|
Colpodellaceae
Chrompodellids are a phylum of single-celled protists belonging to the Alveolata supergroup. It comprises two different polyphyletic groups of flagellates: the colpodellids, phagotrophic predators, and the chromerids, photosynthetic algae that live as symbionts of corals. These groups were independently discovered and described, but molecular phylogenetic analyses demonstrated that they are intermingled in a clade that is the closest relative to Apicomplexa, and they became collectively known as chrompodellids. Due to the history of their research, they are variously known in biological classification as Chromerida or Colpodellida (ICZN)/Colpodellales ( ICN). Description and life cycle Chrompodellids are a phylum of unicellular protists containing two functionally different groups: the photosynthetic "chromerids" and the predatory phagotrophic "colpodellids". Like other Alveolata, they present tubular mitochondrial cristae and highly flattened cortical alveoli with micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitrella Brassicaformis
''Vitrella brassicaformis'' (CCMP3155) is a unicellular alga belonging to the eukaryotic supergroup Alveolata. ''V. brassicaformis'' and its closest known relative, '' Chromera velia,'' are the only two currently described members of the phylum Chromerida, which in turn constitutes part of the taxonomically unranked group Colpodellida. Chromerida is phylogenetically closely related to the phylum Apicomplexa, which includes ''Plasmodium'', the agent of malaria. Notably, both ''V. brassicaformis'' and ''C. velia'' are photosynthetic, each containing a complex secondary plastid. This characteristic defined the discovery of these so-called ' chromerids,' as their photosynthetic capacity positioned them to shed light upon the evolution of Apicomplexa's non-photosynthetic parasitism. Both genera lack chlorophyll ''b'' or '' c''; these absences link the two taxonomically, as algae bearing only chlorophyll ''a'' are rare amid the biodiversity of life. Despite their similarities, ''V. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in question. In addition to their use for inferring phylogenetic pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myzocytosis
Myzocytosis (from Greek: myzein, (') meaning "to suck" and kytos (') meaning "container", hence referring to "cell") is a method of feeding found in some heterotrophic organisms. It is also called "cellular vampirism" as the predatory cell pierces the cell wall and/or cell membrane of the prey cell with a feeding tube, the conoid, sucks out the cellular content and digests it. Myzocytosis is found in Myzozoa and also in some species of Ciliophora (both comprise the alveolates). A classic example of myzocytosis is the feeding method of the infamous predatory ciliate, '' Didinium'', where it is often depicted devouring a hapless ''Paramecium''. The suctorian ciliate The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a ...s were originally thought to have fed exclusively through myzocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a Protein dimer, dimer of two globular proteins, Tubulin#Eukaryotic, alpha and beta tubulin into #Structure, protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortical Alveolum
The cortical alveolum () is a cellular organelle consisting of a vesicle located under the cytoplasmic membrane, to which they give support. The term " corticate" comes from an evolutionary hypothesis about the common origin of kingdoms Plantae and Chromista, because both kingdoms have cortical alveoli in at least one phylum. At least three protist lineages exhibit these structures: Telonemia, Alveolata and Glaucophyta. Definition Cortical alveoli have been defined as flattened membranous sacs or vesicles that strengthen the cellular cortex through the firm fixation to the underlying membrane and microtubules. They typically form a continuous layer that acts as a flexible film, although they can also constitute a semi-rigid structure or the scales of a theca. Occurrence Cortical alveoli are the defining cellular characteristic of the protist clade Alveolata, otherwise united solely by molecular phylogeny. The name 'Alveolata' is a reference to this trait, present in all re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
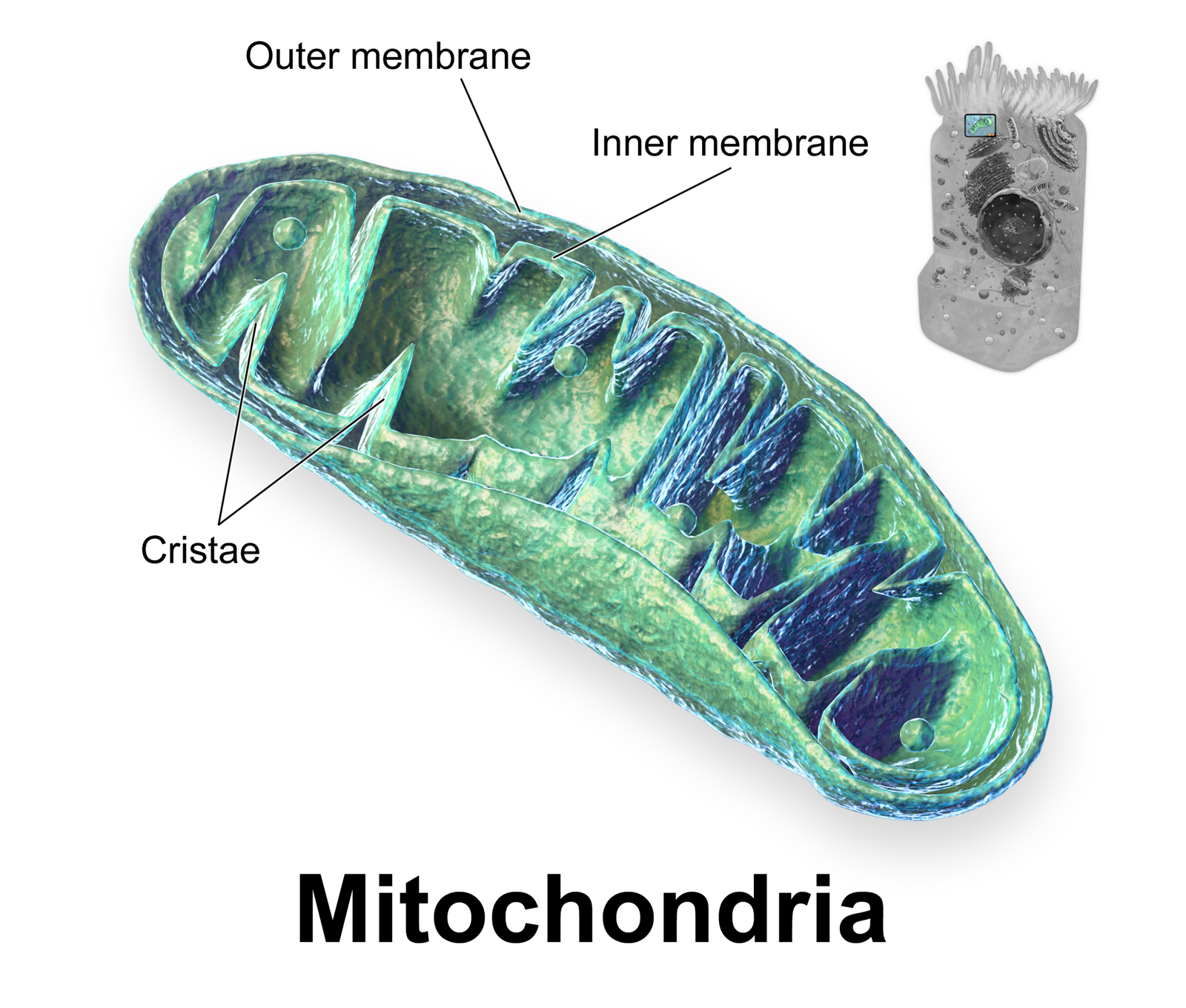
Crista
A crista (; : cristae) is a fold in the inner mitochondrial membrane, inner membrane of a mitochondrion. The name is from the Latin for ''crest'' or ''plume'', and it gives the inner membrane its characteristic wrinkled shape, providing a large amount of surface area for chemical reactions to occur on. This aids cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, aerobic cellular respiration, because the mitochondrion requires oxygen. Cristae are studded with proteins, including ATP synthase and a variety of cytochromes. Background With the discovery of the dual-membrane nature of mitochondria, the pioneers of mitochondrial ultrastructure, ultrastructural research proposed different models for the organization of the mitochondrial inner membrane. Three models proposed were: *Baffle model – According to George Emil Palade, Palade (1953), the mitochondrial inner membrane is convoluted in a baffle-like manner with broad openings towards the intra-cristal space. This model entered most text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolate
The alveolates (meaning "pitted like a honeycomb") are a group of protists, considered a major unranked clade or superphylum within Eukaryota. They are currently grouped with the Stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate mitochondria into the SAR supergroup. Characteristics The most notable shared characteristic is the presence of cortical (near the surface) alveoli (sacs). These are flattened vesicles (sacs) arranged as a layer just under the membrane and supporting it, typically contributing to a flexible pellicle (thin skin). In armored dinoflagellates they may contain stiff plates. Alveolates have mitochondria with tubular cristae ( invaginations), and cells often have pore-like intrusions through the cell surface. The group contains free-living and parasitic organisms, predatory flagellates, and photosynthetic organisms. Almost all sequenced mitochondrial genomes of ciliates and apicomplexa are linear. The mitochondria almost all carry mtDN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a Multicellular organism, multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. The two main cells that do this are the Macrophages and the Neutrophils of the immune system. Where phagocytosis is used as a means of feeding and provides the organism part or all of its nourishment, it is called phagotrophy and is distinguished from osmotrophy, which is nutrition taking place by absorption. History The history of phag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabolism. ''Photosynthesis'' usually refers to oxygenic photosynthesis, a process that produces oxygen. Photosynthetic organisms store the chemical energy so produced within intracellular organic compounds (compounds containing carbon) like sugars, glycogen, cellulose and starches. To use this stored chemical energy, an organism's cells metabolize the organic compounds through cellular respiration. Photosynthesis plays a critical role in producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and it supplies most of the biological energy necessary for complex life on Earth. Some bacteria also perform anoxygenic photosynthesis, which uses bacteriochlorophyll to split hydrogen sulfide as a reductant instead of water, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroups, such as Archaeplastida ( photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and " Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, including extreme habitats. Their diversity, larger than for all other eukaryotes, has only been discovered in rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Code Of Nomenclature For Algae, Fungi, And Plants
The ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN or ICNafp) is the set of rules and recommendations dealing with the formal botanical names that are given to plants, fungi and a few other groups of organisms, all those "traditionally treated as algae, fungi, or plants".. It was formerly called the ''International Code of Botanical Nomenclature'' (ICBN); the name was changed at the International Botanical Congress in Melbourne in July 2011 as part of the ''Melbourne Code''. which replaced the ''Vienna Code'' of 2005. The current version of the code is the ''Shenzhen Code'' adopted by the International Botanical Congress held in Shenzhen, China, in July 2017. As with previous codes, it took effect as soon as it was ratified by the congress (on 29 July 2017), but the documentation of the code in its final form was not published until 26 June 2018. For fungi the ''Code'' was revised by the ''San Juan Chapter F'' in 2018. The 2025 edition of ICBN, the ''Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |