|
Cistern (neuroanatomy)
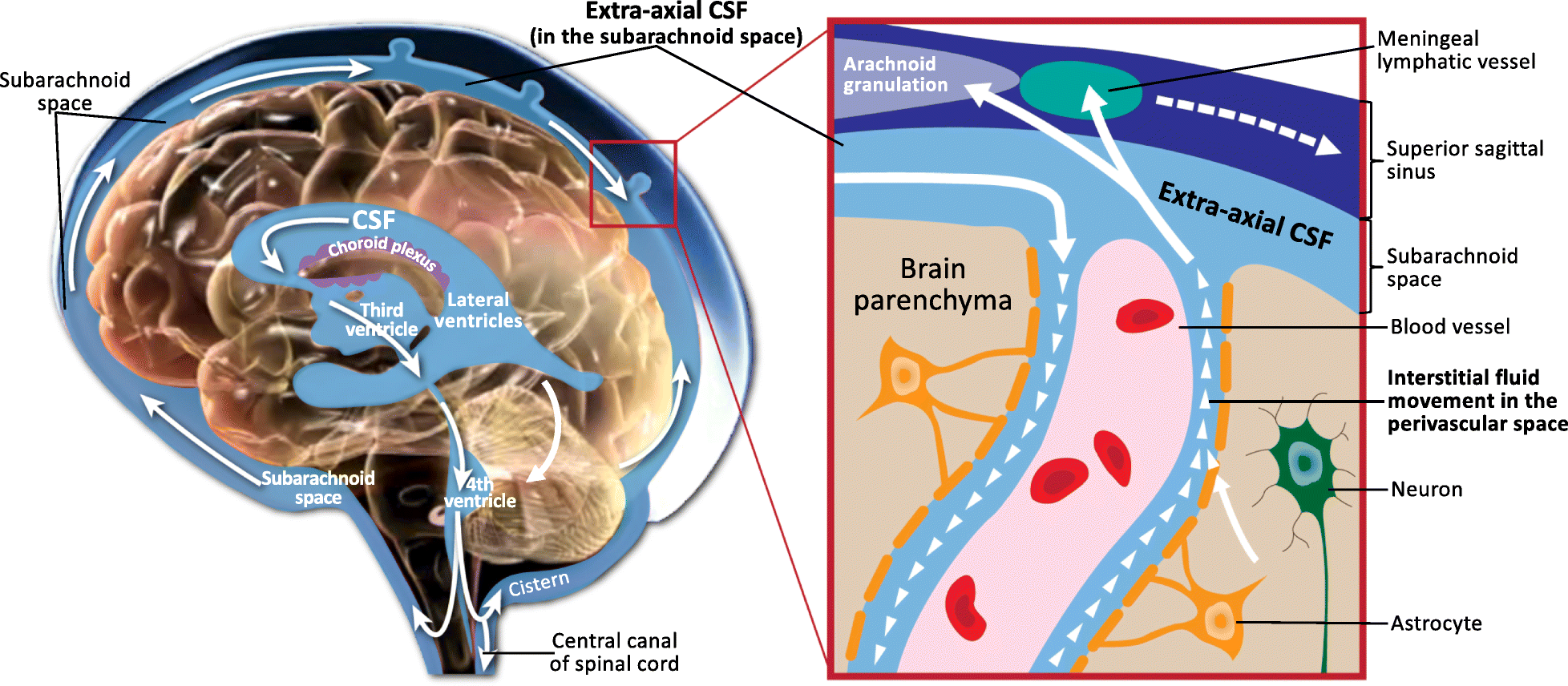
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space is situated between the Leptomeninges, two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Structure Although the pia mater adheres to the surface of the brain, closely following the contours of its gyrus, gyri and sulcus (neuroanatomy), sulci, the arachnoid mater only covers its superficial surface, bridging across the gyri. This leaves wider spaces between the pia and arachnoid and the cavities are known as the subarachnoid cisterns. Although they are often described as distinct compartments, the subarachnoid cisterns are not truly anatomically distinct. Rather, these subarachnoid cisterns are separated from each other by a trabeculated porous wall with various-sized openings. Cisterns There are many cisterns in the brain with several large ones noted with their own name. At the ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisterna Magna
The cisterna magna (posterior cerebellomedullary cistern, or cerebellomedullary cistern) is the largest of the subarachnoid cisterns. It occupies the space created by the angle between the caudal/inferior surface of the cerebellum, and the dorsal/posterior surface of the medulla oblongata (it is created by the arachnoidea that bridges this angle). The fourth ventricle communicates with the cistern via the unpaired midline median aperture. It is continuous inferiorly with the subarachnoid space of the spinal canal. The cisterna magna contains the two vertebral arteries, the origins of the two posterior inferior cerebellar arteries, the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X), accessory nerve (CN XI), hypoglossal nerve (XII), and choroid plexus. The vertebral artery and posterior inferior cerebellar artery of either side pass traverse either lateral portion of the cistern. Etymology The '' Terminologia Anatomica'' classifies the terms ''cisterna magna'' and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Aperture
The median aperture (median aperture of fourth ventricle or foramen of Magendie) is an opening at the caudal portion of the roof of the fourth ventricle. It allows the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the fourth ventricle into the cisterna magna. The other openings of the fourth ventricle are the lateral apertures - one on either side. The median aperture varies in size but accounts for most of the outflow of CSF from the fourth ventricle. Structure Relations The median foramen on axial images is posterior to the pons and anterior to the caudal cerebellum. It is surrounded by the obex and gracile tubercles of the medulla, tela choroidea of the fourth ventricle and its choroid plexus, which is attached to the cerebellar vermis The cerebellar vermis (from Latin ''vermis,'' "worm") is located in the medial, cortico-nuclear zone of the cerebellum, which is in the posterior cranial fossa, posterior fossa of the cranium. The primary fissure in the vermis curves ventr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpeduncular Cistern
The interpeduncular cistern (or basal cistern) is the subarachnoid cistern situated between the dorsum sellae (anteriorly) and the two cerebral peduncles at the front of the midbrain. Its roof is represented by the floor of the third ventricle (i.e. posterior perforated substance, and the two mammillary bodies). Its floor is formed by the arachnoid membrane extending between the temporal lobes of either side. Anteriorly, it extends to the optic chiasm. The cistern communicates superiorly with the chiasmatic cistern, and inferiorly with the pontine cistern. The chiasmatic cistern, cistern of lamina terminalis, and supracallosal cistern are all extensions of the interpeduncular cistern. Anatomy Contents The cistern contains: * the posterior portion of the circle of Willis: ** basilar artery (including its bifurcation), ** (origins of the) posterior cerebral arteries, ** posterior communicating arteries, * (the origin of the) posterior thalamo-perforating arteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) is one of three pairs of artery, arteries that supplies blood to the cerebellum. It arises from the basilar artery on each side at the level of the junction between the medulla oblongata and the pons in the brainstem. It has a variable course, passing backward to be distributed to the anterior part of the undersurface of the cerebellum, anastomosis, anastomosing with both the posterior inferior cerebellar artery, posterior inferior cerebellar (PICA) branch of the vertebral artery and the superior cerebellar artery. It also gives off the internal auditory or labyrinthine artery in most cases; however, the labyrinthine artery can less commonly emerge as a branch of the basilar artery. The amount of tissue receiving blood supply from the AICA is variable, depending upon whether the PICA is more or less dominant, but usually includes the anteroinferior surface of the cerebellum, the flocculus, middle cerebellar peduncle and inferolatera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilar Artery
The basilar artery (U.K.: ; U.S.: ) is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood. The two vertebral arteries and the basilar artery are known as the vertebral basilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part of the circle of Willis and joins with blood supplied to the anterior part of the circle of Willis from the internal carotid arteries. Structure The diameter of the basilar artery range from 1.5 to 6.6 mm. Origin The basilar artery arises from the union of the two vertebral arteries at the junction between the medulla oblongata and the pons between the abducens nerves (CN VI). Course It ascends along the basilar sulcus of the ventral pons. It divides at the junction of the midbrain and pons into the posterior cerebral arteries. Branches Its branches from caudal to rostral include: *anterior inferior cerebellar artery *labyrinthine artery (<15% of people, usually branches from the anterior inferior cerebellar artery) * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Aperture
The lateral aperture, lateral aperture of fourth ventricle or foramen of Luschka (after anatomist Hubert von Luschka) at whonamedit.com is an opening at the lateral extremity of either of the opening anteriorly into (sources differ) the pontine cistern/ lateral cerebellomedullary cistern at [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75). This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways and tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus. Structure The pons in humans measures about in length. It is the part of the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata. The horizontal ''medullopontine sulcus'' demarcates the boundary between the pons and medulla oblongata on the ventral aspect of the brainstem, and the roots of cranial nerves VI/VII/VIII emerge from the brainstem along this groove. The junction of pons, medulla oblongata, and cerebellum forms the cerebellopontine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontine Cistern
The prepontine cistern, or pontine cistern is one of the subarachnoid cisterns situated ventral to the pons. It contains the basilar artery. Each lateral aperture opens into the pontine cistern just posterior to the cranial nerve VIII. Anatomy The pontine cistern is situated ventral to the pons, in the interval between ventral aspect of the pons, and the clivus. Contents The cistern contains the origin of the abducens nerve (CN VI), the basilar artery and the origin of the basilar artery and of its branches, and the anterior inferior cerebellar artery, and superior cerebellar artery. Relations It is continuous inferiorly with the subarachnoid space of the spinal canal, posterolaterally with the cerebellopontine cistern of either side, and rostrally/anteriorly with the interpeduncular cistern The interpeduncular cistern (or basal cistern) is the subarachnoid cistern situated between the dorsum sellae (anteriorly) and the two cerebral peduncles at the front of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of Visual perception, vision, taste, Olfaction, smell, and hearing. The cranial nerves emerge from the central nervous system above the level of the Atlas (anatomy), first vertebra of the vertebral column. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides. There are conventionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves, which are described with Roman numerals I–XII. Some considered there to be thirteen pairs of cranial nerves, including the non-paired cranial nerve zero. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain and brainstem, from front to back. The terminal nerves (0), olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerves (II) emerge f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglossal Nerve
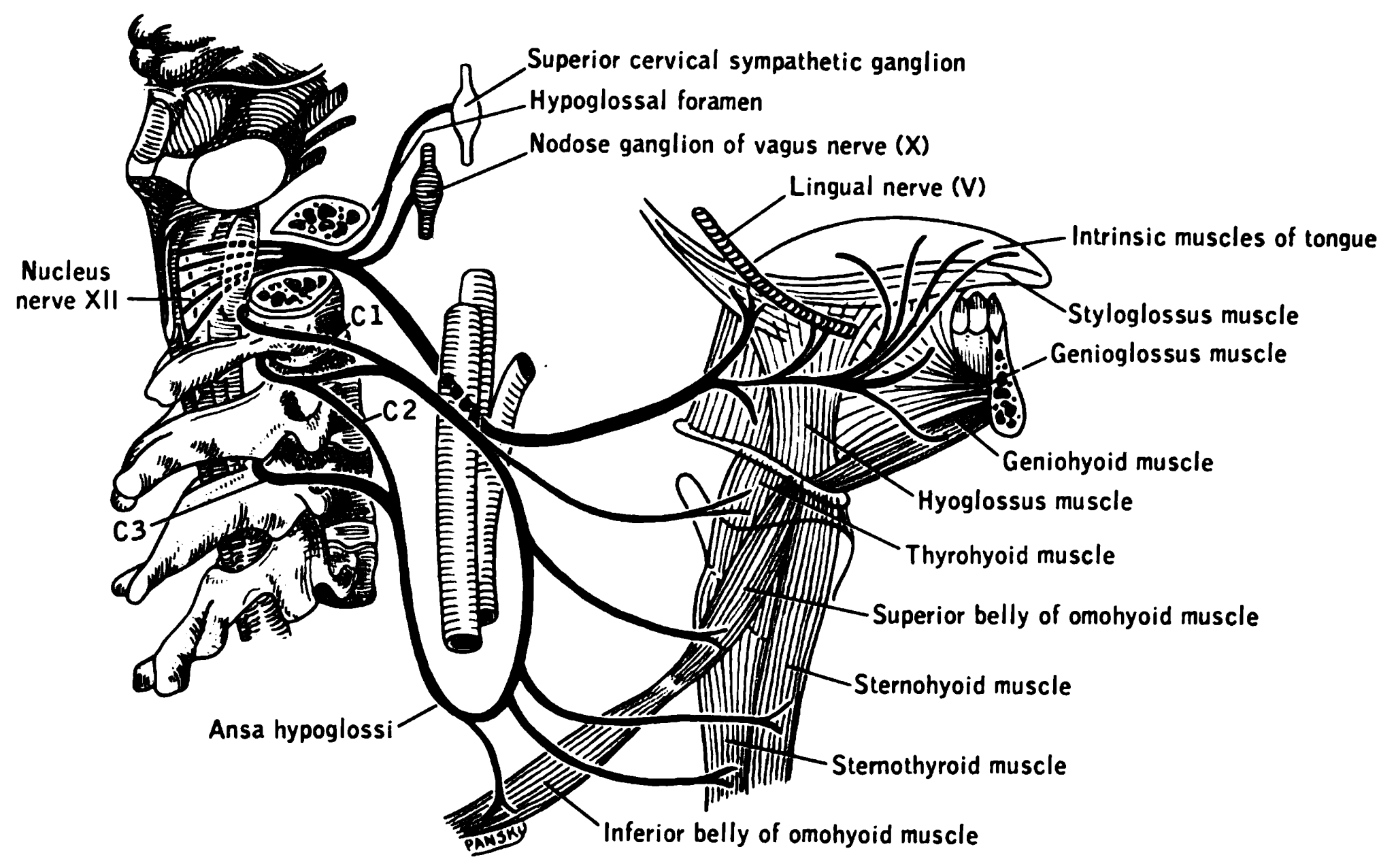
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve. CN XII is a nerve with a sole motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, pass through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue. The nerve is involved in controlling tongue movements required for speech and swallowing, including sticking out the tongue and moving it from side to side. Damage to the nerve or the neural pathways which control it can affect the ability of the tongue to move and its appearance, with the most common sources of damage being injury from trauma or surgery, and motor neuron disease. The first recorded description of the nerve was by Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerves because part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain. The sternocleidomastoid muscle tilts and rotates the head, whereas the trapezius muscle, connecting to the scapula, acts to shrug the shoulder. Traditional descriptions of the accessory nerve divide it into a spinal part and a cranial part. The cranial component rapidly joins the vagus nerve, and there is ongoing debate about whether the cranial part should be considered part of the accessory nerve proper. Consequently, the term "accessory nerve" usually refers only to nerve supplying the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, also called the spinal accessory nerve. Strength testing of these muscles can be measured during a neurological examination to assess func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibers and serves as a major pathway that connects the brain to various organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. As a key part of the parasympathetic nervous system, the vagus nerve helps regulate essential involuntary functions like heart rate, breathing, and digestion. By controlling these processes, the vagus nerve contributes to the body's "rest and digest" response, helping to calm the body after stress, lower heart rate, improve digestion, and maintain homeostasis. The vagus nerve consists of two branches: the right and left vagus nerves. In the neck, the right vagus nerve contains approximately 105,000 fibers, while the left vagus nerve has about 87,000 fibers, according to one source. However, other sources report sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |