|
Citroën DS
The Citroën DS () is a Front-mid-engine, front-wheel-drive layout, front mid-engined, front-wheel drive executive car manufactured and marketed by Citroën from 1955 to 1975, in fastback/sedan, wagon/estate, and convertible body configurations, across three series of one generation. Marketed with a less expensive variant, the Citroën ID, the DS was known for its aerodynamic, futuristic body design; unorthodox, quirky, and innovative technology, and set new standards in ride quality, car handling, handling, and braking, thanks to both being the first mass production car equipped with hydropneumatic suspension, as well as disc brakes. The 1967 series 3 also introduced ''directional headlights'' to a mass-produced car.After this feature was first introduced on the 1948 Tucker 'Torpedo', of which 50 were built. Italian sculptor and industrial designer Flaminio Bertoni and the French aeronautical engineer André Lefèbvre styled and engineered the car, and Paul Magès developed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citroën
Citroën ()The double-dot diacritic over the 'e' is a diaeresis () indicating the two vowels are sounded separately, and not as a diphthong. is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded on 4 June 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën has been owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired 89.95% share in 1976. Citroën's head office is located in the Stellantis Poissy Plant in Saint-Ouen-sur-Seine since 2021 (previously in Rueil-Malmaison) and its offices studies and research in Vélizy-Villacoublay, Poissy (CEMR), Carrières-sous-Poissy and Sochaux-Montbéliard. In 1934, the firm established its reputation for innovative technology with the Citroën Traction Avant, Traction Avant. This was the world's first car to be mass-produced with front-wheel drive and four-wheel independent suspension, as well as unibody construction, omitting a separate chassis, and instead using the body of the car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front Mid-engine, Front-wheel-drive Layout
In automotive design, a front-mid-engine, front-wheel-drive layout (also called more simply "mid-engine, front-wheel-drive layout", and abbreviated MF or FMF) is one in which the front road wheels are driven by an internal-combustion engine placed just behind them, in front of the passenger compartment. In contrast to the front-engine, front-wheel-drive layout (FF), the center of mass of the engine is behind the front axle. This layout is typically chosen for its better weight distribution (the heaviest component is near the center of the car, lowering its moment of inertia). Many early successful (and mostly French) mass-produced front-wheel drive cars used the MF layout, until the 1959 BMC (Austin / Morris) Mini demonstrated the layout and passenger car packaging benefits of mounting the engine transversely in front of the front axle. At first – when well executed – the packaging, space utilization and user experience of MF layout, even in a subcompact or supermini, like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
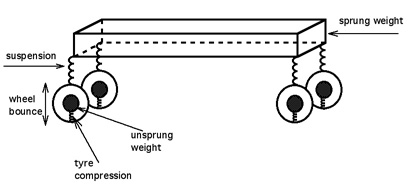
Self-levelling Suspension
Self-levelling refers to an automobile suspension system that maintains a constant ride height of the vehicle above the road, regardless of load. Purpose Many vehicle systems on a conventional vehicle are negatively affected by the change in attitude coming from changes in load - specifically a heavy load in the rear seat or luggage compartment. This change in attitude affects aerodynamic properties, headlight aim, braking, bumpers, shock absorption from the suspension and the vehicle's performance in a collision. Most of the braking power is on the front wheels of a vehicle, which means you will have more effective braking when more weight is over the front wheels. When the rear end has a heavy load, the braking is not as effective. The weight is concentrated on the rear end of the vehicle, and the rear brakes need to do all of the work. When braking quickly in this situation, the front brakes will be easier to lock up because of the lack of weight transfer to the front of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Magès
Paul Ernest Mary Magès (1908–1999) is known for his invention of the first self-leveling automobile suspension, known as hydro-pneumatic suspension. This system replaced conventional steel springs with an adaptive system of hydraulic struts, resulting in a motoring experience that felt like no other automobile of the era. This suspension achieved its initial design brief: fast travel on poor road surfaces. This advantage is still noted today, especially in applications where ride quality is important, like ambulance design. His formal schooling was modest. He earned his National diploma (''Brevet d'Etudes du Premier Cycle''), a preparatory course for the Académie des Arts et Métiers in Marseille. At age 17, he sent his résumé to Citroën, one of the major automobile manufacturers in France, where he was hired to maintain equipment. In 1936 he became a technical draftsman, and in January 1942, CEO Pierre-Jules Boulanger assigned him to the development department to solve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Lefèbvre
André Lefèbvre (19 August 1894 – 4 May 1964) was a French automobile engineer. André René Lefèbvre was born in Louvres, France (North of Paris, Val d'Oise). He began his career as an aviation engineer working for Voisin, then later for Renault and Citroën. He was also a racing driver and racing car designer. After studying at Supaéro, he began to work for Gabriel Voisin in March 1916. Voisin placed Lefebvre in charge of his Laboratoire where he worked, until the end of World War I, on aviation projects and then automobiles. He is particularly noted for creating the Voisin C6 Laboratoire, which was a racing car prepared for the 1923 French Grand Prix. When Voisin ran into business problems in 1931, Lefèbvre was recommended to Louis Renault. Renault was persuaded to recruit Lefèbvre by François Lehideux, himself a senior executive within the company (who was also married to the daughter of Renault's brother). Lefèbvre remained with Renault only until 1933, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disc Brakes
Disc or disk may refer to: * Disk (mathematics), a two dimensional shape, the interior of a circle * Disk storage * Optical disc * Floppy disk Music * Disc (band), an American experimental music band * ''Disk'' (album), a 1995 EP by Moby Other uses * Disc harrow, a farm implement * Discus throw or disc throw, a track and field event involving a heavy disc * Intervertebral disc, a cartilage between vertebrae * Disk (functional analysis), a subset of a vector space * ''Disc'' (magazine), a British music magazine * Disk, a part of a flower * Disc number, numbers assigned to Inuit by the Government of Canada * Galactic disc, a disc-shaped group of stars Abbreviations * Death-inducing signaling complex * DISC assessment, a group of psychometric tests * Defence Intelligence and Security Centre or Joint Intelligence Training Group, the headquarters of the Defence College of Intelligence and the British Army Intelligence Corps * Delaware Independent School Conference, a high-schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydropneumatic Suspension
Hydropneumatic suspension is a type of motor vehicle suspension system, invented by Paul Magès, produced by Citroën, and fitted to Citroën cars, as well as being used under licence by other car manufacturers. Similar systems are also widely used on modern tanks and other large military vehicles. The suspension was referred to as ' in early literature, pointing to oil and air as its main components. The purpose of this system is to provide a sensitive, dynamic and high-capacity suspension that offers superior ride quality on a variety of surfaces. A hydropneumatic system combines the advantages of hydraulic systems and pneumatic systems so that gas absorbs excessive force and liquid in hydraulics directly transfers force. The suspension system usually features both self-leveling and driver-variable ride height, to provide extra clearance in rough terrain. This type of suspension for automobiles was inspired by the pneumatic suspension used for aircraft landing gear, which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Production
Mass production, also known as mass production, series production, series manufacture, or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and batch production, it is one of the three main production methods. The term ''mass production'' was popularized by a 1926 article in the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' supplement that was written based on correspondence with Ford Motor Company. ''The New York Times'' used the term in the title of an article that appeared before the publication of the ''Britannica'' article. The idea of mass production is applied to many kinds of products: from fluids and particulates handled in bulk (food, fuel, chemicals and mined minerals), to clothing, textiles, parts and assemblies of parts ( household appliances and automobiles). Some mass production techniques, such as standardized sizes and production lines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Handling
Automobile handling and vehicle handling are descriptions of the way a wheeled vehicle responds and reacts to the inputs of a driver, as well as how it moves along a track or road. It is commonly judged by how a vehicle performs particularly during cornering, acceleration, and braking as well as on the vehicle's directional stability when moving in steady state condition. In the automotive industry, handling and braking are the major components of a vehicle's "active" safety. They also affect its ability to perform in auto racing. The maximum lateral acceleration is, along with braking, regarded as a vehicle’s ''road holding'' ability. Automobiles driven on public roads whose engineering requirements emphasize handling over comfort and passenger space are called sports cars. Design factors that affect automobile handling Weight distribution Centre of mass height The centre of mass height, also known as the centre of gravity height, or CGZ, relative to the track, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ride Quality
Ride quality refers to a vehicle's effectiveness in insulating the occupants from undulations in the road surface such as bumps or corrugations. A vehicle with good ride quality provides comfort for the driver and the passengers. Importance Good ride quality provides comfort for the people inside the car, minimises damage to cargo and can reduce driver fatigue on long journeys in uncomfortable vehicles, and also because road disruption can impact the driver's ability to control the vehicle. Suspension design is often a compromise between ride quality and car handling because cars with firm suspension can result in greater control of body movements and quicker reactions. Similarly, a lower center of gravity is more ideal for handling, but low ground clearance limits suspension travel and requires stiffer springs. Ambulances have a special need for a high level of ride quality to avoid further injury to the already-ill passengers. Technology Early vehicles, like the Ford Model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Car
Executive car is a British term for a large car, and is considered equivalent to the European E-segment and American full-size classifications. Executive cars are larger than compact executive cars (and the non-luxury equivalent mid-size cars), but smaller than luxury saloons / full-size luxury sedans. The term has also been adopted by Euro NCAP, a European organization founded to test car safety. Background The term was coined in the 1960s to describe cars targeted at successful professionals and middle-to-senior managers. It was used by businesses as an incentive for employees in senior roles and to exploit Britain and Europe's tax schemes as a company-owned vehicle. Early executive cars typically offered engines with displacements of , compared with for an equivalent sized—but less luxurious—"large family car". Prior to the 1990s, executive cars were typically sedans; however, in recent years, they have also been produced in other body styles, such as estates (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front-mid-engine, Front-wheel-drive Layout
In automotive design, a front-mid-engine design, mid-engine, front-wheel-drive layout (also called more simply "mid-engine, front-wheel-drive layout", and abbreviated MF or FMF) is one in which the front road wheels are driven by an internal-combustion engine placed just behind them, in front of the passenger compartment. In contrast to the front-engine, front-wheel-drive layout (FF), the center of mass of the engine is behind the front axle. This layout is typically chosen for its better weight distribution (the heaviest component is near the center of the car, lowering its moment of inertia). Many early successful (and mostly French) mass-produced front-wheel drive cars used the MF layout, until the 1959 Mini, BMC (Austin / Morris) Mini demonstrated the layout and passenger car packaging benefits of mounting the engine transversely in front of the front axle. At first – when well executed – the packaging, space utilization and user experience of MF layout, even in a subcompa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |