|
Château De Porrentruy
Porrentruy (; ; ) is a Swiss municipality and seat of the district of the same name located in the canton of Jura. Porrentruy is home to National League team, HC Ajoie. History The first trace of human presence in Porrentruy is a Mesolithic tool that was found in the backyard of the Hôtel-Dieu. Scattered, individual objects have also been found from the Neolithic, the late Bronze Age and the Iron Age. The first known settlement in what became Porrentruy goes back to the Roman era. In 1983, the ruins of a Gallo-Roman temple were discovered in the cemetery on the north of town, and Roman coins were found there. Near the town, a kilometre long (0.6 mile) section of the Augst- Epomanduodurum (now Mandeure) Roman road was discovered. In the backyard of the Hôtel-Dieu the charred remains of a building from the 10th or 11th century were discovered. However, the first historical mention of the name occurs in 1136 as ''Purrentru''. The name presumably comes from the Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porrentruy (district)
Porrentruy District (, ) is one of the three districts of the canton of Jura, Switzerland. Its capital is the town of Porrentruy. The French language, French-speaking district has a population of (as of ). Municipalities Porrentruy is divided into a total of 20 municipalities of Switzerland, municipalities: Coat of arms The blazon of the district coat of arms is ''Gules a Fess Argent, overall a Cockatrice Or volant holding in legs and beak a Crosier of the same.'' Demographics Porrentruy has a population () of . Most of the population () speaks French language, French (22,008 or 91.8%) as their first language, German language, German is the second most common (1,001 or 4.2%) and Italian language, Italian is the third (306 or 1.3%). There are 8 people who speak Romansh language, Romansh. , the population was 48.8% male and 51.2% female. The population was made up of 10,585 Swiss men (43.7% of the population) and 1,243 (5.1%) non-Swiss men. There were 11,322 Swiss women (46. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in Epipaleolithic Near East, the Levant and Epipaleolithic Caucasus, Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and the Middle East, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 Before Present, BP; in the Middle East (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 Before Present, BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Middle Ages of History of Europe, European history, following the decline of the Roman Empire, decline of the Western Roman Empire, and preceding the High Middle Ages ( 11th to 14th centuries). The alternative term ''Late antiquity#Terminology, late antiquity'', for the early part of the period, emphasizes elements of continuity with the Roman Empire, while ''Early Middle Ages'' is used to emphasize developments characteristic of the earlier medieval period. The period saw a continuation of trends evident since late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, Medieval Warm Period, a small rise in average temperatures in the North Atlantic region and Migration Period, increased m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagobert I
Dagobert I (; 603/605 – 19 January 639) was King of the Franks. He ruled Austrasia (623–634) and Neustria and Burgundy (629–639). He has been described as the last king of the Merovingian dynasty to wield real royal power, after which the Mayor of the palace rose as the political and war leader. Dagobert was the first Frankish king to be buried in the royal tombs at the Basilica of Saint-Denis. Rule in Austrasia Dagobert was the eldest son of Chlothar II and Haldetrude (575–604) and the grandson of Fredegund. Chlothar had reigned alone over all the Franks since 613. In 622, Chlothar made Dagobert king of Austrasia, almost certainly to bind the Austrasian nobility to the ruling Franks. As a child, Dagobert lived under the care of the Carolingian dynasty forebears and Austrasian magnates, Arnulf of Metz and Pepin of Landen. Chlothar attempted to manage the unstable alliances he had with other noble families throughout much of Dagobert's reign. When Chlothar granted Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which was the most northerly province of the Roman Empire in continental Europe. These Frankish tribes lived for centuries under varying degrees of Roman hegemony and influence, but after the collapse of Roman institutions in western Europe they took control of a large empire including areas which had been ruled by Rome, and what it meant to be a Frank began to evolve. Once they were deeply established in Gaul, the Franks became a multilingual, Catholic Christian people, who subsequently came to rule over several other post-Roman kingdoms both inside and outside the old empire. In a broader sense much of the population of western Europe could eventually described as Franks in some contexts. The term "Frank" itself first appeared in the third cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porrentruy Rathaus
Porrentruy (; ; ) is a Swiss municipality and seat of the district of the same name located in the canton of Jura. Porrentruy is home to National League team, HC Ajoie. History The first trace of human presence in Porrentruy is a Mesolithic tool that was found in the backyard of the Hôtel-Dieu. Scattered, individual objects have also been found from the Neolithic, the late Bronze Age and the Iron Age. The first known settlement in what became Porrentruy goes back to the Roman era. In 1983, the ruins of a Gallo-Roman temple were discovered in the cemetery on the north of town, and Roman coins were found there. Near the town, a kilometre long (0.6 mile) section of the Augst- Epomanduodurum (now Mandeure) Roman road was discovered. In the backyard of the Hôtel-Dieu the charred remains of a building from the 10th or 11th century were discovered. However, the first historical mention of the name occurs in 1136 as ''Purrentru''. The name presumably comes from the Latin ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
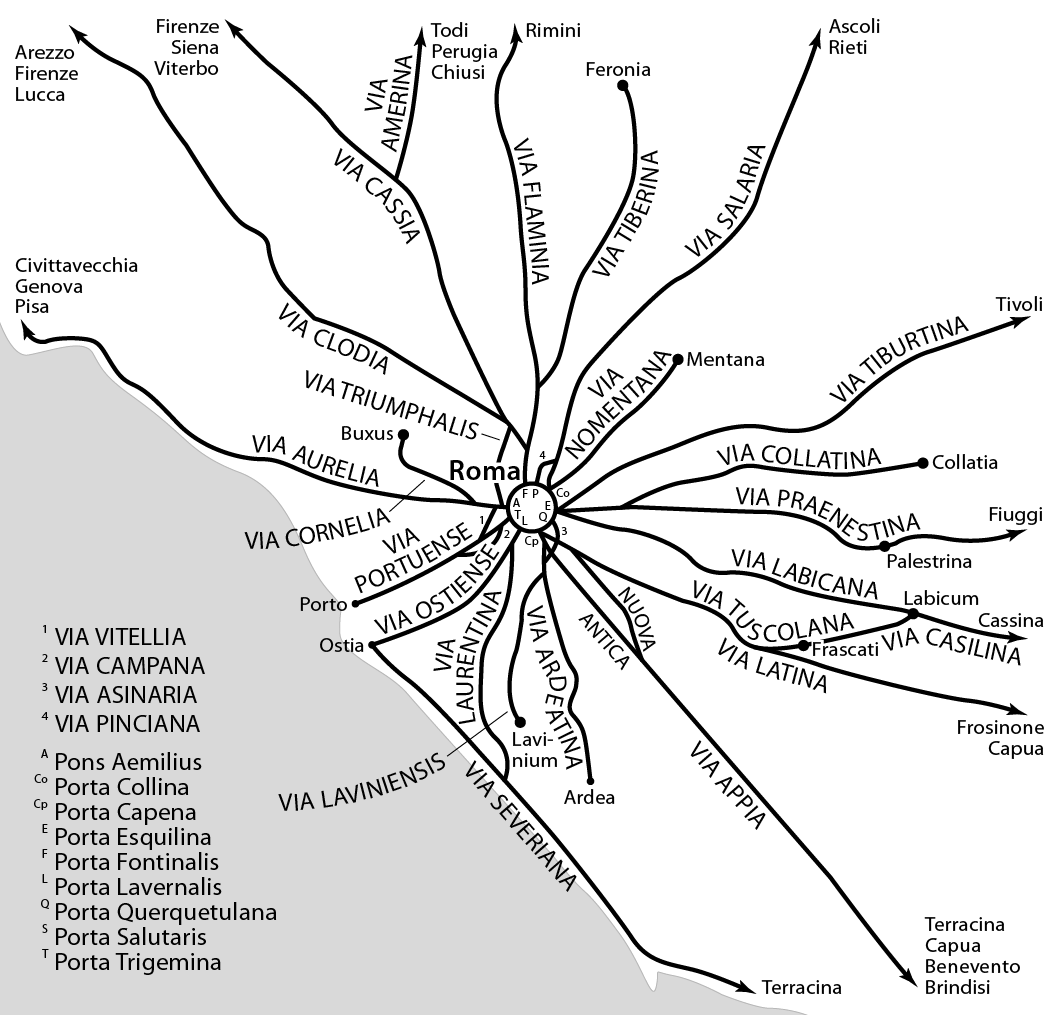
Roman Roads
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of Military history of ancient Rome, armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and Roman commerce, trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, Bridle path, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandeure
Mandeure () is a commune in the Doubs department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in eastern France. History Mandeure was a Roman town called Epamanduodurum. It reached its apogee in the 2nd century. The Roman theater was one of the largest in Gaul, measuring 142 m with four levels of seats that could seat 12,000 to 15,000 spectators. Free guided tours are available by contacting the mayor's office. Population See also * Communes of the Doubs department The following is a list of the 563 communes of the Doubs department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025): References External links Mande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augst
Augst (Swiss German: ''Augscht'') is a municipality in the district of Liestal in the canton of Basel-Country in Switzerland. It was known as Augusta Raurica in Roman times. History Augst is first mentioned in 615 as ''Augustodunensem praesulem''. In 752 it was mentioned as ''Augusta'' and in 1288 as ''Augst''. Geography Augst has an area, , of . Of this area, or 34.8% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 6.7% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 40.2% is settled (buildings or roads), or 17.1% is either rivers or lakes.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data accessed 25 March 2010 Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 6.1% of the total area while housing and buildings made up 11.0% and transp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallo-Roman Culture
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire in Roman Gaul. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, language, morals and way of life in a uniquely Gaulish context. The well-studied meld of cultures in Gaul gives historians a model against which to compare and contrast parallel developments of Romanization in other less-studied Roman provinces. ''Interpretatio romana'' offered Roman names for Gaulish deities such as the smith-god Gobannus; however, of the Celtic deities, only the horse-patroness Epona penetrated Romanized cultures beyond the confines of Gaul. The barbarian invasions began in the late 3rd century and forced upon Gallo-Roman culture fundamental changes in politics, economic underpinning and military organization. The Gothic settlement of 418 offered a double loyalty, as Western Roman authority disintegrated at Rome. The plight of the highly-Romanized governing clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland In The Roman Era
The territory of modern Switzerland was a part of the Roman Republic and Empire An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ... for a period of about six centuries, beginning with the step-by-step conquest of the area by Roman armies from the 2nd century BC and ending with the Fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. The mostly Celts, Celtic tribes of the area were subjugated by successive Roman campaigns aimed at control of the strategic routes from Italy across the Alps to the Rhine and into Gaul, most importantly by Julius Caesar's defeat of the largest tribal group, the Helvetii, in the Gallic Wars in 58 BC. Under the ''Pax Romana'', the area was smoothly integrated into the prospering Empire, and its population Romanization (cultural), assimilated into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |