|
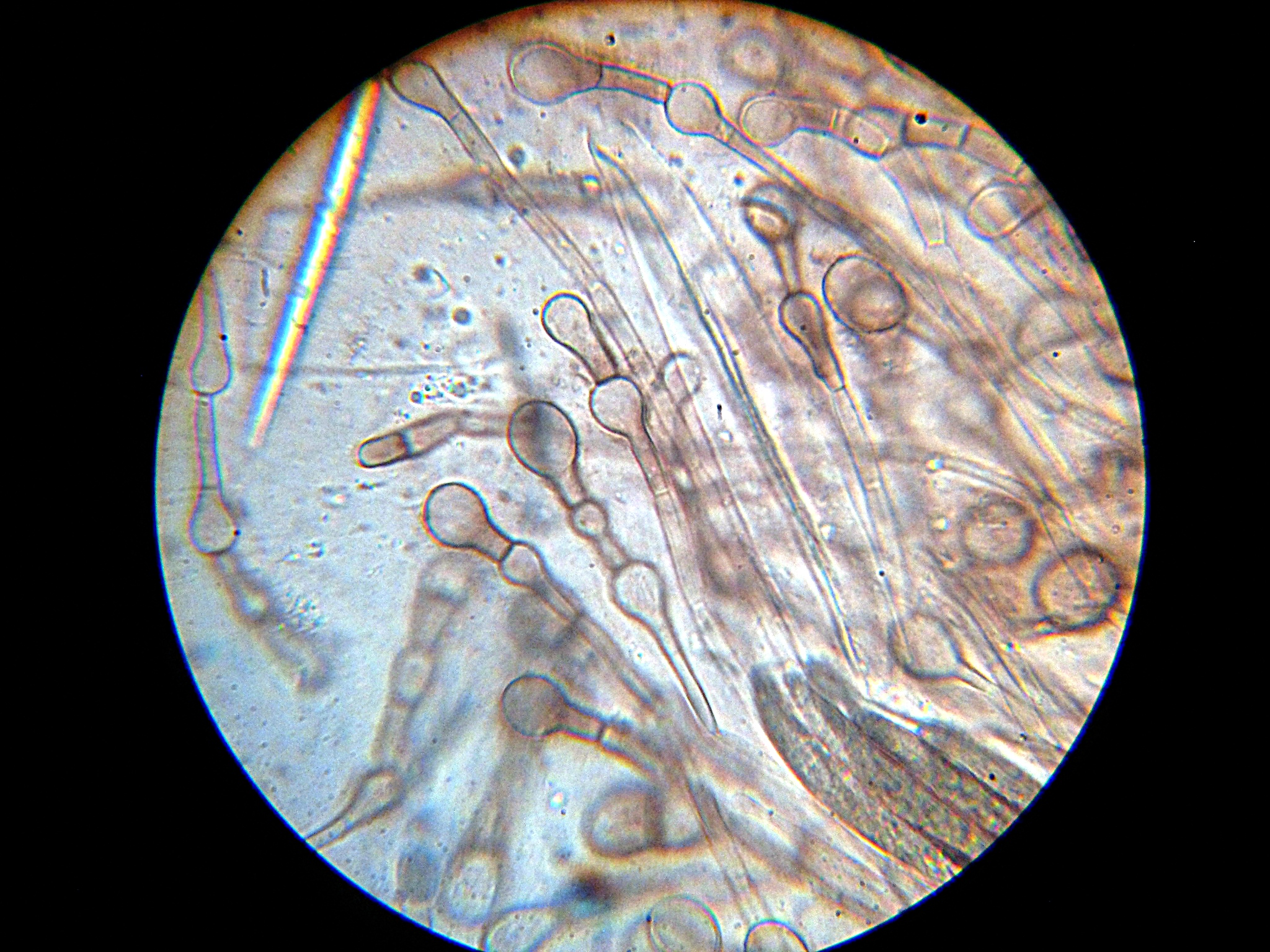
Chroodiscus Anomalus
''Chroodiscus'' is a genus of leaf-dwelling lichens in the family Graphidaceae. These lichens form thin, smooth crusts directly on living leaves and are characterized by distinctive star-shaped fruiting bodies that split into triangular segments, with centres ranging from grey to bright scarlet-red depending on their chemical composition. The genus is found throughout tropical regions worldwide, growing in the shaded understory of rainforests from lowland areas to mountain cloud forests, where they serve as sensitive indicators of undisturbed forest conditions. Taxonomy ''Chroodiscus'' was first introduced by the Swiss lichenologist Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1883 as a section of the genus '' Ocellularia''. In his original description, Müller characterized the section by its layer being phyllactideum (containing green algae arranged in a specific pattern) and its apothecia (fruiting bodies) being pale or variously coloured. He described the type species, '' Ocellulari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocellularia
''Ocellularia'' is a genus of lichens in the family Graphidaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Georg Friedrich Wilhelm Meyer Georg may refer to: * Georg (film), ''Georg'' (film), 1997 *Georg (musical), Estonian musical * Georg (given name) * Georg (surname) * , a Kriegsmarine coastal tanker * Spiders Georg, an Internet meme See also * George (other) {{di ... in 1825. Species *'' Ocellularia africana'' *'' Ocellularia allosporoides'' *'' Ocellularia andamanica'' *'' Ocellularia antillensis'' *'' Ocellularia aptrootiana'' *'' Ocellularia arecae'' *'' Ocellularia asiatica'' *'' Ocellularia auberianoides'' *'' Ocellularia auratipruinosa'' *'' Ocellularia aurulenta'' *'' Ocellularia bahiana'' *'' Ocellularia baileyi'' *'' Ocellularia balangoda'' *'' Ocellularia bicuspidata'' *'' Ocellularia bipindensis'' *'' Ocellularia bonplandiae'' *'' Ocellularia brunneospora'' *'' Ocellularia bullata'' *'' Ocellularia cameroonensis'' *'' Ocellularia cavata'' *'' Ocellularia chiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthraquinone
Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic hydrocarbon, aromatic organic compound with formula . Several isomers exist but these terms usually refer to 9,10-anthraquinone (IUPAC: 9,10-dioxoanthracene) wherein the ketone, keto groups are located on the central ring. It is used as a digester additive to Pulp (paper), wood pulp for papermaking. Many Anthraquinones, anthraquinone derivatives are generated by organisms or synthesised industrially for use as Anthraquinone dyes, dyes, pharmaceuticals, and Catalysis, catalysts. Anthraquinone is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly solubility, soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite. Synthesis There are several current industrial methods to produce 9,10-anthraquinone: # The oxidation of anthracene. Chromium(VI) is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloid (mycology)
In mycology a tissue (biology), tissue or feature is said to be amyloid if it has a positive amyloid reaction when subjected to a crude chemical test using iodine as an ingredient of either Melzer's reagent or Lugol's solution, producing a blue to blue-black staining. The term "amyloid" is derived from the Latin ''amyloideus'' ("starch-like"). It refers to the fact that starch gives a similar reaction, also called an amyloid reaction. The test can be on microscopic features, such as spore walls or hyphae, hyphal walls, or the apical apparatus or entire ascus wall of an ascus, or be a macroscopic reaction on tissue where a drop of the reagent is applied. Negative reactions, called inamyloid or nonamyloid, are for structures that remain pale yellow-brown or clear. A reaction producing a deep reddish to reddish-brown staining is either termed a dextrinoid reaction (pseudoamyloid is a synonym) or a hemiamyloid reaction. Melzer's reagent reactions Hemiamyloidity Hemiamyloidity in mycol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascospore
In fungi, an ascospore is the sexual spore formed inside an ascus—the sac-like cell that defines the division Ascomycota, the largest and most diverse Division (botany), division of fungi. After two parental cell nucleus, nuclei fuse, the ascus undergoes meiosis (halving of genetic material) followed by a mitosis (cell division), ordinarily producing eight genetically distinct haploid spores; most yeasts stop at four ascospores, whereas some moulds carry out extra post-meiotic divisions to yield dozens. Many asci build turgor, internal pressure and shoot their spores clear of the calm boundary layer, thin layer of still air enveloping the fruit body, whereas subterranean truffles depend on animals for biological dispersal, dispersal. Ontogeny, Development shapes both form and endurance of ascospores. A hook-shaped crozier aligns the paired nuclei; a double-biological membrane, membrane system then parcels each daughter nucleus, and successive wall layers of β-glucan, chitosan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thelotrema
''Thelotrema'' is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Graphidaceae, the family to which all taxa in the former Thelotremataceae now belong. Members of the genus ''Thelotrema'' are commonly called barnacle lichens. Description ''Thelotrema'' lichens have a thallus with colours ranging from white to yellow-grey or light olive. The texture of the thallus can be smooth, uneven, or , with the presence of either an surface or a loosely to rarely dense to cortex. The and medulla frequently contain clusters of calcium oxalate crystals. The apothecia can be immersed or sessile and appear rounded or angular-rounded. The is partially covered by remnants of the , while the margin can be entire, undulate, or fissured, displaying a distinct double margin. The is absent in this genus. The excipulum is paraplectenchymatous, , and varies in colour from colourless to brown. It has distinct , and the are unbranched. ''Thelotrema'' are transversely septate to , fusiform-ellips ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascus
An ascus (; : asci) is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores (or octad), produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one (e.g. '' Monosporascus cannonballus''), two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci (e.g. '' Tympanis'') with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some '' Cordyceps'', also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic (lacking a septum), and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm (the portion of cytoplasm not used in ascospore formation) that is surrounded by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyses
Paraphyses are erect sterile filament-like support structures occurring among the reproductive apparatuses of fungi, ferns, bryophytes and some thallophytes. The singular form of the word is paraphysis. In certain fungi, they are part of the fertile spore-bearing layer. More specifically, paraphyses are sterile filamentous hyphal end cells composing part of the hymenium of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota interspersed among either the asci or basidia respectively, and not sufficiently differentiated to be called cystidia A cystidium (: cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are o ..., which are specialized, swollen, often protruding cells. The tips of paraphyses may contain the pigments which colour the hymenium. In ferns and mosses, they are filament-like structures that are found on sporangi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in others some cells develop into sterile cells called cystidia ( basidiomycetes) or paraphyses ( ascomycetes). Cystidia are often important for microscopic identification. The subhymenium consists of the supportive hyphae from which the cells of the hymenium grow, beneath which is the hymenophoral trama, the hyphae that make up the mass of the hymenophore. The position of the hymenium is traditionally the first characteristic used in the classification and identification of mushrooms. Below are some examples of the diverse types which exist among the macroscopic Basidiomycota and Ascomycota. * In agarics, the hymenium is on the vertical faces of the gills. * In boletes and polypores, it is in a spongy mass of downward-pointing tubes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomata
An ascocarp, or ascoma (: ascomata), is the fruiting body (sporocarp (fungi), sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded ascus, asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallus
Thallus (: thalli), from Latinized Greek (), meaning "a green shoot" or "twig", is the vegetative tissue of some organisms in diverse groups such as algae, fungi, some liverworts, lichens, and the Myxogastria. A thallus usually names the entire body of a multicellular non-moving organism in which there is no organization of the tissues into organs. Many of these organisms were previously known as the thallophytes, a polyphyletic group of distantly related organisms. An organism or structure resembling a thallus is called thalloid, thalloidal, thalliform, thalline, or thallose. Even though thalli do not have organized and distinct parts ( leaves, roots, and stems) as do the vascular plants, they may have analogous structures that resemble their vascular "equivalents". The analogous structures have similar function or macroscopic structure, but different microscopic structure; for example, no thallus has vascular tissue. In exceptional cases such as the Lemnoideae, where th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocellularia Argillacea
''Ocellularia'' is a genus of lichens in the family Graphidaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Georg Friedrich Wilhelm Meyer Georg may refer to: * Georg (film), ''Georg'' (film), 1997 *Georg (musical), Estonian musical * Georg (given name) * Georg (surname) * , a Kriegsmarine coastal tanker * Spiders Georg, an Internet meme See also * George (other) {{di ... in 1825. Species *'' Ocellularia africana'' *'' Ocellularia allosporoides'' *'' Ocellularia andamanica'' *'' Ocellularia antillensis'' *'' Ocellularia aptrootiana'' *'' Ocellularia arecae'' *'' Ocellularia asiatica'' *'' Ocellularia auberianoides'' *'' Ocellularia auratipruinosa'' *'' Ocellularia aurulenta'' *'' Ocellularia bahiana'' *'' Ocellularia baileyi'' *'' Ocellularia balangoda'' *'' Ocellularia bicuspidata'' *'' Ocellularia bipindensis'' *'' Ocellularia bonplandiae'' *'' Ocellularia brunneospora'' *'' Ocellularia bullata'' *'' Ocellularia cameroonensis'' *'' Ocellularia cavata'' *'' Ocellularia chiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |