|
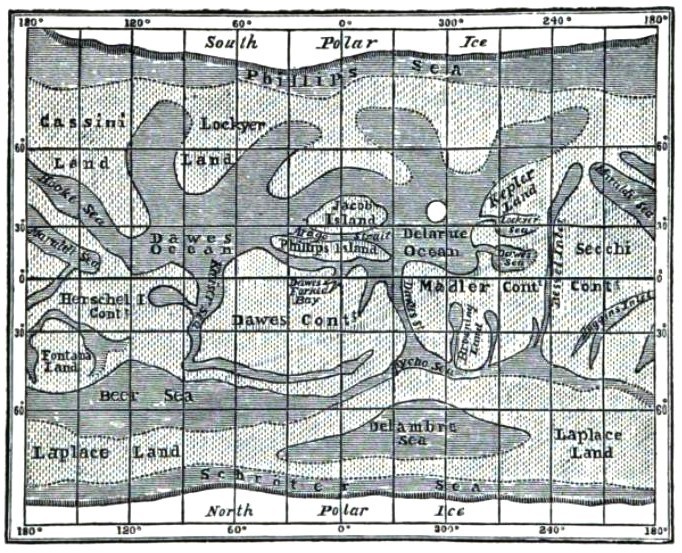
Classical Albedo Features On Mars
The classical albedo features of Mars are the light and dark features that can be seen on the planet Mars through an Earth-based telescope. Before the age of space probes, several astronomers created maps of Mars on which they gave names to the features they could see. The most popular system of nomenclature was devised by Giovanni Schiaparelli, who used names from classical antiquity. Today, the improved understanding of Mars enabled by space probes has rendered many of the classical names obsolete for the purposes of cartography; however, some of the old names are still used to describe geographical features on the planet. History Observing albedo features Early telescopic astronomers, observing Mars from a great distance through primitive instruments (though they were advanced for their day), were limited to studying albedo contrasts on the surface of the planet. These lighter and darker patches rarely correspond to topographic features and in many cases obscure them. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo Feature
In planetary geology, an albedo feature is a large area on the surface of a planet (or other Solar System body) which shows a contrast in brightness or darkness (albedo) with adjacent areas. Historically, albedo features were the first (and usually only) features to be seen and named on Mars and Mercury. Early classical maps (such as those of Schiaparelli and Antoniadi) showed only albedo features, and it was not until the arrival of space probes that other surface features such as craters could be seen. On bodies other than Mars and Mercury, an albedo feature is sometimes called a regio. On bodies with a very thick atmosphere like Venus or Titan, permanent albedo features cannot be seen using ordinary optical telescopes because the surface is not visible, and only clouds and other transient atmospheric phenomena are seen. The ''Cassini–Huygens'' probe observed multiple albedo features on Titan after its arrival in Saturn's orbit in 2004. The first albedo feature ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathaniel Everett Green
Nathaniel Everett Green FRAS (21 August 1823 – 10 November 1899) was an English painter, art teacher and astronomer. He professionally painted landscapes and portraits, and also gained fame with his drawings of planets. Born in Bristol, the son of Benjamin Holder Green (1793–1865), then a haberdasher, and Elizabeth ‘Betsey’ née Everett (1795–1837); his interest in astronomy dated from 1859 when he built a telescope for himself. He produced "soft-pencil" drawings of Mars in 1877, which were widely known. Shortly after drawing them, he was the first to suggest that canals on Mars were an optical illusion. In 1880 he was called to Balmoral and taught art to some members of the royal family, including Queen Victoria. He was founding member of the British Astronomical Association The British Astronomical Association (BAA) was formed in 1890 as a national body to support the UK's amateur astronomers. Throughout its history, the BAA has encouraged observers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abalos Mensa
Abalos Mensa is a wedge-shaped mound, or mensa and one of the named features in the vicinity of Planum Boreum, the Martian North pole. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars. Its name was officially approved by IAU in 2006. It extends from latitude 80.21°N to 82.4°N and from longitude 279.34°E to 290.52°E (69.48°W – 80.66°W). Its centre is located at latitude 81.17°N, longitude 284.4°E (75.6°W), and has a diameter of 129.18 km. Abalos Mensa is a convex formation of approximately 180 kilometer span, with a top-view shaped like a wedge, and lies immediately to the south of the Rupes Tenuis scarp, approximately at 285ºE. In the neighbourhood of Abalos Mensa is the beginning of the dune field of Abalos Undae which continues in a southwestward direction after it emerges from the western end of a narrow channel separating Rupes Tenuis from Abalos Mensa. Crotone crater, located at 82.2ºN, 290.0ºE with a 6.4 km diameter, is situated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abalos Colles
Abalos Colles (Latin for "Abalos Hills") is a Stratum, stratified fragment of the Rupes Tenuis basal unit of Planum Boreum, located south of the Rupes Tenuis scarp and west of the Escorial crater. It contains 16 mounds. Abalos Colles is one of the named features in the vicinity of Planum Boreum, the Mars, Martian North pole. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars located at latitude 72°N, longitude 70°W. Its name was officially approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2003. It extends from latitude 74.81°N to 78.78°N and from longitude 284.54°E to 293.39°E (66.61°W – 75.46°W). Its centre is located at latitude 71.65°N, longitude 76.83°W, and has a diameter of 235.83 km. The Abalos Colles mounds are of irregular, angular, or conical form. The tops of the conical forms can feature craters, and can also be flat. Their height varies between less than a hundred to less than 700 metres, with top diameters in the range of 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPA For English
English language, English phonology is the system of speech sounds used in spoken English. Like many other languages, English has wide variation in pronunciation, both History of the English language, historically and from List of dialects of the English language, dialect to dialect. In general, however, the regional dialects of English share a largely similar (but not identical) phonological system. Among other things, most dialects have vowel reduction in unstressed syllables and a complex set of phonological features that distinguish fortis and lenis consonants (stop consonant, stops, affricates, and fricatives). Phonological analysis of English often concentrates on prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige or standard language, standard accents, such as Received Pronunciation for England, General American for the United States, and Australian English, General Australian for Australia. Nevertheless, many other dialects of English are spoken, which have developed differently from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martian Canals
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, it was erroneously believed that there were "canals" on the planet Mars. These were a network of long straight lines in the equatorial regions from 60° north to 60° south latitude on Mars, observed by astronomers using early telescopes without photography. They were first described by the Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli during the opposition of 1877, and attested to by later observers. Schiaparelli called these ''canali'' (" channels"), which was mis-translated into English as "canals". The Irish astronomer Charles E. Burton made some of the earliest drawings of straight-line features on Mars, although his drawings did not match Schiaparelli's. Around the turn of the century there was even speculation that they were engineering works, irrigation canals constructed by a civilization of intelligent aliens indigenous to Mars. By the early 20th century, improved astronomical observations revealed that, with the possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schiaparelli Versus Mars
Schiaparelli may refer to: * Schiaparelli (surname), an Italian surname * Maison Schiaparelli, an Italian fashion house * Schiaparelli (lunar crater) * Schiaparelli (Martian crater) Schiaparelli ( , , ) is an impact crater on Mars, located near the planet's equator at latitude 3° south and longitude 344° in the Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle. It measures approximately 459 kilometers (285-miles) in diameter and was named after ... * ''Schiaparelli'' EDM, a Mars lander See also * Alejandro Schiapparelli (born 1980), Argentine footballer {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Albedo Features NASA 1970
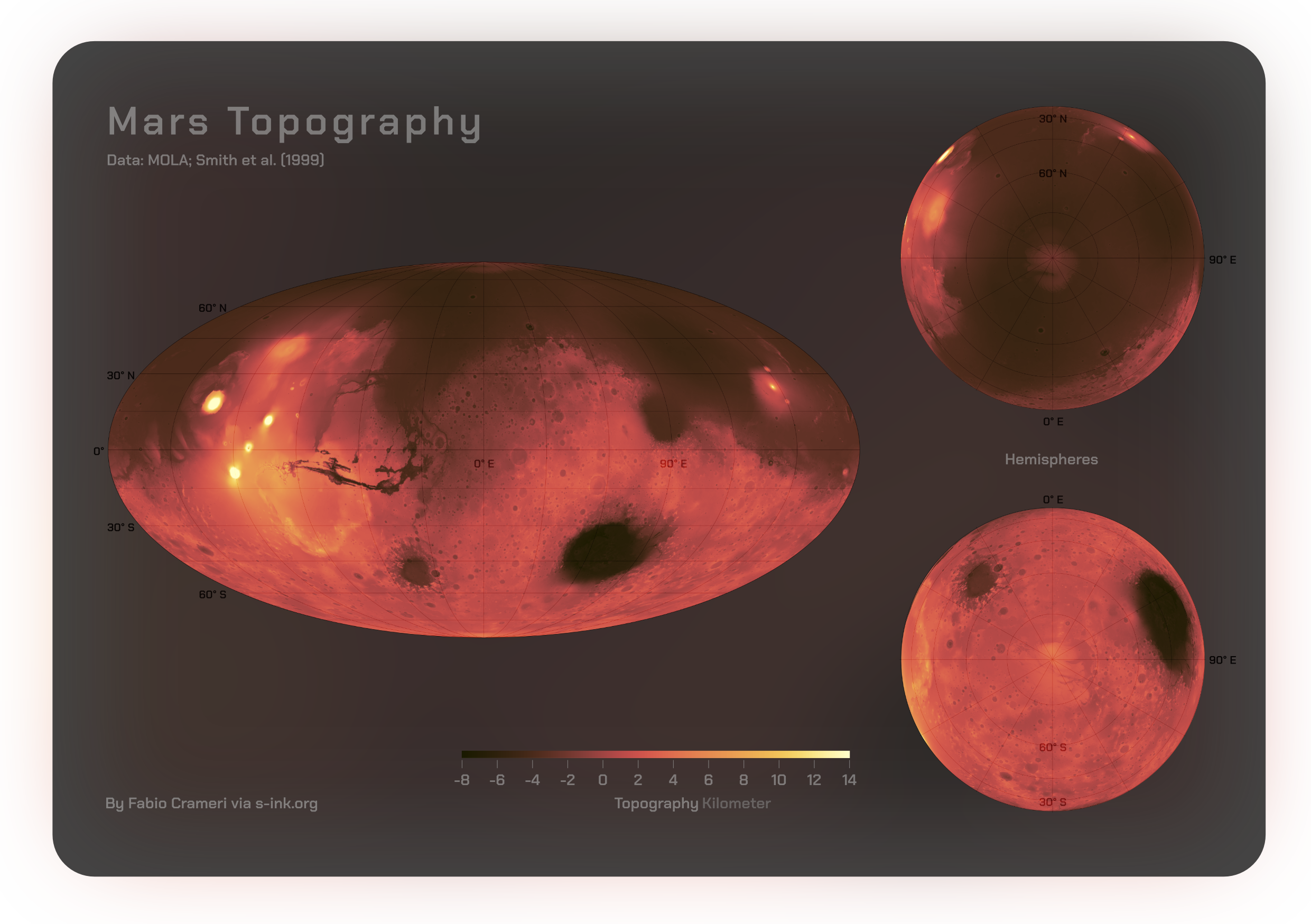
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Géolocalisation
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south divid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascraeus Mons
Ascraeus Mons is a large shield volcano located in the Tharsis region of the planet Mars. It is the northernmost and tallest of three shield volcanoes collectively known as the Tharsis Montes. Discovery The volcano's location corresponds to the classical albedo feature Ascraeus Lacus. Ascraeus Mons was discovered by the Mariner 9 spacecraft in 1971. The volcano was originally called North Spot because it was the northernmost of only four spots visible on the surface due to a global dust storm that was then enshrouding the planet. As the dust cleared, the spots were revealed to be extremely tall volcanoes whose summits had projected above the dust-laden, lower atmosphere. Name Ascraeus Lacus had been named after Ascra, the rustic birthplace of Hesiod; in Greek, the word "ascraeus" is a poetic metonym for "rural." The volcano's name officially became Ascraeus Mons in 1973. General description The volcano is located in the southeast-central portion of the Tharsis quadrangle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percival Lowell
Percival Lowell (; March 13, 1855 – November 12, 1916) was an American businessman, author, mathematician, and astronomer who fueled speculation that there were canals on Mars, and furthered theories of a ninth planet within the Solar System. He founded the Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona, and formed the beginning of the effort that led to the discovery of Pluto 14 years after his death. Life and career Early life and work Percival Lowell was born on March 13, 1855, in Boston, Massachusetts, the first son of Augustus Lowell and Katherine Bigelow Lowell. A member of the Brahmin Lowell family, his siblings included the poet Amy Lowell, the educator and legal scholar Abbott Lawrence Lowell, and Elizabeth Lowell Putnam, an early activist for prenatal care. They were the great-grandchildren of John Lowell and, on their mother's side, the grandchildren of Abbott Lawrence. Percival graduated from the Noble and Greenough School in 1872 and Harvard College in 1876 w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audouin Dollfus
Audouin Charles Dollfus (12 November 1924 – 1 October 2010) was a French astronomer and aeronaut, specialist in studies of the Solar System and discoverer of Janus, a moon of Saturn. Life and career Dollfus was born in Paris to aeronaut Charles Dollfus. Dollfus studied at the University of Paris, obtaining a doctorate in physical sciences in 1955. Beginning in 1946, Dollfus worked as an astronomer at the Meudon Observatory, following his advisor and mentor Bernard Lyot. In particular, he directed the Laboratory of Solar System Physics there. Until his death, he was an honorary astronomer at the Paris Observatory. Most of his work was carried out based on observations from the Pic du Midi Observatory, and his preferred research method is the use of polarized light as a diagnostic of the properties of Solar System objects. Through patient and persistent research and the development of new observational techniques, he was able to obtain many remarkable results. Dollfus published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |