|
Colada Hanover
Colada is one of the two best-known swords, along with Tizona, of El Cid Campeador. Won in combat from the Count of Barcelona, the sword was presented (along with Tizona) to his sons in law. According to the heroic verses of the Cantar de mio Cid, after his sons-in-law beat his daughters and then abandoned them on the side of the road, El Cid asked for his gifts to be returned. Afterward, he bestowed the sword upon one of his knights, Martín Antolínez. Though its authenticity is doubted, a blade named ''Colada'' and traditionally identified with that of El Cid, with the addition of a 16th-century hilt, is preserved in the Royal Palace of Madrid. It is necessary to add that El Cid's sword is displayed in the Museum as the "Tizona" Sword, the name Colada could have easily been appointed by popular culture since Bards at the time shared stories of folklorical nature which were far from being based on historical facts. According to Sebastián de Covarrubias,Sebastián de Covarr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degen - Fig
Degen may refer to: __NOTOC__ Weaponry *Swiss degen, a type of short sword of the late medieval and Renaissance period *the German term for a dress sword **Degen (SS), a type of straight saber used by the German SS **the German term for the épée in modern sport fencing Places * Degen, Switzerland, a former municipality in Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland *Dêgên, a township in Nagqu prefecture, Tibet Other uses * Degen (surname) Degen is a surname of Swiss, German or Croatian origin. There are numerous unrelated families sharing the name, which can originate in a number of given names beginning in ''Degen-'' ("hero"); compare the '' Degener'' surname, from the German given ... * Dejen Gebremeskel (born 1989), Ethiopian long-distance runner See also * * Degeneracy (other) {{disambiguation, geo, given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tizona
''Tizona'' (also ''Tizón'') is the name of one of the swords carried by Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar, El Cid, according to the '' Cantar de Mio Cid''. The name of the second sword of El Cid is '' Colada''. A sword identified as ''Tizona'' was given by Ferdinand II of Aragon to Pedro de Peralta, count of Santisteban de Lerín in c. 1470. This sword was long kept in Marcilla Castle, later in the Army Museum in Madrid and since 2007 in the Museo de Burgos. Name The name used in the '' Cantar de Mio Cid'' is ''Tizón''. The form ''Tizona'' has been in use since the late medieval period (14th century). The blade inscription on the Marcilla sword, presumably of the 13th or 14th century, has the form ''TIZONA''. The older form of the name, '' tizón'', is a word for "firebrand" (''leño encendido'', from Latin '' titionem''). Sebastián de Covarrubias (1611) recognizes this as the plausible origin of the name ''Tizona'', but also adduces possible derivation from τυχωνα, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Cid
Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar (c. 1043 – 10 July 1099) was a Castilian knight and warlord in medieval Spain. Fighting with both Christian and Muslim armies during his lifetime, he earned the Arabic honorific ''al-sīd'', which would evolve into El Cid ("the lord"), and the Spanish moniker El Campeador ("the valiant"). He was born in Vivar, a village near the city of Burgos. As the head of his loyal knights, he came to dominate the Levante of the Iberian Peninsula at the end of the 11th century. He reclaimed the Taifa of Valencia from Moorish control for a brief period during the '' Reconquista'', ruling the principality as its Prince () from 17 June 1094 until his death in 1099. His wife, Jimena Díaz, inherited the city and maintained it until 1102 when it was reconquered by the Moors. Díaz de Vivar became well known for his service in the armies of both Christian and Muslim rulers. After his death, El Cid became Spain's celebrated national hero and the protagonist of the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
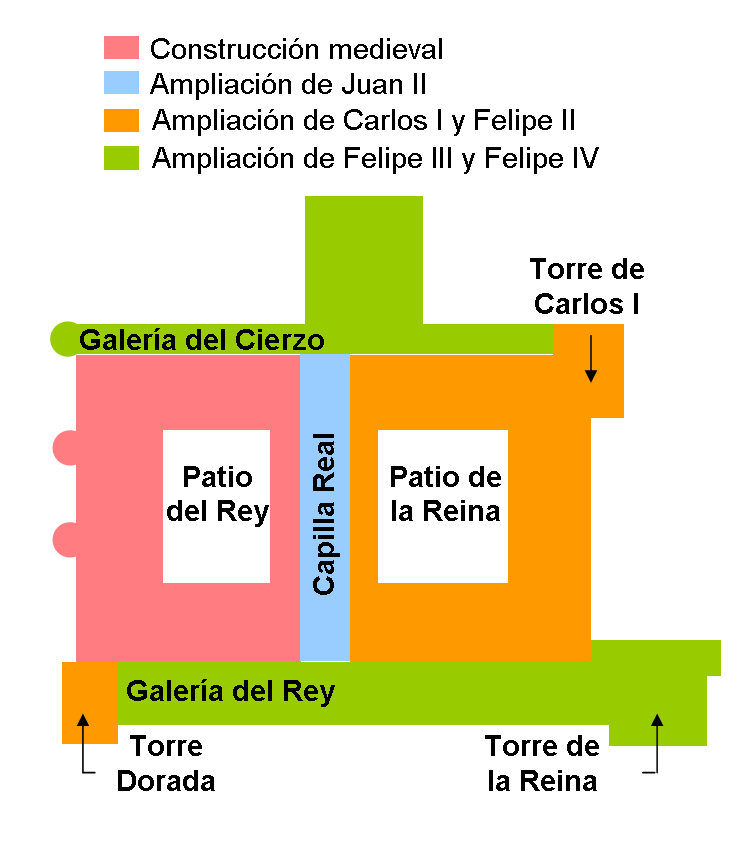
Royal Palace Of Madrid
The Royal Palace of Madrid ( es, Palacio Real de Madrid) is the official residence of the Spanish royal family at the city of Madrid, although now used only for state ceremonies. The palace has of floor space and contains 3,418 rooms. It is the largest royal palace in Europe. The palace is now open to the public, except during state functions, although it is so large that only a selection of rooms are on the visitor route at any one time, the route being changed every few months. An admission fee of €13 is charged; however, at some times it is free. The palace is owned by the Spanish state and administered by the Patrimonio Nacional, a public agency of the Ministry of the Presidency. The palace is on Calle de Bailén ("Bailén Street") in the western part of downtown Madrid, east of the Manzanares River, and is accessible from the Ópera (Madrid Metro), Ópera metro station. Felipe VI and the royal family do not reside in the palace, choosing instead the Palace of Zarzuela in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Poem
An epic poem, or simply an epic, is a lengthy narrative poem typically about the extraordinary deeds of extraordinary characters who, in dealings with gods or other superhuman forces, gave shape to the mortal universe for their descendants. Etymology The English word ''epic'' comes from Latin ''epicus'', which itself comes from the Ancient Greek adjective (''epikos''), from (''epos''), "word, story, poem." In ancient Greek, 'epic' could refer to all poetry in dactylic hexameter (''epea''), which included not only Homer but also the wisdom poetry of Hesiod, the utterances of the Delphic oracle, and the strange theological verses attributed to Orpheus. Later tradition, however, has restricted the term 'epic' to ''heroic epic'', as described in this article. Overview Originating before the invention of writing, primary epics, such as those of Homer, were composed by bards who used complex rhetorical and metrical schemes by which they could memorize the epic as received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infante
''Infante'' (, ; f. ''infanta''), also anglicised as Infant or translated as Prince, is the title and rank given in the Iberian kingdoms of Spain (including the predecessor kingdoms of Aragon, Castile, Navarre, and León) and Portugal to the sons and daughters (''infantas'') of the king, regardless of age, sometimes with the exception of the heir apparent or heir presumptive to the throne who usually bears a unique princely or ducal title.de Badts de Cugnac, Chantal. Coutant de Saisseval, Guy. ''Le Petit Gotha''. Nouvelle Imprimerie Laballery, Paris 2002, p. 303, 364-369, 398, 406, 740-742, 756-758 (French) A woman married to a male ''infante'' was accorded the title of ''infanta'' if the marriage was dynastically approved (e.g., Princess Alicia of Bourbon-Parma), although since 1987 this is no longer automatically the case in Spain (e.g., Princess Anne d'Orléans). Husbands of born ''infantas'' did not obtain the title of ''infante'' through marriage (unlike most hered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobera (sword)
The sword Lobera ( es, la espada lobera, literally: "the wolf-slaying sword") was the symbol of power used by Saint Ferdinand III of Castile, instead of the more traditional rod, and so the king will be depicted with orb and sword in hand. History Lobera was the sword of Saint Ferdinand III, King of Castile from 1217 and King of León from 1230, He finished the work done by his maternal grandfather Alfonso VIII of Castile and consolidated the Reconquista. In 1231, he permanently united Castile and León. He was considered an exemplary knight in his time. Pope Innocent IV named him "invincible champion of Jesus Christ". Etymology Lobera is a Spanish word meaning ''wolf huntress''. Legend Don Juan Manuel, Prince of Villena, grandson of King Ferdinand III, wrote in his ''Libro de los ejemplos del conde Lucanor y de Patronio'' (1337) ("Book of the examples of Count Lucanor and of Patronio"), that Lobera was the sword of Fernán González of Castile (epic hero from the Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fictional Swords
Fiction is any creative work, chiefly any narrative work, portraying individuals, events, or places that are imaginary, or in ways that are imaginary. Fictional portrayals are thus inconsistent with history, fact, or plausibility. In a traditional narrow sense, "fiction" refers to written narratives in prose often referring specifically to novels, novellas, and short stories. More broadly, however, fiction encompasses imaginary narratives expressed in any medium, including not just writings but also live theatrical performances, films, television programs, radio dramas, comics, role-playing games, and video games. Definition Typically, the fictionality of a work is publicly marketed and so the audience expects the work to deviate in some ways from the real world rather than presenting, for instance, only factually accurate portrayals or characters who are actual people. Because fiction is generally understood to not fully adhere to the real world, the themes and contex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval European Swords
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |