada, a village in Azerbaijan {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H M Ershad
Lt. Gen. Hussain Muhammad Ershad ( bn, হুসেইন মুহাম্মদ এরশাদ; 1 February 1930 – 14 July 2019) was a Bangladeshi Army Chief politician who served as the President of Bangladesh from 1983 to 1990, a time many consider to have been a military dictatorship. He seized power as head of the army during a bloodless coup against President Abdus Sattar on 24 March 1982 (by imposing martial law and suspending the Constitution). He declared himself President in 1983, and subsequently won the controversial 1986 Bangladeshi presidential election. Despite claims to have legitimately won the 1986 election, many consider his regime as an era of military dictatorship. Ershad served in the Presidential office until 1990, when he was forced to resign following a popular pro-democracy mass uprising led by Khaleda Zia and Sheikh Hasina. Ershad founded the Jatiya Party in 1986 and became a Member of Parliament for that party in the constituency of Rangpur-3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Bangladesh
The president of Bangladesh ( bn, বাংলাদেশের রাষ্ট্রপতি — ) officially the President of the People's Republic of Bangladesh ( bn, গণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশের রাষ্ট্রপতি —) is the head of state of Bangladesh and commander-in-chief of the Bangladesh Armed Forces. The role of the president has changed three times since Bangladesh achieved independence in 1971. Presidents had been given executive power. In 1991, with the restoration of a democratically elected government, Bangladesh adopted a parliamentary democracy based on a Westminster system. The President is now a largely ceremonial post elected by the Parliament."Background Note: Bangladesh" US Department of State, May 2007 In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sectors In The Bangladesh Liberation War
During the Bangladesh War of Independence, the Bangladesh Forces (not to be confused with Mukti Bahini) were divided in the geographical area of Bangladesh into eleven divisions designated as sectors. Each sector had a sector commander I.e. Division Commanders who directed the military operation further coordinated through several sub-sectors under sub-sector commanders who fought along with their troops and civilian resistance fighters. Most of the Sector Commanders and quite a number of sub-sector commanders remained in security under Indian BSF border camps such as Wing Commander Bashar, Major Shafiullah, Major Mir Shawkat Ali. History Bangladesh Sector Commanders Conference The history of the Bangladesh war of Independence dates back to April 1971 when it began its inception with the title of Bangladesh Forces during the first Bangladesh Sector Commanders Conference held in the week of July 11–17, 1971. It was at this conference during which time BD Forces was organized an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in East Pakistan, which resulted in the independence of Bangladesh. The war began when the Pakistani military junta based in West Pakistan—under the orders of Yahya Khan—launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971, initiating the Bangladesh genocide. In response to the violence, members of the Mukti Bahini—a guerrilla resistance movement formed by Bengali military, paramilitary and civilians—launched a mass guerrilla war against the Pakistani military, liberating numerous towns and cities in the initial months of the conflict. At first, the Pakistan Army regained momentum during the monsoon, but Bengali guerrillas counterattac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gowainghat
Gowainghat ( bn, গোয়াইনঘাট) is an upazila of Sylhet District in the Division of Sylhet, Bangladesh. History The British Empire conquered the Jaintia Kingdom on 25 March 1835, finally incorporating Gowainghat in its Sylhet District Collectorate. In 1908, the Gowainghat Thana was founded with the union of 5 parganas; Dhargram, Araikha, Piyaingul, Panchbhag and Jaflong and then separated into 9 union councils. During the Bangladesh Liberation War, the Pakistani army launched an attack in Ujuhat, Alirgaon killing 25 freedom fighters on the night of 28 November 1971. 7 mass graves are found in the upazila in Ujuhat, Atgram, Tamabil Zero Point, Health Complex and Birkuli. To commemorate the loss of lives, a memorial has been built. The thana prospered, officially upgrading to an upazila on 14 March 1983. Geography Gowainghat is located at . It has 34,133 households and a total area of 486.1 km2. The rivers are quarried for their stones, in areas like Bichnaka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |