|
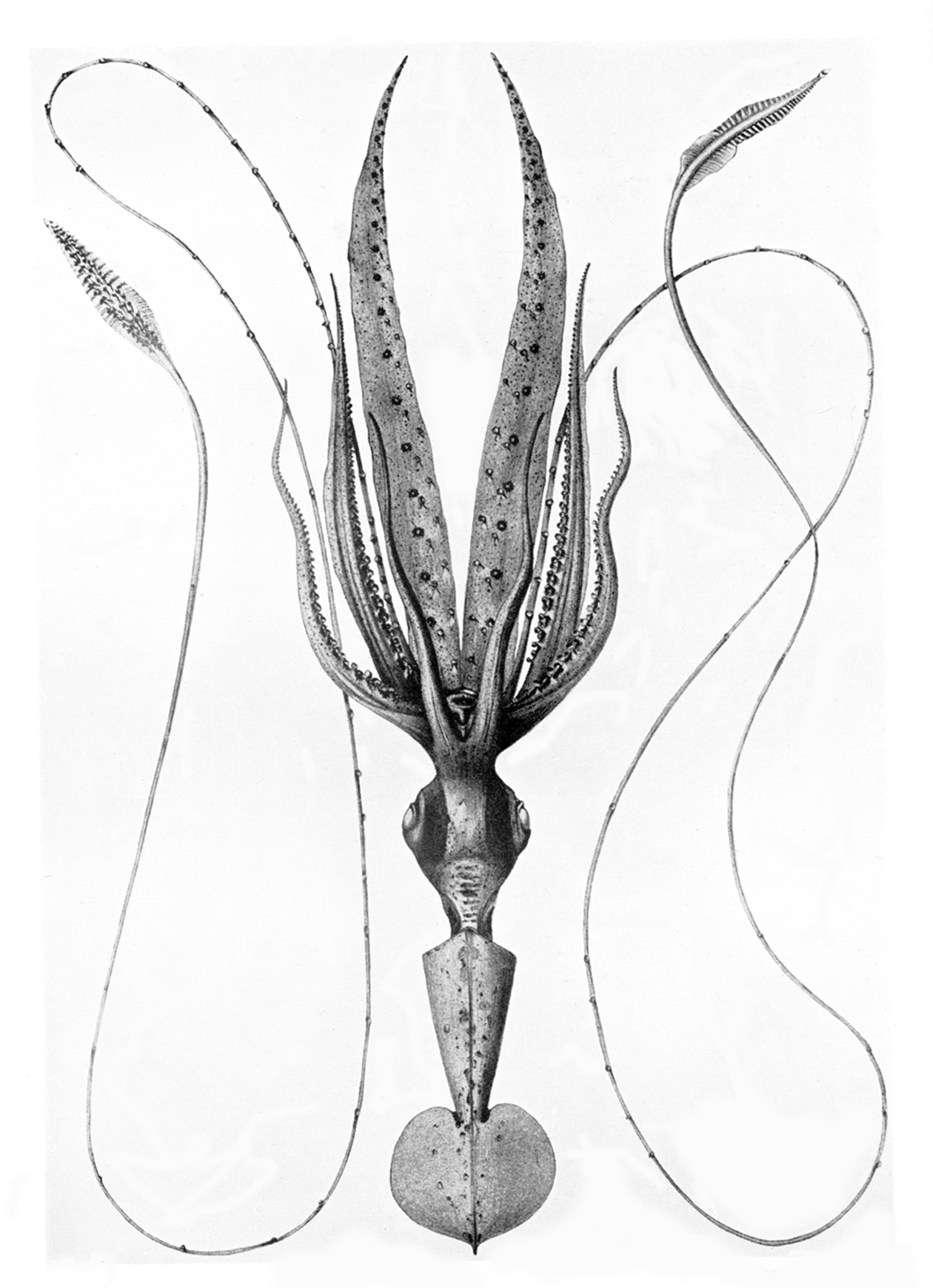
Chtenopteryx Chuni
''Chtenopteryx'' is a genus of small, muscular, midwater squid in the monotypic family Chtenopterygidae. Four species are presently recognized in the genus, but more are believed to exist. These squid occupy tropical to subtropical waters, probably at depths of between during the day and near-surface waters at night. The genus contains bioluminescent species. Species * '' Chtenopteryx canariensis'' Salcedo-Vargas & Guerrero-Kommritz, 2000 * '' Chtenopteryx chuni'' * Pfeffer, 1912 * '' Chtenopteryx sepioloides'' Rancurel, 1970 * ''Chtenopteryx sicula ''Chtenopteryx sicula'', also known as the comb-finned squid or toothed-fin squid, is a species of squid native to at least the Mediterranean Sea. It is characterised by several distinct morphological features: ocular photophores are present but ...'' (Vérany, 1851), comb-finned squid or toothed-fin squid The species listed above with an asterisk (*) is questionable and needs further study to determine if it is a valid speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chtenopteryx Sicula
''Chtenopteryx sicula'', also known as the comb-finned squid or toothed-fin squid, is a species of squid native to at least the Mediterranean Sea. It is characterised by several distinct morphological features: ocular photophores are present but visceral photophores are absent, cephalopod arm, arm suckers are arranged in at least 4 series distally, and club suckers are borne in more than 8 series. The type specimen was collected off Messina, Italy; the specific name ''sicula'' means "of Sicily". It is deposited at the Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle (Musée Barla) in Nice. Gallery [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Grimpe
Johann Georg Grimpe (16 February 1889, in Leipzig – 22 January 1936) was a German zoologist and malacologist. He studied zoology and comparative anatomy at the University of Leipzig Leipzig University (), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world's oldest universities and the second-oldest university (by consecutive years of existence) in Germany. The university was founded on 2 December 1409 by Frederick I, Electo ..., where under the influence of Carl Chun (1852–1914), he focused his energies towards research of marine fauna, especially cuttlefish. He conducted studies at marine biology stations in Naples, Villefranche-sur-Mer, Helgoland and Monaco. In 1912 he obtained his doctorate with a dissertation on the vascular system of Octopoda.Grimpe, Johann Georg @ NDB/ADB Deutsche Biographie After graduation, he worked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Appellöf
Jakob Johan Adolf Appellöf ( Garda on Gotland 2 November 1857 – Uppsala 5 January 1921) was a Swedish marine zoologist. Appellöf matriculated at Uppsala University in 1877, earned his PhD in 1886 and became a docent of zoology in 1887. In 1889 he received the position of conservator at the University Museum of Bergen. He was appointed professor of comparative anatomy in Uppsala in 1910. With a donation from the sawmill magnate Bünsow, Appellöf established the Klubban Biological Station of Uppsala University, a station for the study of marine biology located on the west coast of Sweden. In 1919 he was elected a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences and in 1920 of the Royal Society of Sciences in Uppsala. He made several important contributions to the knowledge of cephalopods. Partial bibliography *"Die schalen von Sepia, Spirula und Nautilus, Studien über ihren Bau und Wachsthum" (in: ''Kungl. Svenska vetenskapsakademiens handlingar'', SSN 0023-5377 N.F., 25:7) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baptiste Vérany
Chevalier Jean Baptiste Vérany (1800, in Nice – 1865) was a French pharmacist and naturalist who specialised in the study of cephalopods. In 1846, with Jean-Baptiste Barla (1817–1896), he founded the Muséum d'histoire naturelle de Nice. Vérany discovered and described many species. André Étienne d'Audebert de Férussac named ''Chiroteuthis veranyi'' for him. File:Chiroteuthis veranyi Haeckel.jpg, ''Chiroteuthis veranii'' File:Chromolithographie de Poulpe (Octopus Macropus) en Méditerranée.jpg, ''Callistoctopus macropus'' See also *:Taxa named by Jean Baptiste Vérany Works Partial list: * 1842 – Illustrations. ''Isis von Oken'', pp. 252–253. * 1844 – Description de deux genres nouveaux de mollusques nudibranches. ''Revue Zoologique par la Societe Cuvierienne'', pp. 302–303. * 1845 – Janus spinolae. ''Guerin Magazin de Zoologie'', series 2, 7:121-122, pl. 136. * 1846 – Descrizione di Genova e del Genovesato 1(2): ''Regno Animale Molluschi'', pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squid
A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called ''squid'' despite not strictly fitting these criteria). Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, Symmetry (biology)#Bilateral symmetry, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle (mollusc), mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar Ecological niche, role to teleost fish as open-water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open-water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's axial tilt; the width of the tropics (in latitude) is twice the tilt. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). Due to the overhead sun, the tropics receive the most solar energy over the course of the year, and consequently have the highest temperatures on the planet. Even when not directly overhead, the sun is still close to overhead throughout the year, therefore the tropics also have the lowest seasonal variation on the planet; "winter" and "summer" lose their temperature contrast. Instead, seasons are more commonly divided by precipitation variations than by temperature variations. The tropics maintain wide diversity of local climates, such as rain forests, monsoons, sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical zone#Temperate zones, temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° to 40° north and south. The horse latitudes lie within this range. Subtropical climates are often characterized by hot summers and mild winters with infrequent frost. Most subtropical climates fall into two basic types: humid subtropical climate, humid subtropical (Köppen climate classification: Cfa/Cwa), where rainfall is often concentrated in the warmest months, for example list of regions of China, Southeast China and the Southeastern United States, and Mediterranean climate, dry summer or Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification: Csa/Csb), where seasonal rainfall is concentrated in the cooler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chtenopteryx Canariensis
''Chtenopteryx'' is a genus of small, muscular, midwater squid in the monotypic family Chtenopterygidae. Four species are presently recognized in the genus, but more are believed to exist. These squid occupy tropical to subtropical waters, probably at depths of between during the day and near-surface waters at night. The genus contains bioluminescent species. Species * '' Chtenopteryx canariensis'' Salcedo-Vargas & Guerrero-Kommritz, 2000 * ''Chtenopteryx chuni'' * Pfeffer, 1912 * '' Chtenopteryx sepioloides'' Rancurel, 1970 * ''Chtenopteryx sicula ''Chtenopteryx sicula'', also known as the comb-finned squid or toothed-fin squid, is a species of squid native to at least the Mediterranean Sea. It is characterised by several distinct morphological features: ocular photophores are present but ...'' (Vérany, 1851), comb-finned squid or toothed-fin squid The species listed above with an asterisk (*) is questionable and needs further study to determine if it is a valid species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Johann Pfeffer
Georg Johann Pfeffer (1854–1931) was a German zoologist, primarily a malacologist, a scientist who studies mollusks. Pfeffer was born in Berlin. In 1887 he became curator of the , which was established in 1843 and destroyed during World War II. Pfeffer's published writings were mainly about cephalopods. The World Register of Marine Species database lists 133 marine Taxon, taxa named by Pfeffer When Pfeffer's name is listed as an authority for a taxon such as the land snail genus ''Lamellaxis'' Hermann Strebel, Strebel & Pfeffer, 1882, his name is ''not'' simply an orthography, orthographic error for the more commonly encountered molluscan authority Pfeiffer, i.e. Ludwig Karl Georg Pfeiffer, who lived 50 years earlier, from 1805 to 1877. Georg Johann Pfeffer also studied amphibians and reptiles, naming several Species description, new species. Two species of reptiles are named in his honor, ''Calamaria pfefferi'' and ''Trioceros, Trioceros pfefferi''.Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chtenopteryx Sepioloides
''Chtenopteryx'' is a genus of small, muscular, midwater squid in the monotypic family Chtenopterygidae. Four species are presently recognized in the genus, but more are believed to exist. These squid occupy tropical to subtropical waters, probably at depths of between during the day and near-surface waters at night. The genus contains bioluminescent species. Species * ''Chtenopteryx canariensis'' Salcedo-Vargas & Guerrero-Kommritz, 2000 * ''Chtenopteryx chuni'' * Pfeffer, 1912 * '' Chtenopteryx sepioloides'' Rancurel, 1970 * ''Chtenopteryx sicula ''Chtenopteryx sicula'', also known as the comb-finned squid or toothed-fin squid, is a species of squid native to at least the Mediterranean Sea. It is characterised by several distinct morphological features: ocular photophores are present but ...'' (Vérany, 1851), comb-finned squid or toothed-fin squid The species listed above with an asterisk (*) is questionable and needs further study to determine if it is a valid species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |