|
Collagraphy
Collagraphy (sometimes spelled collography) is a printmaking process in which materials are glued or sealed to a rigid substrate (such as paperboard or wood) to create a plate. Once inked, the plate becomes a tool for imprinting the design onto paper or another medium. The resulting print is termed a collagraph. The term "collagraph" was coined by Glen Alps in the 1950s, and is derived from the Greek language, Greek word ''koll'' or ''kolla'', meaning adhesive, glue, and ''graph'', meaning the activity of drawing. Artists use a variety of materials in collagraphy, including yarn, fabric, tape, different varieties of cut paper or card, leaves, feathers, and acrylic mediums. The application of ink onto the collagraph plate is versatile, consisting of Intaglio (printmaking), intaglio-inking into recesses, brayer or paintbrush inking onto Relief printing, relief surfaces, or a combination of these methods. A print can be made with, or without use of a Printing press, press. See als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glen Alps
Glen Alps (1914-1996) was a printmaker and educator who is credited with having developed the collagraph. A collagraph is a print whose plate is a board or other substrate onto which textured materials are glued. The plate may be inked for printing in either the intaglio (printmaking), intaglio or the relief print, relief manner and then printed onto paper. Although the inventor of the process is not known, Alps made collagraphy his primary art form and coined the word "collagraph" in 1956. He disseminated the techniques he developed for making collagraphs during his long career as both an artist and a teacher. Early life and education Alps was born in 1914 on a farm near Loveland, Colorado. He attended Colorado State College of Education (today University of Northern Colorado) in Greeley, Colorado, where he received the Bachelor of Arts in 1940. After graduation he worked as an art instructor in the Greeley County school system until 1942, when he took a job in the publishing de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beatrice Winn Berlin
Beatrice Winn Berlin (née Beatrice Winn; May 27, 1922 – August 11, 1999) was an American printmaker, painter, and teacher. Early life and education Beatrice Winn Berlin was born as Beatrice Winn on May 27, 1922, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to parents Pauline (née Neubauer) and Benjamin Winn. She attended Moore College of Art and Design, Fleischer Art Memorial, and Philadelphia Colleges of the Arts (now University of the Arts, Philadelphia), and was a student under Samuel Maitin, Victor Lasuchin, Hitoshi Nakazato, and Kenjilo Nanao. In 1945, she married Herbert Edward Berlin, and paused her arts education to raise their two daughters. In 1963, Berlin enrolled in an introduction to printmaking course at Pennsylvania Museum and School of Industrial Art, which inspired her to pursue further courses in printmaking. Career She found inspiration in collagraphy, and Japanese modernism. In the late 1960s, Berlin began teaching drawing, painting, and printmaking at v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
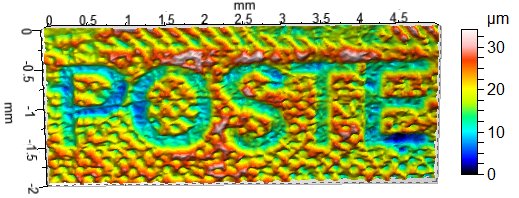
Collagraph Plates
Collagraphy (sometimes spelled collography) is a printmaking process in which materials are glued or sealed to a rigid substrate (such as paperboard or wood) to create a plate. Once inked, the plate becomes a tool for imprinting the design onto paper or another medium. The resulting print is termed a collagraph. The term "collagraph" was coined by Glen Alps in the 1950s, and is derived from the Greek word ''koll'' or ''kolla'', meaning glue, and ''graph'', meaning the activity of drawing. Artists use a variety of materials in collagraphy, including yarn, fabric, tape, different varieties of cut paper or card, leaves, feathers, and acrylic mediums. The application of ink onto the collagraph plate is versatile, consisting of intaglio-inking into recesses, brayer or paintbrush inking onto relief surfaces, or a combination of these methods. A print can be made with, or without use of a press. See also *Carborundum printmaking *Beatrice Winn Berlin Beatrice Winn Berlin (née ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Student Work From A Collagraph And Monoprint Workshop
A student is a person enrolled in a school or other educational institution, or more generally, a person who takes a special interest in a subject. In the United Kingdom and most commonwealth countries, a "student" attends a secondary school or higher (e.g., college or university); those in primary or elementary schools are "pupils". Africa Nigeria In Nigeria, education is classified into four systems known as a 6-3-3-4 system of education. It implies six years in primary school, three years in junior secondary, three years in senior secondary and four years in the university. However, the number of years to be spent in university is mostly determined by the course of study. Some courses have longer study lengths than others. Those in primary school are often referred to as pupils. Those in university, as well as those in secondary school, are referred to as students. The Nigerian system of education also has other recognized categories like the polytechnics and colleges of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating work of art, artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed technique, rather than a photographic reproduction of a visual artwork which would be printed using an electronic machine (Printer (computing), a printer); however, there is some cross-over between traditional and digital printmaking, including risograph. Prints are created by transferring ink from a Matrix (printing), matrix to a sheet of paper or other material, by a variety of techniques. Common types of matrices include: metal plates for engraving, etching and related intaglio printing techniques; stone, aluminum, or polymer for lithography; blocks of wood for woodcuts and wood engravings; and linoleum for linocuts. Screens made of silk or synthetic fabrics are used for the screen printing process. Other types of matrix substrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paperboard
Paperboard is a thick paper-based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker (usually over 0.30 mm, 0.012 in, or 12 Inch#Equivalents, points) than paper and has certain superior attributes such as foldability and rigidity. According to International Organization for Standardization, ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a grammage above 250 g/m2, but there are exceptions. Paperboard can be single- or multi-ply. Paperboard can be easily cut and formed, is lightweight, and because it is strong, is used in packaging. Another end-use is high quality graphic printing, such as book and magazine covers or postcards. Paperboard is also used in fine arts for creating sculptures. Sometimes it is referred to as ''cardboard'', which is a generic, lay term used to refer to any heavy pulp (paper), paper pulp–based board, however this usage is deprecated in the paper, printing, and packaging industries as it does not ade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere, such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree, it performs a mechanical-support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients among the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, woodchips, or fibers. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation. The use of adhesives offers certain advantages over other binding techniques such as sewing, mechanical fastenings, and welding. These include the ability to bind different materials together, the more efficient distribution of stress across a joint, the cost-effectiveness of an easily mechanized process, and greater flexibility in design. Disadvantages of adhesive use include decreased stability at high temperatures, relative weakness in bonding large objects with a small bonding surface area, and greater difficulty in separating objects during testing. Adhesives are typically organized by the method of adhesion followed by ''reactive'' or ''non-reactive'', a term which refers to whether the adhesive chemically reacts in order to harden. Alternatively, they can be organized either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawing
Drawing is a Visual arts, visual art that uses an instrument to mark paper or another two-dimensional surface, or a digital representation of such. Traditionally, the instruments used to make a drawing include pencils, crayons, and ink pens, sometimes in combination. More modern tools include Stylus (computing), computer styluses with graphics tablets and gamepads in Virtual reality, VR drawing software. A drawing instrument releases a small amount of material onto a surface, leaving a visible mark. The most common support for drawing is paper, although other materials, such as Paperboard, cardboard, vellum, wood, plastic, leather, canvas, and Lumber, board, have been used. Temporary drawings may be made on a blackboard or whiteboard. Drawing has been a popular and fundamental means of public expression throughout human history. It is one of the simplest and most efficient means of communicating ideas. The wide availability of drawing instruments makes drawing one of the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intaglio (printmaking)
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print where the parts of the matrix that make the image stand ''above'' the main surface. Normally copper, or in recent times zinc, sheets called plates are used as a surface or matrix, and the incisions are created by etching, engraving, drypoint, aquatint or mezzotint, often in combination. Collagraphs may also be printed as intaglio plates. After the decline of the main relief technique of woodcut around 1550, the intaglio techniques dominated both artistic printmaking as well as most types of illustration and popular prints until the mid 19th century. The word "intaglio" describes prints created from plates where the ink-bearing regions are recessed beneath the plate's surface. Though brass, zinc, and other materials are occasionally utilized, copper is the most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brayer
A brayer is a hand-tool used historically in printing and printmaking to break up and "rub out" (spread) ink, before it was "beaten" using Ink ball, inking balls or composition rollers. A brayer consists of a short wooden cylinder with a handle fitted to one end; the other, flat end is used to rub the ink. History The word is derived from the verb to "bray", meaning "to break, pound, or grind small, as in a mortar". In the late nineteenth century the term was applied in the United States to a small hand-roller, "used for spreading ink on the inking table, and for applying it to the distributing plates or rollers connected with presses". Such small rollers were sold as "brayers" from at least 1912 and later in the century the term was applied in the U.S. to hand-rollers of all sorts and sizes. It retains its original meaning in Europe. Materials Brayers in the original sense were generally made of wood (though Southward refers to their being made of "wood or glass").John South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |