|
Codex Azcatitlan
The Codex Azcatitlan is an Aztec codex detailing the history of the Mexica and their migration journey from Aztlán to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. The exact date when the codex was produced is unknown, but scholars speculate it was crafted some time between the mid-16th and 17th centuries. The name of this important Mexica pictorial manuscript was suggested by its first editor, Robert H. Barlow, who erroneously interpreted the anthill on page 2 as the glyph for “Aztlán.” In the Bibliothèque nationale de France, where it is housed, it is known as ''Histoire mexicaine, anuscritMexicain 59–64''. Characteristics The style of the codex combines traditional Mesoamerican artisanry with European Renaissance technique. Mexican historian noted the use of European methods to depict the codex's content such as the use of three-dimensional objects. The master ''tlacuilo'' also uses overlapping images to create depth, as in European art. Figures in the codex also have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axayacatl
Axayacatl (; ; ; meaning "face of water"; –1481) was the sixth of the of Tenochtitlan and Emperor of the Aztec Triple Alliance. Biography Early life and background Axayacatl was a son of the princess Atotoztli II and her cousin, prince Tezozomoc (son of Itzcoatl), Tezozomoc. He was a grandson of the Emperors Moctezuma I and Itzcoatl. He was a descendant of the king Cuauhtototzin. He was a successor of Moctezuma and his brothers were Emperors Tizoc and Ahuitzotl and his sister was the Queen Chalchiuhnenetzin. He was an uncle of the Emperor Cuauhtémoc and father of Emperors Moctezuma II and Cuitláhuac. Rise to power During his youth, his military prowess gained him the favor influential figures such as Nezahualcoyotl (tlatoani), Nezahualcoyotl and Tlacaelel I, and thus, upon the death of Moctezuma I in 1469, he was chosen to ascend to the throne, much to the displeasure of his two older brothers, Tizoc and Ahuitzotl. It is also important that the Aztec calendar stone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuauhtémoc
Cuauhtémoc (, ), also known as Cuauhtemotzín, Guatimozín, or Guatémoc, was the Aztec ruler ('' tlatoani'') of Tenochtitlan from 1520 to 1521, and the last Aztec Emperor. The name Cuauhtemōc means "one who has descended like an eagle", and is commonly rendered in English as "Descending Eagle", as in the moment when an eagle folds its wings and plummets down to strike its prey; the name thus implies aggressiveness and determination. Cuauhtémoc took power in 1520 as successor of Cuitláhuac and was a cousin of the late emperor Moctezuma II. His young wife, who was later known as Isabel Moctezuma, was one of Moctezuma's daughters. He ascended to the throne when he was around 25 years old, while Tenochtitlan was being besieged by the Spanish and devastated by an epidemic of smallpox brought to the Americas by Spanish conquerors. After the killings in the Great Temple, there were probably few Aztec captains available to take the position. Early life Cuauhtemoc's date of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
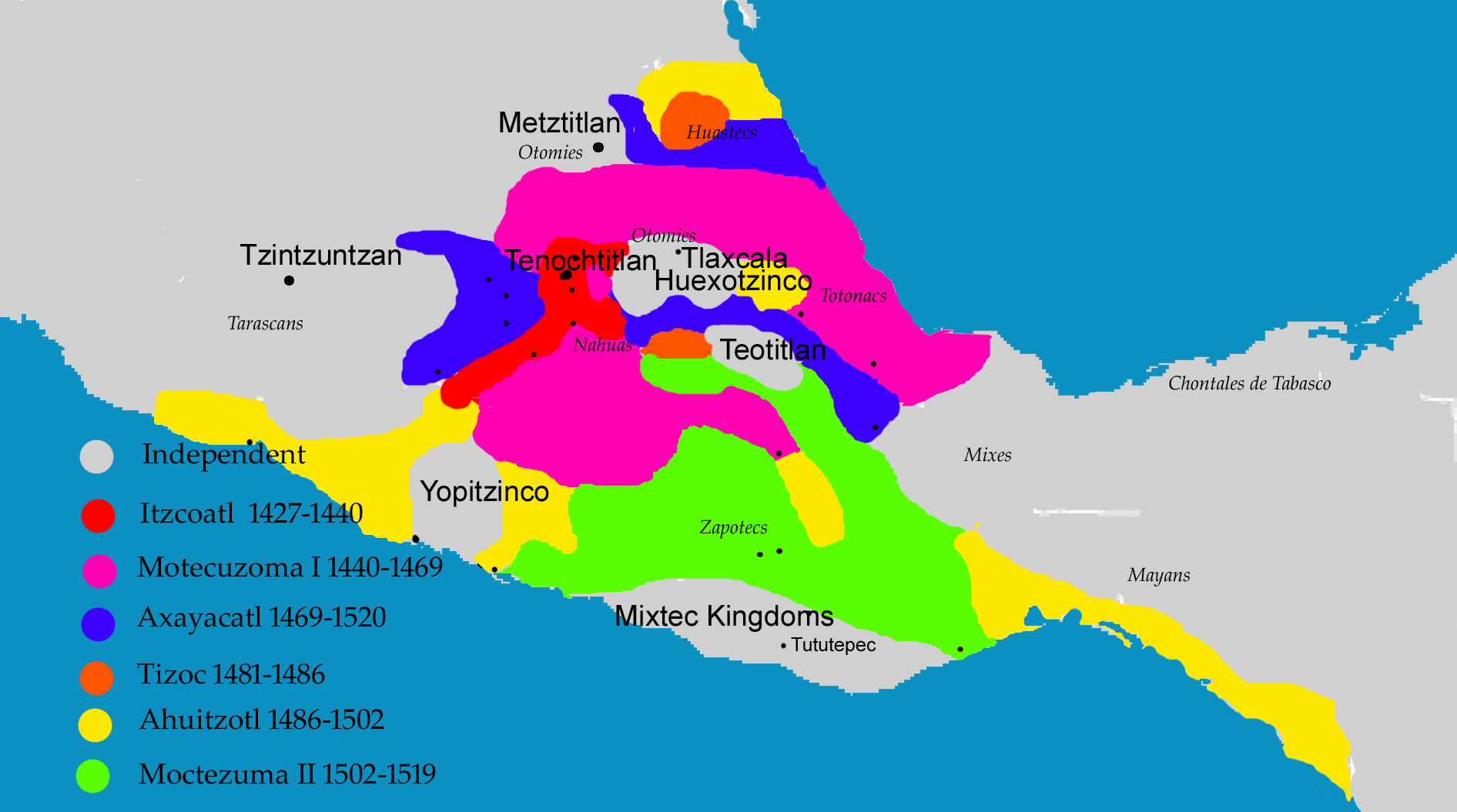
Aztecs
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states ('' altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, the capital city of the Mexica or Tenochca, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821). The definitions of Azt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staff Of Office
A staff of office is a staff, the carrying of which often denotes an official's position, a social rank or a degree of social prestige. Apart from the #Eccleasiastical use, ecclesiastical and #Ceremonial, ceremonial usages mentioned below, there are less formal usages. A gold- or silver-topped Walking stick, cane can express social standing (or dandyism). Teachers or prefects in schools traditionally carried less elaborate canes which marked their right (and potential threat) to administer canings, and military officers carry a residual threat of physical punishment in their swagger sticks. Orchestral Conducting, conductors have in their Baton (conducting), batons symbols of authority as well as tools of their trade. Ecclesiastical use Churchwardens (and sometimes sidesman, sidesmen) traditionally carry staves or wands on special occasions as an emblem of their office. In the Eastern Orthodox Church and some of the Oriental Orthodox Churches an ecclesiastical walking stick is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locative Case
In grammar, the locative case ( ; abbreviated ) is a grammatical case which indicates a location. In languages using it, the locative case may perform a function which in English would be expressed with such prepositions as "in", "on", "at", and "by". The locative case belongs to the general local cases, together with the lative and ablative case. The locative case exists in many language groups. Indo-European languages The Proto-Indo-European language had a locative case expressing "place where", an adverbial function. The endings are reconstructed as follows: In most later Indo-European languages, the locative case merged into other cases (often genitive or dative) in form and/or function, but some daughter languages retained it as a distinct case. It is found in: * modern Balto-Slavic languages, except Bulgarian and Macedonian, although it is mostly used with prepositions in the other Slavic languages * some classical Indo-European languages, particularly Sanskrit and O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boturini Codex
Codex Boturini, also known as the ''Tira de la Peregrinación de los Mexica'' (Tale of the Mexica Migration), is an Aztec codex, which depicts the migration of the Aztecs, Azteca, later Mexica, people from Aztlán. Its date of manufacture is unknown, but likely to have occurred before or just after the Conquest of the Aztec Empire (1519–1521). At least two other Aztec codices have been influenced by the content and style of the Boturini Codex. This Codex has become an insignia of Mexica history and pilgrimage and is carved into a stone wall at the entrance of the National Museum of Anthropology (Mexico), National Museum of Anthropology and History in Mexico City.Leibsohn, D. (2001). "Boturini, Codex". In David Carrasco, Davíd Carrasco (ed). The Oxford Encyclopedia of Mesoamerican CulturesVol 1''. : Oxford University Press. The codex is currently located in the National Museum of Anthropology (Mexico), National Museum of Anthropology in Mexico City. Name This codex is referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Writing
The Aztec or Nahuatl script is a pre-Columbian writing system that combines ideographic writing with Nahuatl specific phonetic logograms and syllabic signs which was used in central Mexico by the Nahua people in the Epiclassic and Post-classic periods. It was originally thought that its use was reserved for elites; however, the topographical codices and early colonial catechisms, recently deciphered, were used by ''tlacuilos'' (scribes), ''macehuallis'' (peasants), and '' pochtecas'' (merchants). Origin The Aztec writing system derives from writing systems used in Central Mexico, such as Zapotec script. Mixtec writing is also thought to descend from Zapotec. The first Oaxacan inscriptions are thought to encode Zapotec, partially because of numerical suffixes characteristic of the Zapotec languages. Structure and use Aztec was pictographic and ideographic proto-writing, augmented by phonetic rebuses. It also contained syllabic signs and logograms. There was no alphabet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller populations Nahuatl language in the United States, in the United States. Nahuatl has been spoken in central Mexico since at least the seventh century CE. It was the language of the Mexica, who dominated what is now central Mexico during the Late Postclassic period of Mesoamerican chronology, Mesoamerican history. During the centuries preceding the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, the Aztecs had expanded to incorporate a large part of central Mexico. Their influence caused the variety of Nahuatl spoken by the residents of Tenochtitlan to become a prestige language in Mesoamerica. Following the Spanish conquest, Spanish colonists and missionaries introduced the Latin script, and Nahuatl became a literary language. Many chronicles, gram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlatoani
''Tlahtoāni'' ( , "ruler, sovereign"; plural ' ) is a historical title used by the dynastic rulers of (singular ''āltepētl'', often translated into English as "city-state"), autonomous political entities formed by many pre-Columbian Nahuatl-speaking peoples in the Valley of Mexico during the Postclassic Period. The title of ' (, "great ruler, emperor") was used by the rulers of the Aztec Empire, an alliance between the ''āltepēmeh'' of Tenochtitlan, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan. Each ''āltepētl'' had its own ''tlahtoāni'' who would concurrently function as its ruler, high priest and commander-in-chief. The ''tlahtoāni'' wielded ultimate authority over all land within the ''āltepētl'', overseeing tribute collection, market activities, temple affairs, and the resolution of judicial disputes. Typically a dynastic ruler hailing from the royal lineage, the ''tlahtoāni'' served for life. However, in certain instances, a council of nobles, elders, and priests could elect a ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire, also known as the Triple Alliance (, Help:IPA/Nahuatl, [ˈjéːʃkaːn̥ t͡ɬaʔtoːˈlóːjaːn̥]) or the Tenochca Empire, was an alliance of three Nahuas, Nahua altepetl, city-states: , , and . These three city-states ruled that area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until the combined forces of the Spanish and their native allies who ruled under Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, defeated them in 1521. Its people and civil society are historiographically referred to as the ''Aztecs'' or the ''Culhua-Mexica''. The alliance was formed from the victorious factions of a civil war fought between the city of and its former tributary provinces. Despite the initial conception of the empire as an alliance of three self-governed city-states, the capital became dominant militarily. By the time the Spanish arrived in 1519, the lands of the alliance were effectively ruled from , while other partners of the alliance had taken subsidiary roles. The al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |