|
Clip (firearms)
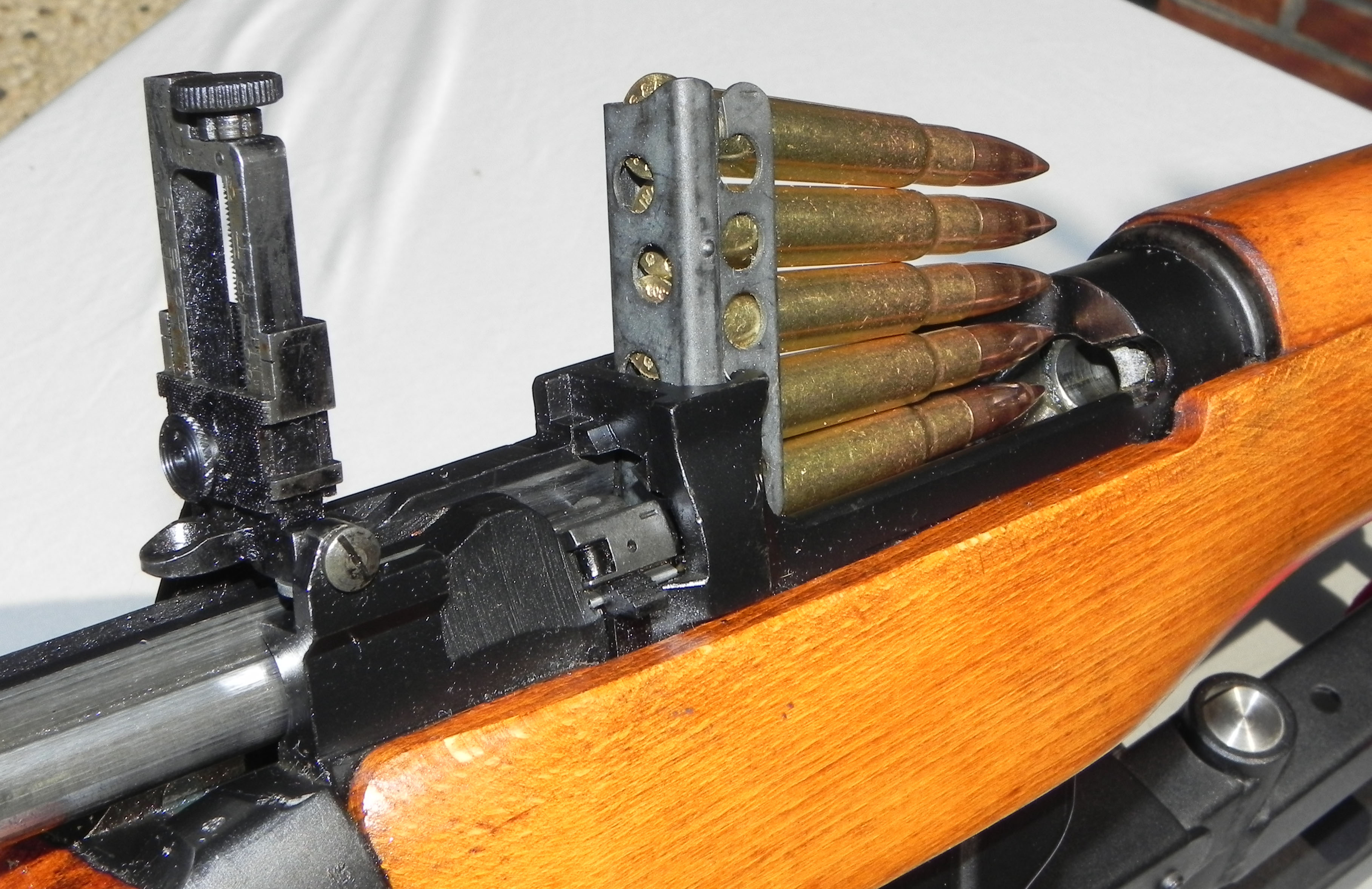
A clip is a device that is used to store multiple rounds of ammunition together as a unit for insertion into the Magazine (firearms), magazine or Cylinder (firearms), cylinder of a firearm. This speeds up the process by loading the firearm with multiple rounds simultaneously, rather than individually, as with loose rounds of ammunition. There are several types, most made of inexpensive Stamped metal, stamped sheet metal, generally they are intended to be disposable, but they are more often retained and reused. Types Stripper A stripper clip (American English) or charger clip (Commonwealth English) is a speedloader that holds several pistol or rifle cartridges as a unit for easier loading into a firearm's internal box magazine. After the bolt is opened and the stripper clip is placed in position (generally in a slot on the receiver or bolt), the cartridges are pressed down, removing or "stripping" them off the clip and into the magazine. The clip is then either removed and tos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clip M1-SKS
Clip or CLIP may refer to: Fasteners * Ammunition clip, a device for storing multiple rounds together as a unit before inserting into a magazine or cylinder * Binder clip, a device for holding thicker materials (such as large volumes of paper) together ** Bulldog clip, a common binder clip * Bread clip, a device for closing bags * Carabiner, Climbing clip, a device used to quickly and reversibly connect elements of climbing equipment * Circlip, a semi-flexible metal ring fastener for holding a pin in place * Crocodile clip, or alligator clip, a temporary electrical connector * Hair clip, a device for holding hair together or attaching materials such as caps to the hair * Money clip, a device for storing cash and credit cards in a very compact fashion * Paper clip, a device for holding several sheets of paper together * Rail fastening system#Clips, Rail clip, a rail fastener * Roach clip, a holder for smoking a cannabis cigarette Arts and entertainment * Clip art, pre-made images ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T48 Rifle
The T48 (marked as "Rifle, Caliber .30, T48") was a battle rifle tested by the U.S. military in the mid 1950s during trials to find a replacement for the M1 Garand. It was a license-produced copy of the Belgian FN FAL rifle. The rifle did not enter service, as the U.S. military decided to adopt the M14 rifle instead. Origin In the wake of World War II, the NATO "Rifle Steering Committee" was formed to encourage the adoption of a standardized NATO rifle. The Committee and the US interest in the FAL proved to be a turning point in the direction of the FAL's development. The U.S. and NATO interest in small arms standardization was the primary reason why the FAL was redesigned to use the newly developed 7.62×51mm NATO cartridge, instead of the intermediate cartridge designs originally tested by FN. Two political factors are worth noting: the U.S. Government tacitly indicated to NATO, and specifically to the United Kingdom, that if the FAL were redesigned for the new American 7.62×5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusil Automatique Modèle 1917
The ''Fusil Automatique Modèle 1917'' ("Model 1917 Automatic Rifle"), also called the RSC M1917, was a gas-operated, semi-automatic rifle placed into service by the French Army during the latter part of World War I in May 1916. It was chambered in 8mm Lebel, the rimmed cartridge used in other French Army infantry weapons of the time. In total, the French national armories, primarily ''Manufacture d'armes de Saint-Étienne'' (MAS) and '' Manufacture Nationale d'Armes de Tulle'' (MAT), manufactured 86,000 RSC M1917 rifles until production ended in late November 1918. However, very few examples have survived in fully functional, semi-automatic condition and those have become highly sought-after collectibles. Development The adoption of the Modèle 1917 can be traced to early attempts by the French Army to replace its Lebel rifles with a more advanced semi-automatic design in the years before the outbreak of the First World War. In 1913, a semi-automatic rifle was selected to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berthier Carbine
The Berthier rifles and carbines were a family of bolt-action small arms in 8mm Lebel, used in the French Army, and French Colonial Forces, from the 1890s to the beginning of World War II (1940). After the introduction of the Lebel rifle in 1886, the French Army wanted a repeating carbine using the same ammunition as the Lebel to replace their single shot carbine based on the Gras rifle. At the time, many armies based their carbines on their standard rifle model, however the Lebel rifle's tube magazine made it difficult to follow this approach. The Modele 1890 Berthier Cavalry Carbine addressed this issue by combining a modified Lebel action with an en-bloc clip magazine. With its successful cavalry introduction, the Berthier would go on to be produced in many different carbine and full-length rifle versions. History and usage The Berthier was originally introduced as a partial replacement for the French 1886 Lebel rifle. The Lebel, a revolutionary concept at the time of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mondragón Rifle
The Mondragón rifle refers to one of two rifle designs developed by Mexican artillery officer General Manuel Mondragón. These designs include the straight-pull bolt-action M1893 and M1894 rifles, and Mexico's first self-loading rifle, the M1908 - the first of the designs to see combat use. Straight-pull bolt-action rifles Mondragón began working on his initial rifle design in 1891. During his stay in Belgium, he filed a patent application for which he had received a grant on March 23, 1892 (No. 98,947). Mondragón was granted a further Patent on April 20, 1892 from the French Patent Office (No. 221,035). He also filed for a Patent for his design with the United States Patent Office on February 8, 1893, which was granted on March 24, 1896 (No. 557,079). The rifle, referred to as model M1893, was of a straight-pull, bolt-action design, chambered in the 6.5×48mm cartridge (also developed by Mondragón) or the 5.2x68mm cartridge (developed by Colonel Rubin), with a fixed magazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stripper Clip
A stripper clip (also known as a charger or charger clip, especially in Commonwealth English military vocabulary) is a speedloader that holds several cartridges (usually between 5 and 10) together in a single unit for easier and faster loading of a firearm magazine. Stripper clips were originally employed in infantry bolt-action rifles, such as the Russian Mosin–Nagant, the British Lee–Enfield, and the German Mauser Model 1889, Gewehr 98, and its variant the Karabiner 98k, the related American M1903 Springfield and M1917 Enfield, Swiss K31, and many others. Stripper clips were also employed in newer, semi-automatic rifles with internal box magazines, such as the Soviet SKS and the Egyptian Hakim Rifle. Semi and full automatic firearms using both stripper feed inserts and detatchable box magazines are the Canadian (FNC1A1) version of the L1A1 self-loading rifle, the US OA-96 carbine and T48 rifles and the Chinese Type 63 and Type 81 assault rifles. Current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gewehr 1888
The Gewehr 88 (commonly called the Model 1888 commission rifle) was a late 19th-century German bolt-action rifle, adopted in 1888. The invention of smokeless powder in the late 19th century immediately rendered all of the large-bore black powder rifles then in use obsolete. To keep pace with the French (who had adopted smokeless powder "small bore" ammunition for their Lebel Model 1886 rifle) the Germans adopted the Gewehr 88 using its own new Patrone 88 cartridge, which was also designed by the German Rifle Commission.8×57mm IS cartridge portrait – Totgesagte leben länger, Wild und Hund 11/2006 The rifle was one of many weapons in the |
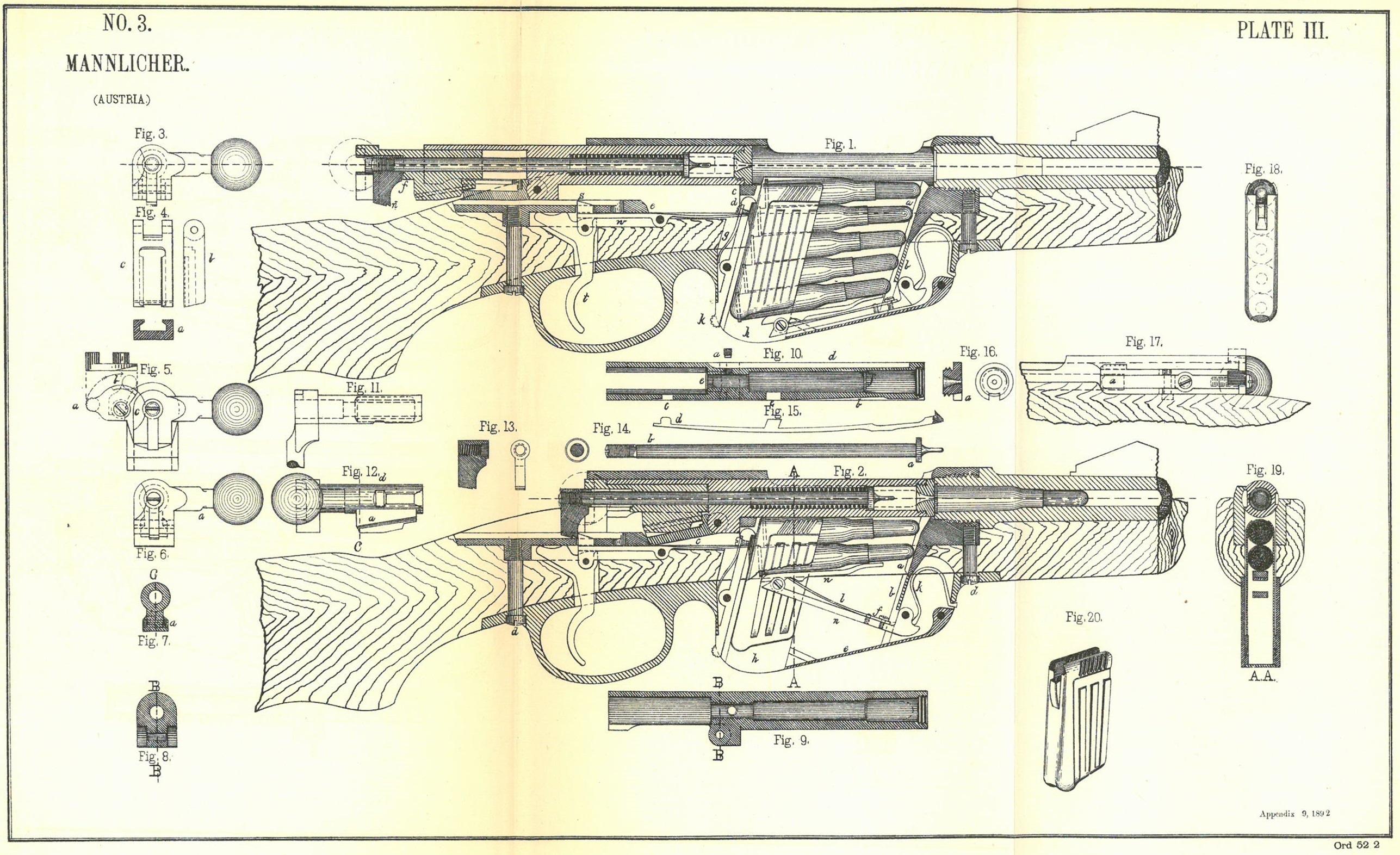
Mannlicher M1888
Within military :8 mm firearms, 8 mm firearms, the Repeating Rifle Mannlicher 1888, better known as the Mannlicher M1888, was a bolt-action rifle used by several armies from 1888 to 1945. Derived from the Mannlicher M1885, M1885 and later Mannlicher M1886, M1886 models, it was Ferdinand Mannlicher's third rifle that utilized the "en bloc clip". It was succeeded by the Mannlicher M1895 as the standard service rifle of the Austro-Hungarian Army. The M95 uses a more secure rotating-bolt, in contrast to the M88's wedge-lock bolt. History The M1888 was a direct and immediate descendant of the Mannlicher M1886, M1886 Austrian Mannlicher. This rifle too was a straight-pull, bolt-action, box magazine repeater. As early as the beginning of production of the M1886 the need and desirability for a small-bore rifle was evident. This rifle is virtually identical to its predecessor but for chambering a newly designed 8 mm cartridge, loaded originally with black powder and denominated 8� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannlicher M1886
The Repeating Rifle Model 1886, commonly known as Mannlicher Model 1886, was a late 19th-century Austrian straight-pull bolt-action rifle, adopted in 1886. It used a wedge-lock straight pull action bolt. It was the first straight-pull bolt-action service rifle of any nation. History The M1886 itself was an improvement of the Mannlicher M1885 trials rifle (patented in the UK in May 1885) that was a prototype meant to replace the by then obsolete M1867 Werndl-Holub drum-breech single-shot rifle. It was the first of the Austro-Hungarian service rifles to introduce the feature of the clip dropping out of the bottom of the magazine when the last round is chambered. Conversions Between 1888 and 1892, 95% of the M1886 rifles were converted (rebarreled) to 8×52mmR Mannlicher under the designation ''M1886-88''. Rifles in original (11 mm) caliber with Austrian acceptance marks are a rare find. Service history The rifle was quickly made obsolete by the introduction of the Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Mannlicher
Ferdinand Ritter von Mannlicher (January 30, 1848 – January 20, 1904) was an Austrian engineer and small arms designer. Along with James Paris Lee, Mannlicher was particularly noted for inventing the en-bloc clip charger-loading box magazine system. Later, while making improvements to other inventors' prototype designs for rotary-feed magazines, Mannlicher, together with his protégé Otto Schönauer, patented a perfected rotary magazine design, the Mannlicher–Schönauer rifle, which was a commercial and military success. Life A scion of a long-established bourgeois family originating from Most () in Bohemia, Mannlicher was born in the German city of Mainz, where his father served as an Austrian '' k.k.'' official in the Austrian garrison at the Confederation Fortress. He returned to the Josefstadt district of Vienna with his parents in 1857, and after receiving his ''Matura'' high-school exam attended the Vienna University of Technology. He started his professional c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifle
A rifle is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting and higher stopping power, with a gun barrel, barrel that has a helical or spiralling pattern of grooves (rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with both hands and braced firmly against the shooter's shoulder via a buttstock for stability during shooting. Rifles are used in warfare, law enforcement, hunting and shooting sports, target shooting sports. The invention of rifling separated such firearms from the earlier smoothbore weapons (e.g., arquebuses, muskets, and other long guns), greatly elevating their accuracy and general effectiveness. The raised areas of a barrel's rifling are called ''lands''; they make contact with and exert torque on the projectile as it moves down the bore, imparting a spin. When the projectile leaves the barrel, this spin persists and lends gyroscopic stability to the projectile due to conservatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |