|
Commodity Money
Commodity money is money whose value comes from a commodity of which it is made. Commodity money consists of objects having value or use in themselves ( intrinsic value) as well as their value in buying goods. This is in contrast to representative money, which has no intrinsic value but represents something of value such as gold or silver, for which it can be exchanged, and fiat money, which derives its value from having been established as money by government regulation. Examples of commodities that have been used as media of exchange include precious metals and stones, grain, animal parts (such as beaver pelts), tobacco, fuel, and others. Sometimes several types of commodity money were used together, with fixed relative values, in various commodity valuation or price system economies. Aspects Commodity money is to be distinguished from representative money, which is a certificate or token which can be exchanged for the underlying commodity, but only by a formal process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Commodity Money Before The 8th Century
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the country's t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard A
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include " Richie", " Dick", " Dickon", " Dickie", " Rich", " Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", " Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English (the name was introduced into England by the Normans), German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Portuguese and Spanish "Ricardo" and the Italian "Riccardo" (see comprehensive variant list below). People named Richard Multiple people with the same name * Richard Andersen (other) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
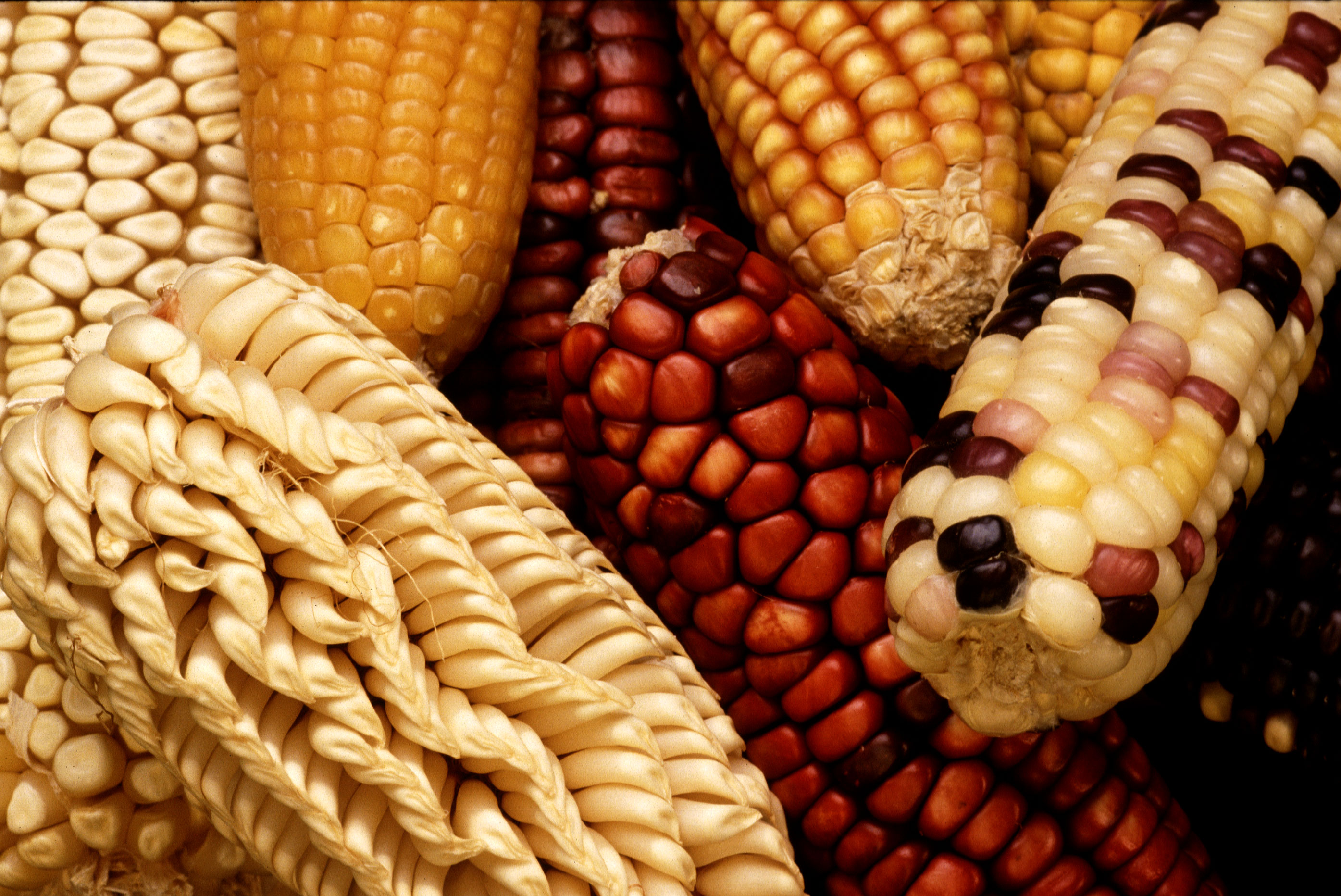
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wampum
Wampum is a traditional shell bead of the Eastern Woodlands tribes of Native Americans. It includes white shell beads hand-fashioned from the North Atlantic channeled whelk shell and white and purple beads made from the quahog or Western North Atlantic hard-shelled clam. In New York, wampum beads have been discovered dating before 1510.Dubin, Lois Sherr. ''North American Indian Jewelry and Adornment: From Prehistory to the Present''. New York: Harry N. Abrams, 1999: 170–171. . Before European contact, strings of wampum were used for storytelling, ceremonial gifts, and recording important treaties and historical events, such as the Two Row Wampum Treaty and the Hiawatha Belt. Wampum was also used by the northeastern Indigenous tribes as a means of exchange, strung together in lengths for convenience. The process to make wampum was labor-intensive with stone tools. Only the coastal tribes had sufficient access to the basic shells to make wampum. These factors increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rupee
Rupee (, ) is the common name for the currency, currencies of Indian rupee, India, Mauritian rupee, Mauritius, Nepalese rupee, Nepal, Pakistani rupee, Pakistan, Seychellois rupee, Seychelles, and Sri Lankan rupee, Sri Lanka, and of former currencies of Afghan rupee, Afghanistan, Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, the United Arab Emirates (as the Gulf rupee), East African rupee, British East Africa, Burmese rupee, Burma, German East African rupie, German East Africa (as German East African rupie, Rupie/Rupien), and Historical money of Tibet, Tibet. In Indonesia and the Maldives, the unit of currency is known as ''rupiah'' and ''rufiyaa'' respectively, cognates of the word rupee. The Indian rupee and Pakistani rupee are subdivided into one hundred paisa, paise (singular ''paisa'') or pice. The Nepalese rupee (रू) subdivides into one hundred paisa (singular and plural) or four sukaas. The Mauritian rupee, Mauritian, Seychellois rupee, Seychellois, and Sri Lankan rupees subdivide into 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seigniorage
Seigniorage , also spelled seignorage or seigneurage (), is the increase in the value of money due to money creation minus the cost of producing the additional money. Monetary seigniorage is where government bonds are exchanged for newly created money by a central bank, allowing debt monetization ("borrowing" without repaying). The increased purchasing power of the government at the expense of public purchasing power imposes what is known as an inflation tax on the public. Seignorage can also refer to: * Seigniorage derived from specie (metal coins) is a tax added to the total cost of a coin (metal content and production costs) that a customer of the mint had to pay, and which was sent to the sovereign of the political region. * Seigniorage derived from banknotes is the difference between interest earned on securities acquired in exchange for banknotes and the cost of printing and distributing the notes. Seigniorage is the positive return, or carry, on issued notes and coin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. Silver is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native metal, native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in currency and as an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 11 element, and one of the noble metals. It is one of the least reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical elements, being the second-lowest in the reactivity series. It is solid under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state (metallurgy), native state), as gold nugget, nuggets or grains, in rock (geology), rocks, vein (geology), veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coin
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by a government. Coins often have images, numerals, or text on them. The faces of coins or medals are sometimes called the ''obverse'' and the ''reverse'', referring to the front and back sides, respectively. The obverse of a coin is commonly called ''heads'', because it often depicts the head of a prominent person, and the reverse is known as ''tails''. The first metal coins – invented in the ancient Greek world and disseminated during the Hellenistic period – were precious metal–based, and were invented in order to simplify and regularize the task of measuring and weighing bullion (bulk metal) carried around for the purpose of transactions. They carried their value within the coins themselves, but the stampings also induced manip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mint (coin)
A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins that can be used as currency. The history of mints correlates closely with the history of coins. In the beginning, hammered coinage or cast coinage were the chief means of coin minting, with resulting production runs numbering as little as the hundreds or thousands. In modern mints, coin dies are manufactured in large numbers and planchets are made into milled coins by the billions. With the mass production of currency, the production cost is weighed when minting coins. For example, it costs the United States Mint much less than 25 cents to make a quarter (a 25 cent coin), and the difference in production cost and face value (called seigniorage) helps fund the minting body. Conversely, a U.S. penny ($0.01) cost $0.015 to make in 2016. History The first minted coins The first mint was likely established in Lydia in the 7th century BC, for coining gold, silver and electrum. The first coins known to be minted on E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
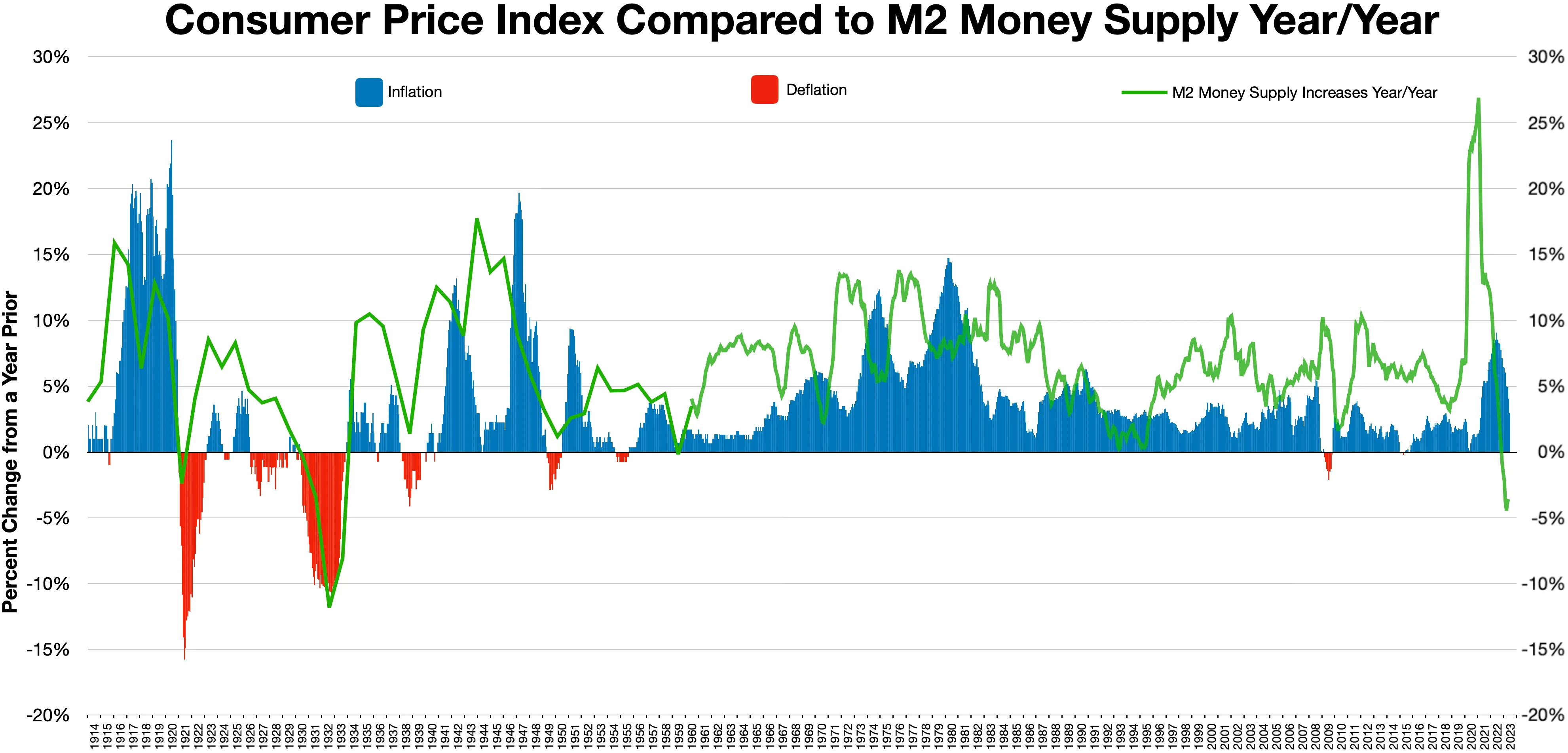
Deflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from '' disinflation'', a slowdown in the inflation rate; i.e., when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive. Economists generally believe that a sudden deflationary shock is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt, especially if the deflation is unexpected. Deflation may also aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral . Some economists argue that prolonged deflationary periods are related to the underlying technological progress in an economy, because as productivity increases ( TFP), the cost of goods decreases. Deflation usually happens when supply is hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |