|
Cissia (area)
Cissia(, ''Kissia'') was a very fertile district of Susiana in the Persian Empire, on the Choaspes. According to Herodotus, the inhabitants, Cissii, were a 'wild', free people, resembling the Persians in their manners. Herodotus and other ancient Greek writers sometimes referred to the region around Susa as "Cissia", a variant of the Kassite name. However, it is not clear if Kassites were actually living in that region so late. History In ancient times Cissia was subjugated by Tiglath-Pileser III. Once the Ionian Revolt was finally crushed by the Persian victory at the Battle of Lade, Darius began to plan to subjugate Greece. In 490 BC, he sent a naval task force under Datis and Artaphernes across the Aegean to subjugate the Cyclades, and then to make punitive attacks on Athens and Eretria. Reaching Euboea in mid-summer after a successful campaign in the Aegean, the Persians proceeded to put Eretria under siege. The siege lasted six days before a fifth column of Eretrian n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susiana
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh and Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital of Elam and the winter capital of the Achaemenid Empire, and remained a strategic centre during the Parthian and Sasanian periods. The site currently consists of three archaeological mounds, covering an area of around . The city of Shush is located on the site of ancient Susa. Name The name Susa is of Elamiate origin and has appeared in many languages: *Middle *Middle and Neo- *Neo-Elamite and Achaemenid *Achaemenid * * * * or *New * Literary references Susa was one of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East. In historic literature, Susa appears in the very earliest Sumerian records: for example, it is described as one of the places obedient to Inanna, patron deity of Uruk, in ''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta''. Biblical text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
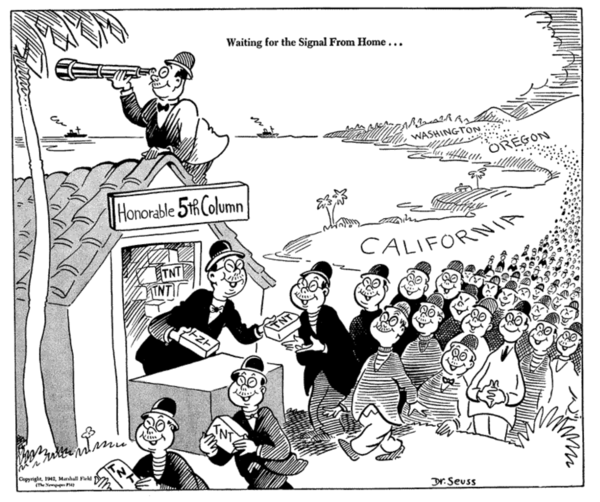
Fifth Column
A fifth column is a group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. The activities of a fifth column can be overt or clandestine. Forces gathered in secret can mobilize openly to assist an external attack. The term is also applied to organized actions by military personnel. Clandestine fifth column activities can involve acts of sabotage, disinformation, espionage or terrorism executed within defense lines by secret sympathizers with an external force. History Internal Enemy in Antiquity The distinction between internal and external enemies to a people or government was a topic of discussion in antiquity, mentioned most notably in Plato's ''Republic''. Origin of Modern Term The term "fifth column" originated in Spain (originally ) during the early phase of the Spanish Civil War. It gained popularity in the Republican faction media in early October 1936 and immediately started to spread abroad. The exac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Regions
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susa
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh River, Karkheh and Dez River, Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital of Elam and the winter capital of the Achaemenid Empire, and remained a strategic centre during the Parthian Empire, Parthian and Sasanian Empire, Sasanian periods. The site currently consists of three archaeological mounds, covering an area of around . The city of Shush, Iran, Shush is located on the site of ancient Susa. Name The name Susa is of Elamiate origin and has appeared in many languages: *Middle *Middle and Neo- *Neo-Elamite language, Elamite and Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid *Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid * * * * or *New * Literary references Susa was one of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East. In Historiography, historic literature, Susa appears in the very earliest Sumerian records: for exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the List of largest empires#Timeline of largest empires to date, largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Basin, Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollonius Of Tyana
Apollonius of Tyana (; ; ) was a Greek philosopher and religious leader from the town of Tyana, Cappadocia in Roman Anatolia, who spent his life travelling and teaching in the Middle East, North Africa and India. He is a central figure in Neopythagoreanism and was one of the most famous " miracle workers" of his day. His exceptional personality and his mystical way of life, which was regarded as exemplary, impressed his contemporaries and had a lasting cultural influence. Numerous legends surrounding him and accounts of his life are contained in the extensive ''Life of Apollonius''. Many of the ancient legends of Apollonius consist of numerous reports about miracles that he was said to have performed as a wandering sage with his lifelong companion Damis. He was tried for allegedly having used magic as a means of conspiring against the emperor; after his conviction and subsequent death-penalty, his followers believed he underwent heavenly ascension. Most modern scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Day's Journey
A day's journey in pre-modern literature, including the Bible and ancient geographers and ethnographers such as Herodotus, is a measurement of distance. In the Bible, it is not as precisely defined as other Biblical measurements of distance; the distance has been estimated from . Judges 19 records a party of three people and two mules who traveled from Bethlehem to Gibeah, a distance of about 10 miles, in an afternoon. Porter notes that a mule can travel about 3 miles per hour, covering 24 miles in an eight-hour day. Another citation comes from Priscus (fr. 8 in Müller's '' Fragmenta Historicorum Graecorum'') and is translated thus by J. B. Bury: ''We set out with the barbarians, and arrived at Sardica, which is thirteen days for a fast traveller from Constantinople.'' From Constantinople (Istanbul) to Sofia Sofia is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darius The Great
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West Asia, parts of the Balkans (Skudra, Thrace–Achaemenid Macedonia, Macedonia and Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia) and the Caucasus, most of the Black Sea's coastal regions, Central Asia, the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley, Indus Valley in the far east, and portions of North Africa and Northeast Africa including History of Persian Egypt, Egypt (), eastern ancient Libya, Libya, and coastal The Sudans, Sudan. Darius ascended the throne by overthrowing the Achaemenid monarch Bardiya (or ''Smerdis''), who he claimed was in fact an imposter named Gaumata. The new king met with rebellions throughout the empire but quelled each of them; a major event in Darius's life was his expedition to subjugate Ancient Greece, Greece and punish Classical At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardericca In Susiana
Ardericca in Susiana (also spelled Arderikka; ) was an ancient village in Cissia mentioned by Herodotus (6.119.2). Described as being located about 40 km from Susa, it is noted for being the location where the Achaemenid king Darius I (r. 522-486 BC) settled the inhabitants of Eretria, after the city was taken by his admiral Datis in 490 BC. The site is commonly identified with the modern-day place of "Kīr-āb", located to the north of Susa. Herodotus further states that the village was famous for a spring located 7 km from it, where salt, oil and asphalt were produced. He also described it as being a ''stathmos'' ("farmstead A farmstead refers to the buildings and service areas associated with a farm. It consists of a house belonging to a farm along with the surrounding buildings. The characteristics of a specific farmstead reflect the local landscape, which provides ...") of Darius I, implying that Ardericca in Susiana was perhaps one of the king's own estates. Hero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
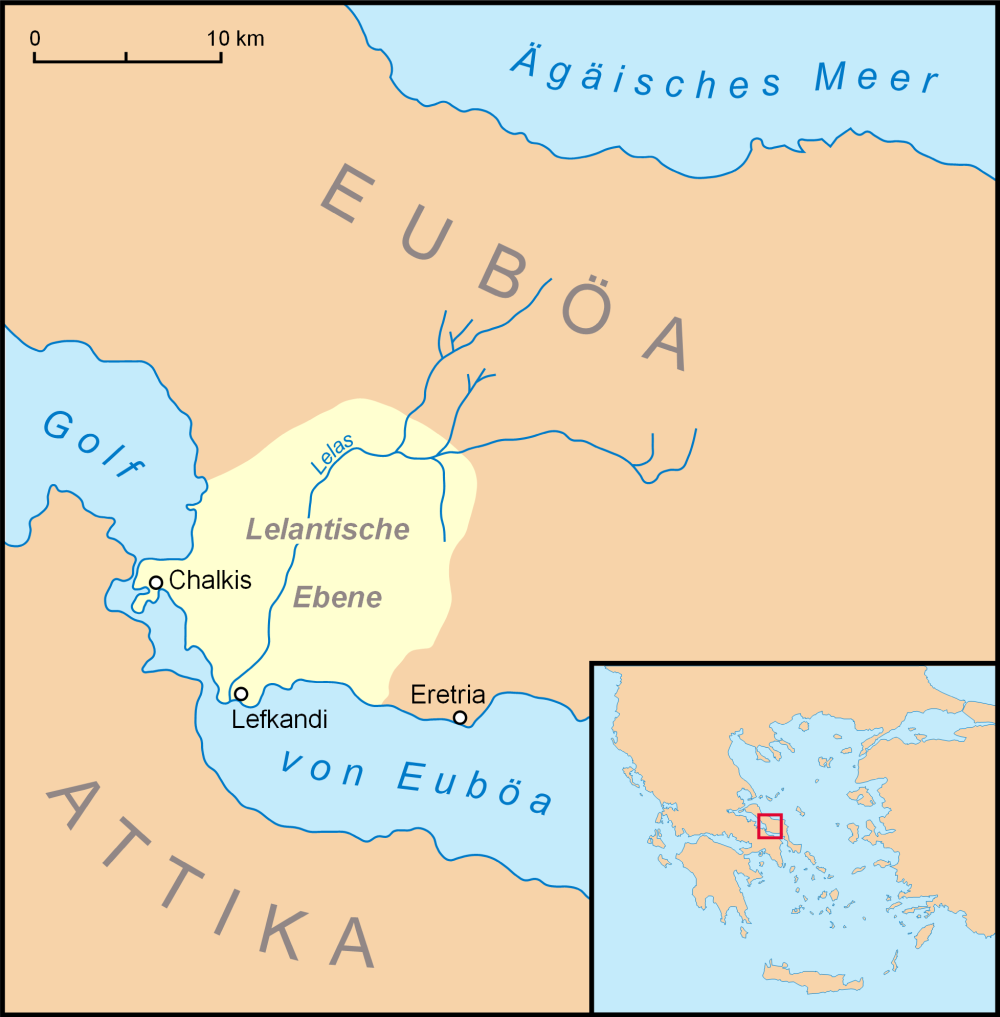
Euboea
Euboea ( ; , ), also known by its modern spelling Evia ( ; , ), is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete, and the sixth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait (only at its narrowest point). In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to . Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos. It forms most of the regional unit of Euboea, which also includes Skyros and a small area of the Greek mainland. Name Like most of the Greek islands, Euboea was known by other names in antiquity, such as ''Macris'' (Μάκρις) and ''Doliche'' (Δολίχη) from its elongated shape, or ''Ellopia'' (after El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a successful model of centralised bureaucratic administration, its multicultural policy, building complex inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eretria
Eretria (; , , , , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain. A granary and several other buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |