|
Circus (building)
A ancient Rome, Roman circus (from the Classical Latin, Latin word that means "circle") was a large open-air venue used mainly for chariot racing, chariot races, although sometimes serving other purposes. It was similar to the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek hippodrome. Along with Roman theatre (structure), theatres and Roman amphitheatre, amphitheatres, circuses were one of the main entertainment venues at the time. Similar buildings, called ''stadium, stadia'' were used for Panhellenic Games, Greek-style athletics particularly in the eastern, Greek speaking, part of the empire, but these were typically smaller than circuses. According to Edward Gibbon the Roman people, at the start of the 5th century AD: Architectural design The performance space of the Roman circus was normally, despite its name, an oblong rectangle of two linear sections of race track, separated by a median strip running along the length of about two thirds the track, joined at one end with a semicircular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antinoöpolis
Antinoöpolis (also Antinoopolis, Antinoë, Antinopolis; ; ''Antinow''; , modern , modern ''Sheikh 'Ibada'' or ''Sheik Abāda'') was a city founded at an older Egyptian village by the Roman emperor Hadrian to commemorate his deified young beloved, Antinoüs, on the east bank of the Nile, not far from the site in Upper Egypt where Antinoüs drowned in 130 AD. Antinoöpolis was a little to the south of the Egyptian village of Besa (), named after the god and oracle of Bes. Antinoöpolis was built at the foot of the hill upon which Besa was seated. The city is located nearly opposite Hermopolis Magna and was connected to Berenice Troglodytica by the Via Hadriana. History New Kingdom During the New Kingdom, the city, ''Hir-we'', was the location of Ramesses II's great temple, dedicated to the gods of Khmun and Heliopolis. Roman period During the Roman Empire, the city of Antinoöpolis was erected in AD 130 by the emperor Hadrian on the site of Hir-we as the cult centre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
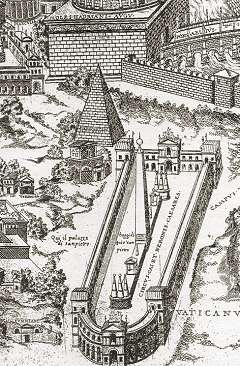
Circus Of Nero
The so-called Circus of Nero or Circus of Caligula was a circus (building), circus in ancient Rome, located mostly in the present-day Vatican City. It was first built under Caligula. History The ''Ager Vaticanus'', the alluvial plain outside the city walls on the west bank of the Tiber, was developed at the end of the first century BC, allowing patrician families to construct luxurious private residences (''Horti''). The Horti Agrippinae villa-estate belonged to Agrippina the Elder and was inherited by her son Caligula (r. 31–41 AD). He was a chariot-racing enthusiast and began construction of the circus which was completed by Claudius (r. 41-54 AD). The privately owned ''circus'' and ''Horti'' were then inherited by Nero who made the circus public so he could invite them to cheer him on. He also used both of these to lodge Romans made homeless by the great fire of 64. The circus was used in 65 to carry out mass executions of the Christians accused as scapegoats of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colchester
Colchester ( ) is a city in northeastern Essex, England. It is the second-largest settlement in the county, with a population of 130,245 at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 Census. The demonym is ''Colcestrian''. Colchester occupies the site of Camulodunum, the first Colonia (Roman), major city in Roman Britain and its first capital. Colchester therefore claims to be Britain's first city. It has been an important military base since the Roman Empire, Roman era, with Colchester Garrison currently housing the 16th Air Assault Brigade (United Kingdom), 16th Air Assault Brigade. On the River Colne, Essex, River Colne, Colchester is northeast of London. It is connected to London by the A12 road (England), A12 road and the Great Eastern Main Line railway. Colchester is less than from London Stansted Airport and from the port of Harwich. Attractions in and around the city include St Botolph's Priory, Colchester Zoo, and several art galleries. Colchester Castle was constructe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circus Of Maxentius
The Circus of Maxentius (known until the 19th century as the Circus of Caracalla) is an ancient structure in Rome, Italy, part of a complex of buildings erected by emperor Maxentius on the Via Appia between AD 306 and 312. It is situated between the second and third miles of the Via Appia, between the basilica and catacombs of San Sebastiano and the imposing late republican tomb of Caecilia Metella, which dominates the hill that rises immediately to the east of the complex. It is part of the Appian Way Regional Park. Overview The Circus of Maxentius is the best preserved circus in the area of Rome, and is second only in size to the Circus Maximus in Rome. The only games recorded at the Circus were its inaugural ones and these are generally thought to have been funerary in character. They would have been held in honour of Maxentius' son Valerius Romulus, who died in AD 309 at a very young age and who was probably interred in the adjacent cylindrical tomb (tomb of Romulus). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
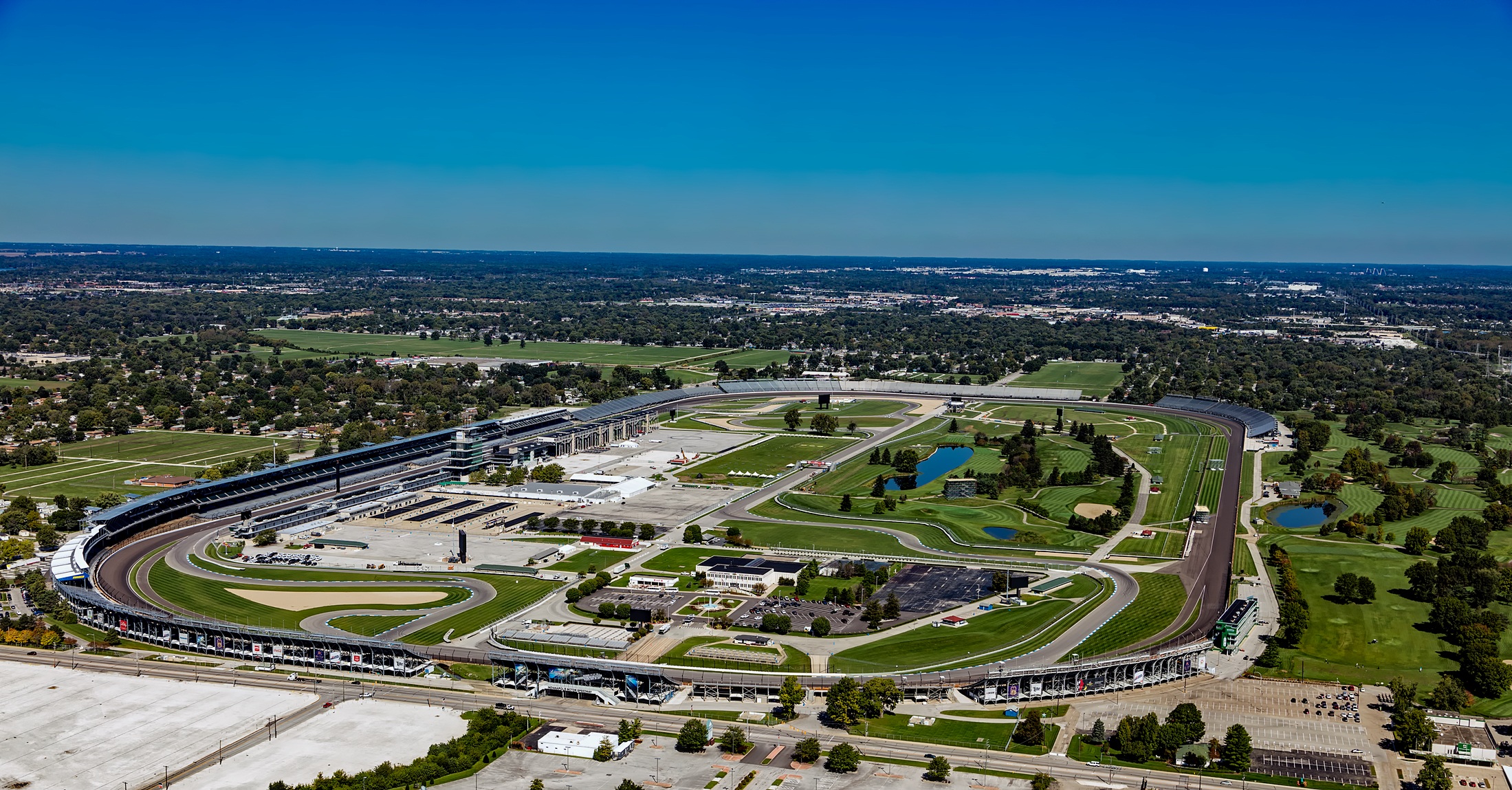
Seating Capacity
Seating capacity is the number of people who can be seated in a specific space, in terms of both the physical space available and limitations set by law. Seating capacity can be used in the description of anything ranging from an automobile that seats two to a stadium that seats hundreds of thousands of people. The largest sports venue in the world, the Indianapolis Motor Speedway, has a permanent seating capacity for more than 235,000 people and infield seating that raises capacity to an approximate 400,000. In transport In venues Safety is a primary concern in determining the seating capacity of a venue: "Seating capacity, seating layouts and densities are largely dictated by legal requirements for the safe evacuation of the occupants in the event of fire". The International Building Code specifies, "In places of assembly, the seats shall be securely fastened to the floor" but provides exceptions if the total number of seats is fewer than 100, if there is a substantial amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |