|
Cicero (typography)
A cicero is a unit of measure used in typography in Italy, France and other continental European countries, first used by Pannartz and Sweynheim in 1468 for the edition of Cicero's ''Epistulae ad Familiares''. The font size thus acquired the name ''cicero''. It is of the historical French inch, and is divided into 12 points, known in English as French points or Didot points. The unit of the cicero is similar to an English pica, although the French inch was slightly larger than the English inch. There are about 1.066 picas to a cicero; a pica is 4.23333333 mm and a cicero is 4.51165812456 mm. Cicero (and the points derived from cicero) was used in the early days of typography in continental Europe. In modern times, all computers use pica (and the points derived from pica) as font size measurement – alongside millimeters in countries using the metric system – for line length and paper size Paper size refers to Technical standard, standardized dimension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typographic Unit
Typographic units are the units of measurement used in typography or typesetting. Traditional wikt:typometry, typometry units are different from familiar SI, metric units because they were established in the early days of printing. Though most printing is digital now, the old terms and units have persisted. Even though these units are all very small, across a line of print they add up quickly. Confusions such as resetting text originally in type of one unit in type of another will result in words moving from one line to the next, resulting in all sorts of typesetting errors (viz. River (typography), rivers, widows and orphans, disrupted tables, and misplaced captions). Before the popularization of desktop publishing, type measurements were done with a tool called a typometer. Development In Europe, the Didot point system was created by Didot family#François-Ambroise Didot, François-Ambroise Didot (1730–1804) in c. 1783. Didot's system was based on Pierre Simon Fournier's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the Drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus, Bosporus Strait. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." Europe covers approx. , or 2% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
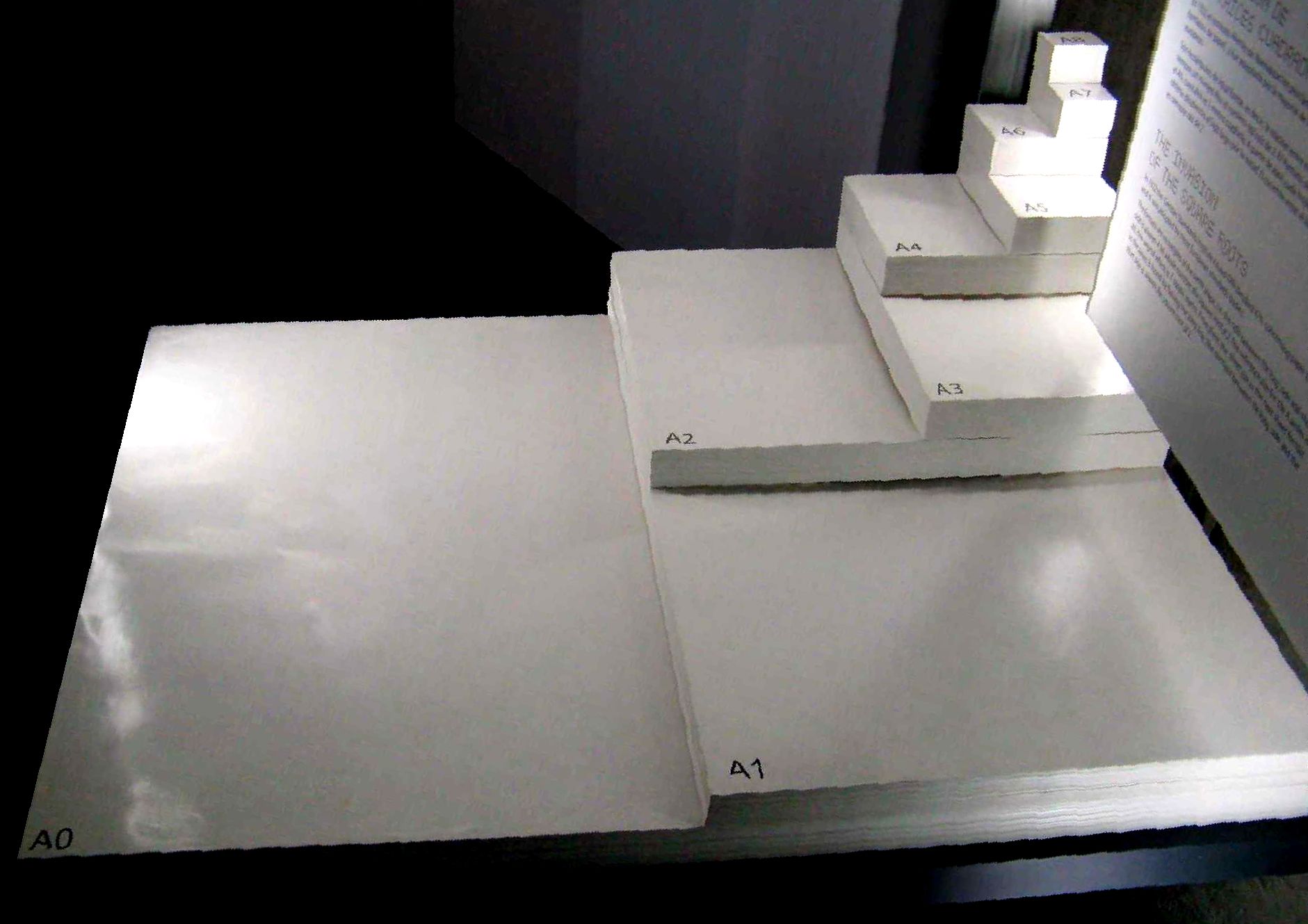
Paper Size
Paper size refers to Technical standard, standardized dimensions for sheets of paper used globally in stationery, printing, and technical drawing. Most countries adhere to the ISO 216 standard, which includes the widely recognized A series (including A4 paper), defined by a consistent aspect ratio of √2. The system, first proposed in the 18th century and formalized in 1975, allows scaling between sizes without distortion. Regional variations exist, such as the #North American paper sizes, North American paper sizes (e.g., Letter (paper size), Letter, Legal paper, Legal, and Ledger paper, Ledger) which are governed by the American National Standards Institute, ANSI and are used in North America and parts of Central and South America. The standardization of paper sizes emerged from practical needs for efficiency. The ISO 216 system originated in late-18th-century Germany as Deutsches Institut für Normung, DIN 476, later adopted internationally for its mathematical precision. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Length
In typography, line length is the width of a block of typeset text, usually measured in units of length like inches or points or in characters per line (in which case it is a measure). A block of text or paragraph has a maximum line length that fits a determined design. If the lines are too short then the text becomes disjointed; if they are too long, the content loses rhythm as the reader searches for the start of each line. Line length is determined by typographic parameters based on a formal grid and template with several goals in mind: balance and function for fit and readability with a sensitivity to aesthetic style in typography. Typographers adjust line length to aid legibility or copy fit. Text can be flush left and ragged right, flush right and ragged left, or justified where all lines are of equal length. In a ragged right setting, line lengths vary to create a ragged right edge. Sometimes this can be visually satisfying. For justified and ragged right settings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inch
The inch (symbol: in or prime (symbol), ) is a Units of measurement, unit of length in the imperial units, British Imperial and the United States customary units, United States customary System of measurement, systems of measurement. It is equal to yard or of a foot (unit), foot. Derived from the Uncia (unit), Roman uncia ("twelfth"), the word ''inch'' is also sometimes used to translate similar units in other measurement systems, anthropic units, usually understood as deriving from the width of the human thumb. Standards for the exact length of an inch have varied in the past, but since the adoption of the international yard during the 1950s and 1960s the inch has been based on the metric system and defined as exactly 25.4Millimetre, mm. Name The English word "inch" () was an early borrowing from Latin ' ("one-twelfth; Roman inch; Roman ounce"). The vowel change from Latin to Old English (which became Modern English ) is known as Germanic umlaut, umlaut. The consonant c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pica (typography)
The pica is a typographic unit of measure corresponding to approximately of an inch. One pica is further divided into 12 Point (typography), points. In printing, three pica measures are used: * The French pica of 12 Didot points (also called Cicero (typography), cicero) generally is: 12 × 0.376 = . * The American pica of . It was established by the United States Type Founders' Association in 1886. In TeX one pica is of an inch. * The contemporary computer PostScript pica is exactly of an inch, i.e. 0.1 in or 4.2 mm. Publishing applications such as Adobe InDesign and QuarkXPress represent pica measurements with whole-number picas left of a lower-case ''p'', followed by the points number, for example: 5p6 represents 5 picas and 6 points, or 5 picas. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) defined by the World Wide Web Consortium use pc as the abbreviation for pica ( of an inch), and pt for point ( of an inch). The pica is also used in measuring the font capacity and is applied in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point (typography)
In typography, the point is the smallest unit of measure. It is used for measuring font size, leading, and other items on a printed page. The size of the point has varied throughout printing's history. Since the 18th century, the size of a point has been between 0.18 and 0.4 millimeters. Following the advent of desktop publishing in the 1980s and 1990s, digital printing has largely supplanted the letterpress printing and has established the desktop publishing (DTP) point as the ''de facto'' standard. The DTP point is defined as of an inch (or exactly 0.352 mm) and, as with earlier American point sizes, is considered to be of a pica. In metal type, the point size of a font describes the height of the metal body on which that font's characters were cast. In digital type, letters of a computer font are designed around an imaginary space called an '' em square''. When a point size of a font is specified, the font is scaled so that its em square has a side length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epistulae Ad Familiares
''Epistulae ad Familiares'' (''Letters to Friends'') is a collection of letters between Ancient Rome, Roman politician and orator Cicero, Marcus Tullius Cicero and various public and private figures. The letters in this collection, together with Cicero's other letters, are considered the most reliable sources of information for the period leading up to the fall of the Roman Republic. Traditionally spanning 16 books, and featuring letters from 62 to 43 BCE, the collection was likely first published by Cicero's freedman and personal secretary Marcus Tullius Tiro sometime after Cicero's death in 43 BCE. A number of manuscript copies of this collection have reached modern times. The earliest witness to the text is a palimpsest on a single leaf, written in uncials of the fifth or sixth century (Codices Latini Antiquiores, CLA IV.443; it contains portions of letters 6.9 and 6.10. Two more fragments from 12th-century manuscripts – the outer bifolium of an eight-sheet gather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists and the innovator of what became known as "Ciceronian rhetoric". Cicero was educated in Rome and in Greece. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC. He greatly influenced both ancient and modern reception of the Latin language. A substantial part of his work has survived, and he was admired by both ancient and modern authors alike. Cicero adapted the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy in Latin and coined a large portion of Latin philosophical vocabulary via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Pannartz And Konrad Sweynheim
Arnold Pannartz and Conrad Sweynheym were two printers of the 15th century, associated with Johannes Gutenberg and the use of his invention, the mechanical movable-type printing press. Backgrounds Arnold Pannartz was, perhaps, a native of Prague, and Conrad Sweynheym of Eltville near Mainz. Gottfried Zedler believed (''Gutenberg-Forschungen,'' 1901) that Sweynheym worked at Eltville with Johannes Gutenberg in 1461–1464. Whether Pannartz had been connected with Sweynheym in Germany is not known. It is certain that the two brought Gutenberg's invention, the mechanical movable-type printing press, to Italy. Pannartz died about 1476, Sweynheym in 1477. Printing work The Benedictine Abbey of Saint Scholastica in Subiaco (in present-day Lazio) was the cradle of Italian printing. Probably Cardinal Giovanni Turrecremata, who was Abbot '' in commendam'' of Subiaco, summoned the two printers there; they came in 1464. The first book that the Subiaco Press produced was a Donatus; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with Dimension (physical quantity), dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a Base unit (measurement), base unit for length is chosen, from which all other units are derived. In the International System of Units (SI) system, the base unit for length is the metre. Length is commonly understood to mean the most extended size, dimension of a fixed object. However, this is not always the case and may depend on the position the object is in. Various terms for the length of a fixed object are used, and these include height, which is vertical length or vertical extent, width, breadth, and depth. ''Height'' is used when there is a base from which vertical measurements can be taken. ''Width'' and ''breadth'' usually refer to a shorter dimension than ''length''. ''Depth'' is used for the measure of a third dimension. Length is the measure of one spatial dimension, whereas area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |