|
Christopher Saxton
Christopher Saxton (c. 1540 – c. 1610) was an English cartographer who produced the first county maps of England and Wales. Life and family Saxton was probably born in Sowood, Ossett in the parish of Dewsbury, in the West Riding of Yorkshire in either 1542 or 1544. His family subsequently moved to the hamlet of Dunningley near Tingley in the parish of Woodkirk where the Saxton name is recorded in 1567. It is speculated that Saxton may have attended the predecessor school to Queen Elizabeth Grammar School, Wakefield and also speculated that he was a student at Cambridge University but neither is corroborated. It is most likely that John Rudd, the vicar of Dewsbury and Thornhill, a keen cartographer passed his skills to Saxton. Saxton married and had three children. Robert, born in 1585, was his father's assistant in 1601 and drew a map of Snapethorpe in Wakefield when it was surveyed by his father. Robert was commissioned to survey Sandal Magna in 1607. Christopher Saxto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gough Map
The Gough Map or Bodleian Map is a Late Medieval map of the island of Great Britain. Its precise dates of production and authorship are unknown. It is named after Richard Gough, who bequeathed the map to the Bodleian Library in Oxford 1809. He acquired the map from the estate of the antiquarian Thomas "Honest Tom" Martin in 1774. Numerous copies of it have been made, with an interactive online version created at Queen's University, Belfast. It measures 115 by 56 cm. Date There has been no authoritative date for the map's production. Thomas Martin believed it dated from the reign of Edward III, while 19th-century scholarship suggested a date of c. 1300, during the reign of Edward I. More recently, the map was believed to have been made within an eleven-year window, based on historical changes of place names and sizes. The earliest given date is deduced by the depiction of a city wall around Coventry, which was first constructed in 1355. The latter date is usually given a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chetham's Library
Chetham's Library in Manchester, England, is the oldest free public reference library in the English-speaking world.Nicholls (2004), p. 20. Chetham's Hospital, which contains both the library and Chetham's School of Music, was established in 1653 under the will of Humphrey Chetham (1580–1653), for the education of "the sons of honest, industrious and painful parents", and a library for the use of scholars. The library has been in continuous use since 1653. It operates as an independent charity. The library holds more than 100,000 volumes of printed books, of which 60,000 were published before 1851 including a copy of the Nuremberg Chronicle annotated by Thomas Gudlawe. Collections include 16th- and 17th-century printed works, periodicals and journals, local history sources, broadsides and ephemera. In addition to print materials, the library holds a collection of over 1,000 manuscripts, including 41 medieval texts. Chetham's Library is an Accredited Museum under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Cathedral
Manchester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral and Collegiate Church of St Mary, St Denys and St George, in Manchester, England, is the mother church of the Anglican Diocese of Manchester, seat of the Bishop of Manchester and the city's parish church. It is on Victoria Street in Manchester city centre and is a grade I listed building. The former parish church was rebuilt in the Perpendicular Gothic style in the years following the foundation of the collegiate body in 1421. Then at the end of the 15th century, James Stanley (bishop), James Stanley II (warden 1485–1506 and later Bishop of Ely 1506–1515) was responsible for rebuilding the nave and collegiate choir with high clerestory windows; also commissioning the late-medieval wooden internal furnishings, including the pulpitum, choir stalls and the nave roof supported by angels with gilded instruments. The collegiate church became the cathedral of the new Anglican Diocese of Manchester, Diocese of Manchester in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dee
John Dee (13 July 1527 – 1608 or 1609) was an English mathematician, astronomer, teacher, astrologer, occultist, and alchemist. He was the court astronomer for, and advisor to, Elizabeth I, and spent much of his time on alchemy, divination, and Hermetic philosophy. As an antiquarian, he had one of the largest libraries in England at the time. As a political advisor, he advocated the foundation of English colonies in the New World to form a "British Empire", a term he is credited with coining. Dee eventually left Elizabeth's service and went on a quest for additional knowledge in the deeper realms of the occult and supernatural. He aligned himself with several individuals who may have been charlatans, travelled through Europe, and was accused of spying for the English Crown. Upon his return to England, he found his home and library vandalised. He eventually returned to the Queen's service, but was turned away when she was succeeded by James I. He died in poverty in London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelis De Hooghe
Cornelis de Hooghe (1541, in The Hague – 1583, in The Hague) was a 16th-century engraver and mapmaker from the Northern Netherlands. Family background Cornelis de Hooghe, born in 1541 in The Hague (the Netherlands) as a bastard of Charles V, after this emperor's visit to the town in the summer of 1540. As De Hooghe's later friends and co-conspirators were to be found in the upper-class Delft families, it can safely be assumed that his mother was one of the daughters of Cornelis Arendsz. van der Hooch and Petronella van Persijn, wealthy and influential locals of both The Hague and Delft with close ties to the Habsburg government. This family also used names like Verhooch, De Hoogh or De Hooghe and owned a farm in the vicinity of Delft, bearing the name De Hooght. The exaggerated mention in his “Hollandia-map” (1565) of the rather unimportant Persijn manor (Huys te Persijn), that was situated just north of The Hague, underlines his descent from this family. Cartographer career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remigius Hogenberg
Remigius Hogenberg (c. 1536, Mechlin – c. 1588, London) was a Dutch engraver who arrived in England c. 1573. He most likely resided in the parish of St Giles Cripplegate, this parish and St Andrew's Holborn being the main locations for engravers. Parish records list Hogenberg as "Highill", an English approximation of his surname. The parish records also indicate Hogenberg had seven children, though his marriage is not recorded. Hogenberg is recorded as having been buried on 16 March 1588 (old style, 1589 new style). Hogenberg is known for his portrait engravings of the Archbishop of Canterbury The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the Primus inter pares, ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the bishop of the diocese of Canterbury. The first archbishop ..., a genealogy of the English monarchs, and his Maps of the Counties of England. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Hogenberg, Remigius Dutch e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustine Ryther
Augustine Ryther (died 1593) was an English engraver and translator. He engraved some of Christopher Saxton's maps of English counties. He also made scientific instruments. Works Ryther was associated with engraving maps of the counties of England published by Saxton in 1579. His name appears as the engraver of the maps of County Durham and Westmoreland (1576), Gloucester and York (1577), and that of the whole of England, signed ‘Augustinus Ryther Anglus Sculpsit Ano Dñi 1579.’ His name appears in 1588 with those of Jodocus Hondius, Theodore de Bry, and others, among the engravers of the charts to ''The Mariner's Mirrour'' by Sir Anthony Ashley. In 1590 Ryther published a translation of Petruccio Ubaldini's ''Expeditionis Hispaniorum in Angliam vera Descriptio''. The book was printed by A. Hatfield. This work is dedicated by Ryther to Lord Howard of Effingham, and in the dedication he apologises for the two years' delay in its publication. The plates consist of a title and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Drayton
Michael Drayton ( – ) was an English poet who came to prominence in the Elizabethan era, continuing to write through the reign of James I and into the reign of Charles I. Many of his works consisted of historical poetry. He was also the first English-language author to write odes in the style of Horace. He died on 23 December 1631 in London. Early life Drayton was born at Hartshill, near Nuneaton, Warwickshire, England, in early 1563. Not much is documented about his early life, except that in 1580 he was in the service of Thomas Goodere of Collingham, Nottinghamshire. In his early years, it is believed that Drayton entered the service of Sir Henry Goodere, who provided for Drayton's education. Nineteenth- and 20th-century scholars, on the basis of scattered allusions in his poems and dedications, suggested that Drayton might have studied at the University of Oxford, and been intimate with the Polesworth branch of the Goodere family. More recent work has cast doubt on tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Speed
John Speed (1551 or 1552 – 28 July 1629) was an English cartographer, chronologer and historian of Cheshire origins.; superseding . The son of a citizen and Merchant Taylor in London,"Life of John Speed", ''The Hibernian Magazine, Or, Compendium of Entertaining Knowledge'', July 1782p. 348(Google). he rose from his family occupation to accept the task of drawing together and revising the histories, topographies and maps of the Kingdoms of Great Britain as an exposition of the union of their monarchies in the person of King James I and VI. He accomplished this with remarkable success, with the support and assistance of the leading antiquarian scholars of his generation. He drew upon and improved the shire maps of Christopher Saxton, John Norden and others, being the first to incorporate the hundred-boundaries into them, and he was the surveyor and originator of many of the town or city plans inset within them.A. Baynton-Williams, 'John Speed': Relocated since 17 Sept 2012 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred (county Division)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include '' wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' ( Nynorsk Norwegian), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' ( North Frisian), ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), and '' cantref'' (Welsh). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a particularly large townland (most townlands are not divided into hundreds). Etymology The origin of the division of counties into hundreds is described by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') as "exceedingly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
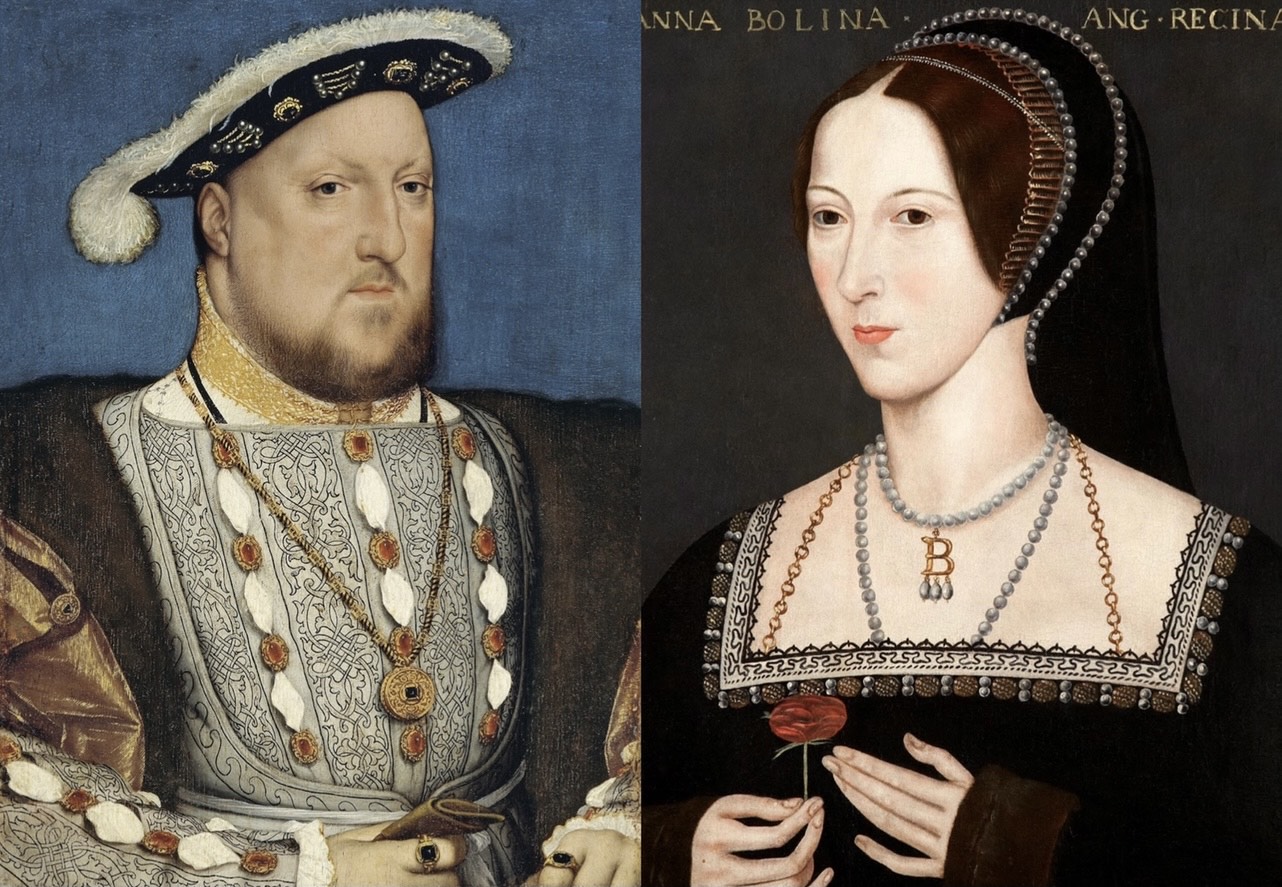
Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudor. Her eventful reign, and its effect on history and culture, gave name to the Elizabethan era. Elizabeth was the only surviving child of Henry VIII and his second wife, Anne Boleyn. When Elizabeth was two years old, her parents' marriage was annulled, her mother was executed, and Elizabeth was declared royal bastard, illegitimate. Henry Third Succession Act 1543, restored her to the line of succession when she was 10. After Henry's death in 1547, Elizabeth's younger half-brother Edward VI ruled until his own death in 1553, bequeathing the crown to a Protestant cousin, Lady Jane Grey, and ignoring the claims of his two half-sisters, Mary I of England, Mary and Elizabeth, despite statutes to the contrary. Edward's will was quickly set aside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |