|
Colonial Naval Defence Act 1865
The Colonial Naval Defence Act 1865 ( 28 & 29 Vict. c. 14) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Background During the Invasion of the Waikato (July 1863 – April 1864) period of the New Zealand Wars the Imperial British forces realised they needed access to colonial ships to fight Māori. The colonial government acquired vessels which were staffed by Royal Navy officers but owned by the colonial government. The vessels were under local and not Admiralty control. An armed ship, HMVS ''Victoria'', owned by the Colony of Victoria transported troops to New Zealand for the campaign and took part in bombardments of Māori. The British government was concerned about its colonies developing their own navies, not under the control of the Royal Navy's Admiralty. This led to the British parliament passing the Colonial Naval Defence Act 1865, which allowed the colonial governments to own ships, including for military purposes, but they would have to be under the Royal Nav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Short Title
In certain jurisdictions, including the United Kingdom and other Westminster system, Westminster-influenced jurisdictions (such as Canada or Australia), as well as the United States and the Philippines, primary legislation has both a short title and a long title. The long title (properly, the title in some jurisdictions) is the formal title appearing at the head of a statute (such as an act of Parliament or of act of Congress, Congress) or other legislative instrument. The long title is intended to provide a summarised description of the purpose or scope of the instrument. Like other descriptive components of an act (such as the preamble, section headings, side notes, and short title), the long title seldom affects the operative provisions of an act, except where the operative provisions are unclear or ambiguous and the long title provides a clear statement of the legislature's intention. The short title is the formal name by which legislation may by law be Legal citation, cited. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
28 & 29 Vict
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. Etymology English ''eight'', from Old English '', æhta'', Proto-Germanic ''*ahto'' is a direct continuation of Proto-Indo-European '' *oḱtṓ(w)-'', and as such cognate with Greek and Latin , both of which stems are reflected by the English prefix oct(o)-, as in the ordinal adjective ''octaval'' or ''octavary'', the distributive adjective is ''octonary''. The adjective ''octuple'' (Latin ) may also be used as a noun, meaning "a set of eight items"; the diminutive ''octuplet'' is mostly used to refer to eight siblings delivered in one birth. The Semitic numeral is based on a root ''*θmn-'', whence Akkadian ''smn-'', Arabic ''ṯmn-'', Hebrew ''šmn-'' etc. The Chinese numeral, written (Mandarin: ''bā''; Cantonese: ''baat''), is from Old Chinese ''*priāt-'', ultimately from Sino-Tibetan ''b-r-gyat'' or ''b-g-ryat'' which also yielded Tibetan '' brgyat''. It has been argued that, as the cardinal num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the English overseas possessions, overseas possessions and trading posts established by Kingdom of England, England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries, and colonisation attempts by Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the 17th century. At its height in the 19th and early 20th centuries, it became the List of largest empires, largest empire in history and, for a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, Westminster system, its constitutional, Common law, legal, English language, linguistic, and Culture of the United Kingdom, cultural legacy is widespread. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Colonial Naval Defence Act 1931
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to: * Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology) Architecture * American colonial architecture * French colonial architecture * Spanish colonial architecture Automobiles * Colonial (1920 automobile), the first American automobile with four-wheel brakes * Colonial (Shaw automobile), a rebranded Shaw sold from 1921 until 1922 * Colonial (1921 automobile), a car from Boston which was sold from 1921 until 1922 Commerce * Colonial Pipeline, the largest oil pipeline network in the U.S. * Inmobiliaria Colonial, a Spanish corporation, which includes companies in the domains of real estate Places * The Colonial (Indianapolis, Indiana) * The Colonial (Mansfield, Ohio), a National Register of Historic Places listing in Richland County, Ohio * Ciudad Colonial (Santo Domingo), a historic central neighborhood of Santo Domingo * Colonial Country Club (Memphis), a golf course in Tennessee * Colonial Country Club (Fort Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New Zealand Legal Information Institute
The New Zealand Legal Information Institute (NZLII) is operated by the University of Otago faculty of law with assistance from the University of Canterbury and Victoria University of Wellington. It contains more than 100 databases of New Zealand law including many decision from courts and tribunals that are not available anywhere else, including from commercial operators. It operates using voluntary labour and grants from thNew Zealand Law Foundation NZLII is a member of the Free Access to Law Movement The Free Access to Law Movement (FALM) is the international organization devoted to providing free online access to legal information such as case law, legislation, treaties, law reform proposals and legal scholarship. The movement began in 1992 .... References * Buckingham ‘What’s in a Name?: New Zealand and the growth of free on-line legal information’ 005CompLRes 2; 7th Law via Internet Conference, Vila, Vanuatu * Section on NZLII in Greenleaf, Legal Information Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parliament Of The United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster in London. Parliament possesses legislative supremacy and thereby holds ultimate power over all other political bodies in the United Kingdom and the Overseas Territories. While Parliament is bicameral, it has three parts: the sovereign, the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. The three parts acting together to legislate may be described as the King-in-Parliament. The Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation. The House of Commons is the elected lower chamber of Parliament, with elections to 650 single-member constituencies held at least every five years under the first-past-the-post system. By constitutional conventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Invasion Of The Waikato
The invasion of the Waikato became the largest and most important campaign of the 19th-century New Zealand Wars. Hostilities took place in the North Island of New Zealand between the military forces of the colonial government and a federation of Māori tribes known as the Kingitanga Movement. The Waikato is a territorial region with a northern boundary somewhat south of the present-day city of Auckland. The campaign lasted for nine months, from July 1863 to April 1864. The invasion was aimed at crushing Kingite power (which European settlers saw as a threat to colonial authority) and also at driving Waikato Māori from their territory in readiness for occupation and settlement by European colonists. The campaign was fought by a peak of about 14,000 Imperial and colonial troops and about 4,000 Māori warriors drawn from more than half the major North Island tribal groups. Plans for the invasion were drawn up at the close of the First Taranaki War in 1861 but the Colonial Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New Zealand Wars
The New Zealand Wars () took place from 1845 to 1872 between the Colony of New Zealand, New Zealand colonial government and allied Māori people, Māori on one side, and Māori and Māori-allied settlers on the other. Though the wars were initially localised conflicts triggered by tensions over disputed land purchases (by European settlers from Māori), they escalated dramatically from 1860 as the government became convinced it was facing united Māori resistance to further land sales and a refusal to acknowledge The Crown, Crown sovereignty. The colonial government summoned thousands of British troops to mount major campaigns to overpower the Māori King Movement, Kīngitanga (Māori King) movement and also conquest of farming and residential land for British settlers. Later campaigns were aimed at quashing the Pai Mārire religious and political movement, which was strongly opposed to the conquest of Māori land and eager to strengthen Māori identity. Religion of Māori people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
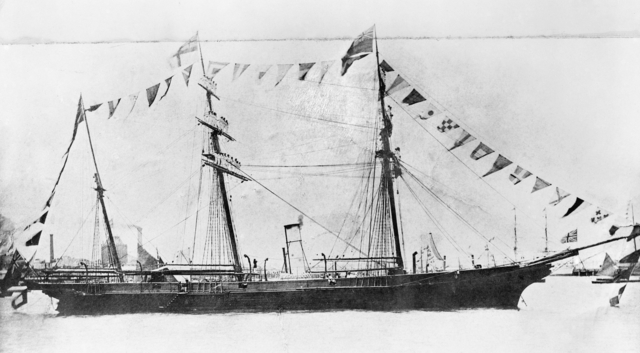
HMVS Victoria (1855)
HMVS ''Victoria'' (Her Majesty's Victorian Ship; also referred to with the prefix HMCSS-Her Majesty's Colonial Steam Sloop) was a 580-ton combined steam/sail sloop-of-war built in England in the 1850s for the colony of Victoria, Australia. She was the second warship to be built for an Australian colonial navy, the first British-built ship given to a colony of the British Empire, and the first Australian warship to be deployed overseas when she supported New Zealand colonists during the First Taranaki War. Construction and acquisition ''Victoria'' was the first warship to be built in England for one of the British colonies. She was the second ship ordered for an Australian colonial navy, after the Australian-built gunboat ''Spitfire'' for the New South Wales colony. She was designed by the British naval architect Oliver Lang and launched in London on 30 June 1855 by Lady Constance Talbot. Commander William Henry Norman sailed ''Victoria'' from Plymouth to Hobsons Bay, arriving o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Colony Of Victoria
The Colony of Victoria was a historical administrative division in Australia that existed from 1851 until 1901, when it federated with other colonies to form the Commonwealth of Australia. Situated in the southeastern corner of the Australian continent, Victoria played a significant role in the country's colonial history and development. History Establishment The Colony of Victoria, established in 1851, was carved out of the southeastern part of the Colony of New South Wales. This separation was fuelled by a combination of economic, political, and social factors, with a burgeoning population and a desire for local governance playing crucial roles. The discovery of gold in the region accelerated its development, transforming Victoria into a vibrant hub of activity and prosperity. The Gold Rush era The discovery of gold in 1851 near Ballarat and Bendigo marked a pivotal moment in Victoria's history. The ensuing gold rush attracted tens of thousands of immigrants from arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early Middle Ages, medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the English Navy of the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the early 18th century until the World War II, Second World War, it was the world's most powerful navy. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Government Ensign Of The United Kingdom
The Blue Ensign is a British ensign that may be used on vessels by certain authorised yacht clubs, Royal Research Ships and British merchant vessels whose master holds a commission in the Royal Naval Reserve or has otherwise been issued a warrant. Defaced versions with a badge or other emblem are used more broadly; in the United Kingdom by authorised government or private bodies; and internationally by nations or organisations previously a part of the British Empire. The evolution of the Blue Ensign followed that of the Union Jack. The ensign originated in the 17th century with the St George's Cross (the Flag of England) in the canton, and with a blue field. The Acts of Union 1707 united England (which included present day Wales) with Scotland in the Kingdom of Great Britain, thus producing a new Blue Ensign with the new Union Flag, containing a saltire, in the canton. With the Act of Union 1800, Ireland became a part of the new United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |