|
Christen Sørensen Longomontanus
Christen Sørensen Longomontanus (also as Longberg or Severin) (4 October 1562 – 8 October 1647) was a Danish astronomer. The name Longomontanus was a Latinized form of the name of the village of Lomborg, Jutland, Denmark, where he was born. His father, a laborer called Søren, or Severin, died when Christen was eight years old. An uncle took charge of the child, and had him educated at Lemvig; but after three years sent him back to his mother, who needed his help to work the fields. She agreed that he could study during the winter months with the clergyman of the parish; this arrangement continued until 1577, when the ill-will of some of his relatives and his own desire for knowledge caused him to run away to Viborg. There he attended the grammar school, working as a labourer to pay his expenses, and in 1588 went to Copenhagen with a high reputation for learning and ability. Engaged by Tycho Brahe in 1589 as his assistant in his great astronomical observatory of Uraniborg, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutland
Jutland (; , ''Jyske Halvø'' or ''Cimbriske Halvø''; , ''Kimbrische Halbinsel'' or ''Jütische Halbinsel'') is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of Denmark and part of northern Germany (Schleswig-Holstein). It stretches from the Grenen spit in the north to the confluence of the Elbe and the Sude (river), Sude in the southeast. The historic southern border river of Jutland as a cultural-geographical region, which historically also included Southern Schleswig, is the Eider (river), Eider. The peninsula, on the other hand, also comprises areas south of the Eider (river), Eider: Holstein, the Saxe-Lauenburg, former duchy of Lauenburg (district), Lauenburg, and most of Hamburg and Lübeck. Jutland's geography is flat, with comparatively steep hills in the east and a barely noticeable ridge running through the center. West Jutland is characterised by open lands, heaths, plains, and peat bogs, while East Jutland is more fertile with lakes and lush fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath who formulated a mathematical model, model of Celestial spheres#Renaissance, the universe that placed heliocentrism, the Sun rather than Earth at its center. Copernicus likely developed his model independently of Aristarchus of Samos, an List of ancient Greek astronomers, ancient Greek astronomer who had formulated such a model some eighteen centuries earlier. The publication of Copernicus' model in his book ' (''On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres''), just before his death in 1543, was a major event in the history of science, triggering the Copernican Revolution and making a pioneering contribution to the Scientific Revolution. Copernicus was born and died in Royal Prussia, a semiautonomous and multilingual region created within the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland from lands regained from the Teutonic Order after the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466), Thirteen Years' War. A Poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the term: the terrestrial planets Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion (astrophysics), accretion. The word ''planet'' comes from the Greek () . In Classical antiquity, antiquity, this word referred to the Sun, Moon, and five points of light visible to the naked eye that moved across the background of the stars—namely, Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoheliocentric
The Tychonic system (or Tychonian system) is a model of the universe published by Tycho Brahe in 1588, which combines what he saw as the mathematical benefits of the Copernican system with the philosophical and "physical" benefits of the Ptolemaic system. The model may have been inspired by Valentin Naboth and Paul Wittich, a Silesian mathematician and astronomer. A similar cosmological model was independently proposed in the Hindu astronomical treatise ''Tantrasamgraha'' () by Nilakantha Somayaji of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. It is conceptually a geocentric model, or more precisely geoheliocentric: the Earth is at the centre of the universe, the Sun and Moon and the stars revolve around the Earth, and the other five planets revolve around the Sun. At the same time, the motions of the planets are mathematically equivalent to the motions in Copernicus' heliocentric system under a simple coordinate transformation, so that, as long as no force law is postula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig (; ; ; ; ; ) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany. The region is also called Sleswick in English. Unlike Holstein and Lauenburg, Schleswig was never a part of the German Confederation. Schleswig was instead a fief of Denmark, and its inhabitants spoke Danish, German, and North Frisian. Both Danish and German National Liberals wanted Schleswig to be part of a Danish or German national state in the 19th century. A German uprising in March 1848 caused the First Schleswig War which ended in 1852. The Second Schleswig War (1864) ended with the three duchies being governed jointly by Austria and Prussia. In 1866, they became a part of Prussia. Name and naming dispute In the 19t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunden
Lunden is a municipality in the district of Dithmarschen, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated on the Eider river, about 16 km north of Heide. It is part of the '' Amt Kirchspielslandgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") of Eider. The first written mention of Lunden is by the Archbishop of Bremen and dates back as early as 1140. The place name probably comes from the Danish "Lunn" (island-like survey) or "Lund"(little forest). In 1513, a Franciscan Friary was constructed in Lunden, fulfilling a vow made by the Dithmarscher soldiers at the Battle of Hemmingstedt in 1500 to donate a monastery in honor of Mary of Nazareth if they won the battle. On 27 February 1529 Lunden was granted a town charter by the National Assembly of Dithmarschen. In 1559, after the peasants' republic in Dithmarschen was defeated by Denmark, this right was lost. From 1806 to 1816, the famous Lutheran theologian Claus Harms served as pastor of Lunden. Lunden is twinned with the town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canonry
Canon () is a Christian title usually used to refer to a member of certain bodies in subject to an canon law, ecclesiastical rule. Originally, a canon was a cleric living with others in a clergy house or, later, in one of the houses within the precinct of or close to a cathedral or other major church and conducting his life according to the customary discipline or rules of the church. This way of life grew common (and is first documented) in the 8th century AD. In the 11th century, some churches required clergy thus living together to adopt the rule first proposed by Augustine of Hippo, Saint Augustine that they renounce private wealth. Those who embraced this change were known as Augustinians or Canons Regular, whilst those who did not were known as Secular clergy, secular canons. Secular canons Latin Church In the Latin Church, canons are the members of a chapter (religion), chapter, that is a body of senior clergy overseeing either a cathedral (a cathedral chapter) or a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian IV Of Denmark
Christian IV (12 April 1577 – 28 February 1648) was King of Denmark and King of Norway, Norway and List of rulers of Schleswig-Holstein, Duke of Holstein and Schleswig from 1588 until his death in 1648. His reign of 59 years and 330 days is the longest in Scandinavian history. A member of the House of Oldenburg, Christian began his personal rule of Denmark-Norway in 1596 at the age of 19. He is remembered as one of the most popular, ambitious, and proactive Danish-Norwegian kings, having initiated many reforms and projects. Christian IV obtained for his kingdoms a level of stability and wealth that was virtually unmatched elsewhere in Europe. He engaged Denmark-Norway in numerous wars, most notably the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), which devastated much of Germany, undermined the Danish economy, and cost Denmark-Norway some of its conquered territories. He rebuilt and renamed the Norwegian capital Oslo as ''Christiania'' after himself, a name used until 1925. Early years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
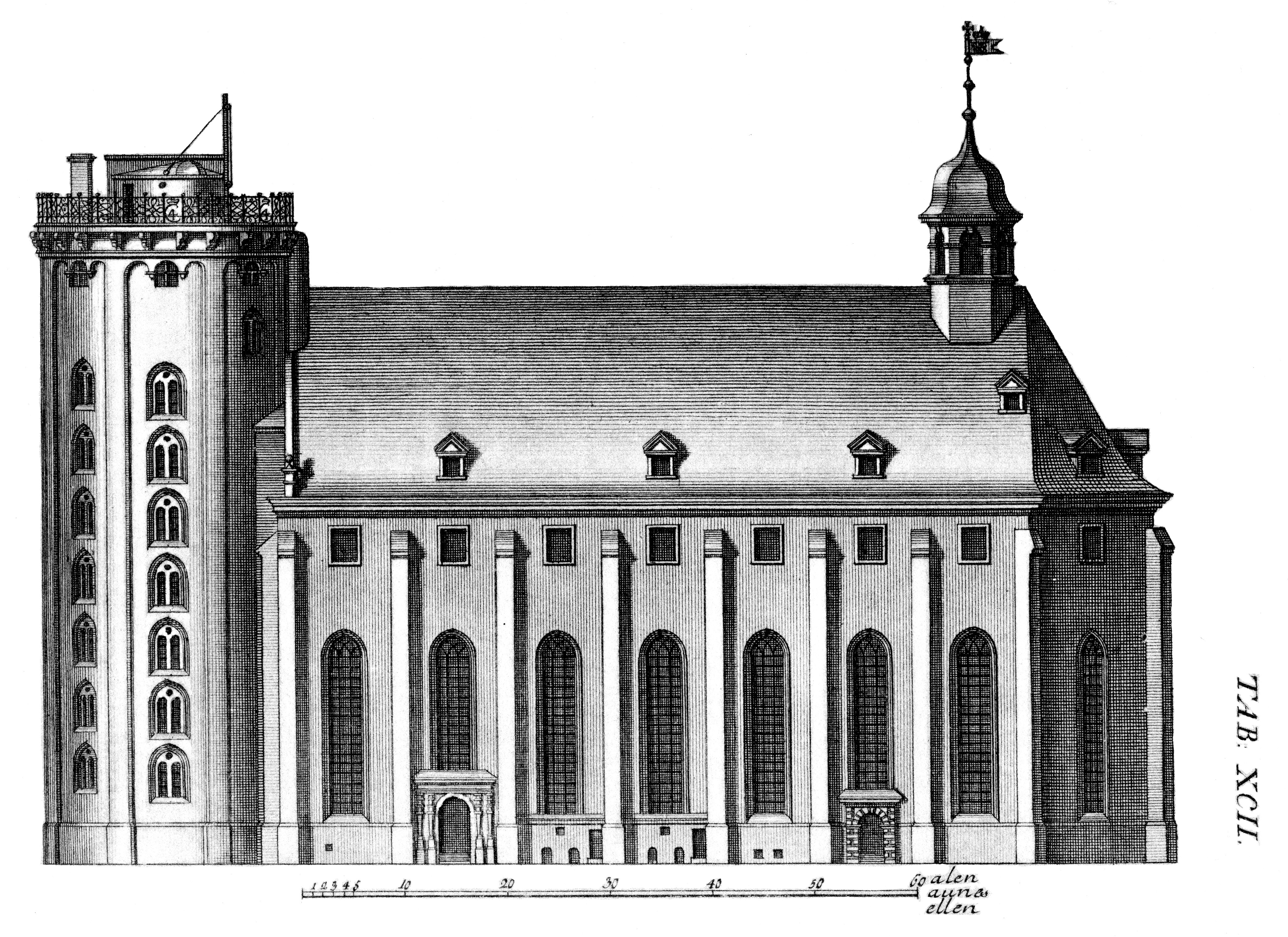
Rundetårn
The Round Tower () is a 17th-century tower in Copenhagen, Denmark, one of the many architectural projects of Christian IV. Built as an astronomical observatory, it is noted for its equestrian staircase, a 7.5-turn helical corridor leading to the platform at the top (34.8 meters above ground), and its views over Copenhagen. The tower is part of the ''Trinitatis Complex'' which also includes a chapel, the Trinitatis Church, and an academic library, which were the first facilities of the Copenhagen University Library founded in 1482. History Background Astronomy had grown in importance in 17th-century Europe. Countries had begun competing with each other in establishing colonies, creating a need for accurate navigation across the oceans. Many national observatories were therefore established, the first in 1632 at Leiden in the Dutch Republic. Only five years later the Round Tower Observatory, first referred to as STELLÆBURGI REGII HAUNIENSIS, would follow. Planning and prep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Pell (mathematician)
John Pell (1 March 1611 – 12 December 1685) was an English mathematician and political agent abroad. He was made Royal Chair of Mathematics at Orange College by the Prince of Orange, and was under the patronage of Sir Charles Cavendish. He was also a compeer and correspondent of René Descartes and Thomas Hobbes. Early life He was born at Southwick in West Sussex, England. His father, also named John Pell, was from Southwick, and his mother was Mary Holland, from Halden in Kent. The second of two sons, Pell's older brother was Thomas Pell. By the time he was six, they were orphans, their father dying in 1616 and their mother the following year. John Pell the elder had a fine library, which proved valuable to the young Pell as he grew up. He was educated at Steyning Grammar School and entered Trinity College, Cambridge, at the age of 13. During his university career he became an accomplished linguist; even before taking a B.A. degree in 1629, he corresponded with Henry B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squaring The Circle
Squaring the circle is a problem in geometry first proposed in Greek mathematics. It is the challenge of constructing a square (geometry), square with the area of a circle, area of a given circle by using only a finite number of steps with a compass and straightedge. The difficulty of the problem raised the question of whether specified axioms of Euclidean geometry concerning the existence of Line (geometry), lines and circles implied the existence of such a square. In 1882, the task was proven to be impossible, as a consequence of the Lindemann–Weierstrass theorem, which proves that pi (\pi) is a transcendental number. That is, \pi is not the zero of a function, root of any polynomial with Rational number, rational coefficients. It had been known for decades that the construction would be impossible if \pi were transcendental, but that fact was not proven until 1882. Approximate constructions with any given non-perfect accuracy exist, and many such constructions have been f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding the nucleus, and sometimes a Comet tail, tail of gas and dust gas blown out from the coma. These phenomena are due to the effects of solar radiation and the outstreaming solar wind plasma acting upon the nucleus of the comet. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. The coma may be up to 15 times Earth's diameter, while the tail may stretch beyond one astronomical unit. If sufficiently close and bright, a comet may be seen from Earth without the aid of a telescope and can Subtended angle, subtend an arc of up to 30° (60 Moons) across the sky. Comets have been observed and recorded since ancient times by many cultures and religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |