|
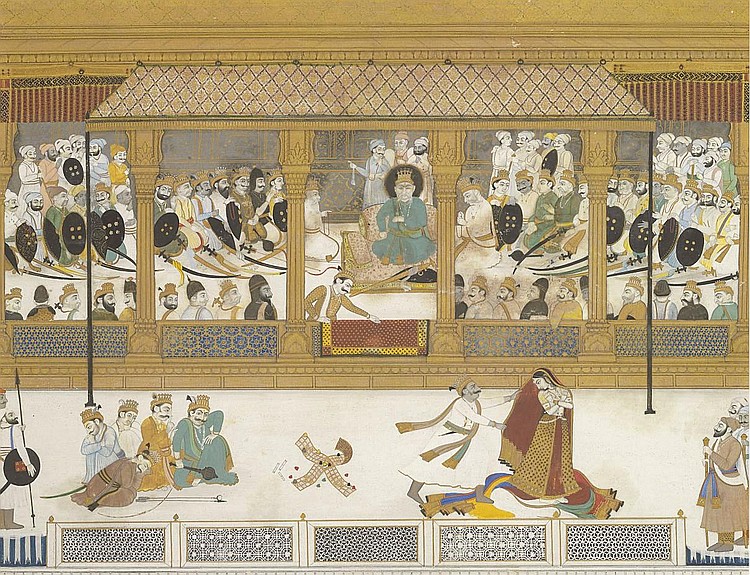
Chitrāngadā
Chitrangada () is a character in the ancient Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. She is introduced as the princess of region named Manipura or Manalura, and the only heir of King Chitravahana. During his exile, the Pandava prince Arjuna fell in love with her and she became his third wife. She had a son named Babhruvahana with him. The story of Chitrāngadā was adapted by Indian writer, Rabindranath Tagore in his play, Chitra. Early life Manipura was a kingdom in India during the ''Mahabharata'' period. It was ruled by a king named Chitravahana. He had a daughter named Chitrāngadā, whom he named after the Madhulika flower. For multiple generations, the dynasty did not have more than one heir. Since Chitravahana did not have any other heir, he trained Chitrāngadā in warfare and rule. Chitrāngadā was well-versed in warfare and acquired the skills to protect the people of her land. Marriage with Arjuna It is not described in ''Mahabharata'' as to how Arjuna, the Pandava prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characters In The Mahabharata
The '' Mahabharata'' is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India composed by Veda Vyasa. At its heart lies the epic struggle between the Pandavas and the Kauravas. The central characters include the five Pandava brothers— Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—along with their wife Draupadi. On the opposing side, the hundred Kaurava brothers are led by the elder brother, Duryodhana. However, the ''Mahabharata'' is richly populated with other notable figures including Krishna, Bhishma, Drona, Karna, Kunti, Dushasana, Kripa, Dhritrashtra, Gandhari, Shakuni, Ashwatthama, Balarama, Subhadra, Vyasa, Abhimanyu, Pandu, Satyavati and Amba. The ''Mahabharata'' manuscripts exist in numerous versions, wherein the specifics and details of major characters and episodes vary, often significantly. Except for the sections containing the ''Bhagavad Gita'' which is remarkably consistent between the numerous manuscripts, the rest of the epic exists in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulupi
Ulupi (), also known as Uluchi and Ulupika, is a Naga princess mentioned in the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. Ulupi is the daughter of the king Kauravya, and is the second wife of Arjuna. She also finds a mention in the ''Vishnu Purana'' and the ''Bhagavata Purana''. Ulupi is said to have met and married Arjuna when he was in exile, and with whom she bore his son Iravan. She played a major part in the upbringing of Babruvahana, Arjuna's son with Chitrangada. She is also credited with redeeming Arjuna from the curse of the Vasus by restoring his life after he was slain in a battle by Babruvahana. Etymology and form Little is said about Ulupi in the ''Mahabharata''. Ulupi is known by numerous names in the ''Mahabharata''—Bhujagātmajā, Bhujagendrakanyakā, Bhujagottamā Kauravī, Kauravyaduhitā, Kauravyakulanandinī, Pannaganandinī, Pannagasutā, Pannagātmajā, Pannageśvarakanyā, Pannagī, and Uragātmajā. Ulupi is described as a mythical form of a ''Nāgakanyā'' (N� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitra (play)
''Chitra'' is a one-act play written by Rabindranath Tagore, first published in English in 1913 by the India Society of London. The play adapts part of the story from the ''Mahabharata'' and centers upon the character of Chitrangada, a female warrior who tries to attract the attention of Arjuna. ''Chitra'' has been performed worldwide and has been adapted into several different formats, such as dance. Synopsis The play adapts the story of Chitrāngadā and Arjuna from the Mahabharata and begins with Chitra beginning a conversation with Madana, the god of love, and Vasanta, the god of springtime and eternal youth. They ask Chitra who she is and what is bothering her, to which she replies that she is the daughter of the king of Manipur and has been raised like a boy as her father had no male heir. She is a great warrior and hero despite being born as a woman, but has never had the chance to truly live as a woman or learn how to use "feminine wiles". Chitra explains that she had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
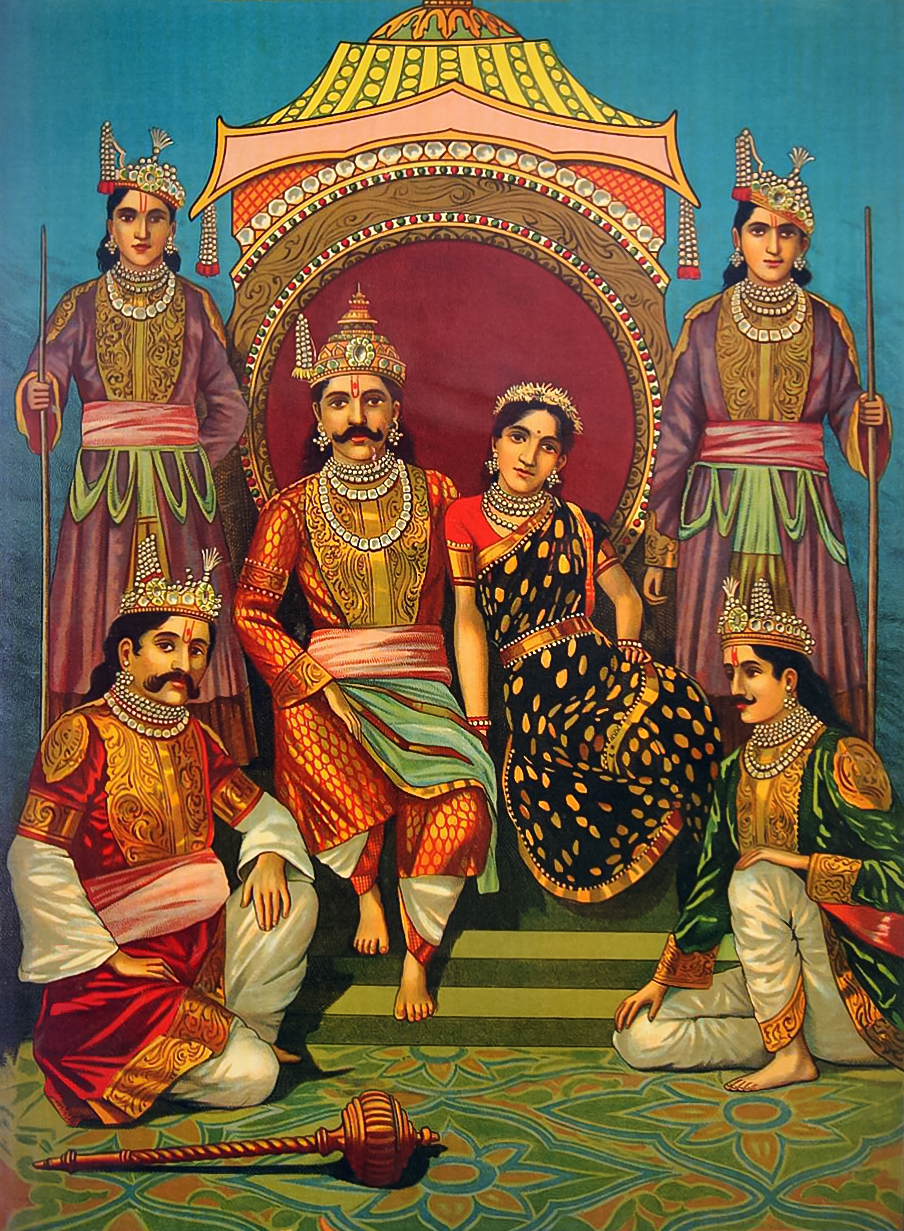
Babruvahana
In the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata'', Babruvahana () is the son of Arjuna, a Pandava prince, and Chitrangada, the princess of Manipur (Mahabharat). Babruvahana was adopted as the heir of Manipura by his maternal grandfather, Chitravahana, and later reigned at the kingdom. Legend Birth Manipura was a kingdom in Eastern India, which was ruled by a king named Chitravahana. He had a daughter named Chitrangada and for multiple generations, for the dynasty it was the first time they had only a daughter and have not an heir. Since Chitravahana did not have any other heir, he trained Chitrangada in warfare and rule. Chitrangada was well-versed in warfare and acquired the skills to protect the people of her land. The account is described in Rabindranath Tagore's play ''Chitra'', where Tagore depicts Chitrangada as a warrior dressed in male clothes. Arjuna fell in love with her on account of her honesty and courage. They had a son named Babruvahana, whom Chitrangada reared up after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arjuna
Arjuna (, , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, [ɐɾd͡ʒun̪ə]) is one of the central characters of the ancient Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is the third of the five Pandava brothers, and is widely regarded as the most important and renowned among them. He is the son of Indra, the king of the Deva (Hinduism), gods, and Kunti, wife of King Pandu of Kuru kingdom, Kuru dynasty—making him a Demigod, divine-born hero. Arjuna is famed for his extraordinary prowess in archery and mastery over Astra (weapon), celestial weapons. Throughout the epic, Arjuna sustains a close friendship with his maternal cousin, Krishna, who serves as his spiritual guide. Arjuna is celebrated for numerous heroic exploits throughout the epic. From childhood, he emerges as an excellent pupil, studying under the warrior-sage Drona. In his youth, Arjuna wins the hand of Draupadi, the princess of the Pañcāla, Panchalas, by excelling in a formidable archery competition. Soon after, he goes on a journey during a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manipura (Mahabharata)
Manipura (), known as Manalura in the Southern and Critical Editions, is the capital city of a kingdom mentioned in the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. According to the epic, it was located near a sea-shore, the Mahendra Mountains and the Kalinga (Mahabharata), Kalinga Kingdom. Arjuna—one of the five Pandava brothers—visited Manipura and married Chitrāngadā, Chitrangada, the princess of the region. They had a son named Babruvahana who later ruled it. Manipur shares its name with a Manipur, modern-day state of India, located in the North East India, North-Eastern part of the country. Some rulers of the state had claimed themselves to be the descendants of Arjuna. Some past scholars support the identification of the state with the city, others oppose this idea. However, the identification of the Manipura kingdom in the Mahabharata with the modern-day Indian state of Manipur is widely regarded by scholars as historically unsubstantiated. Geographic descriptions in the epic place th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subhadra
Subhadra (, ) is a character in the ancient Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. She is a princess from the Yadava clan and the sister of Krishna and Balarama. Subhadra married Arjuna, one of the Pandava brothers and had a son named Abhimanyu. Subhadra is part of the triad of deities worshipped at the Jagannath Temple at Puri, along with Krishna (as Jagannatha) and Balarama (or Balabhadra). One of the chariots in the annual Ratha Yatra is dedicated to her. Etymology and other names The Sanskrit name ''Subhadrā'' is made up of two words: ''su'' and ''bhadrā''. The prefix ''su'' denotes goodness, while ''bhadrā'' is translated as fortune or excellence. The name means 'glorious', 'fortunate', 'splendid', or 'auspicious'. Subhadra is referred to as ''Bhadrā'' (भद्रा), literally 'fortunate', when she is introduced to Arjuna in the ''Mahabharata''. According to the appendix of the ''Mahabharata'', the '' Harivamsa'', her birth name was ''Citrā'' (चित्रा) whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandava
The Pandavas (Sanskrit: पाण्डव, aɳɖɐʋᵊ IAST: Pāṇḍava) is a group name referring to the five legendary brothers, Yudhishtira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva, who are central figures of the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. They are acknowledged as the sons of Pandu, the King of Kuru, but were fathered by different '' Devas'' (gods) due to Pandu's cursed inability to naturally sire children. In the epic, the Pandavas married Draupadi, the princess of Panchala, and founded the city of Indraprastha after the Kuru Kingdom was split to avoid succession disputes. After the split, the other part of the kingdom was ruled by their cousins, the Kauravas. However, the Pandavas lost their kingdom to Duryodhana (eldest and king of the Kauravas) when Yudhishthira gambled it away during a game of dice. The bet Yudhishtira agreed to was that the Pandavas would hand the kingdom over to the Kauravas and go into exile for 12 followed by an year in hiding. After this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
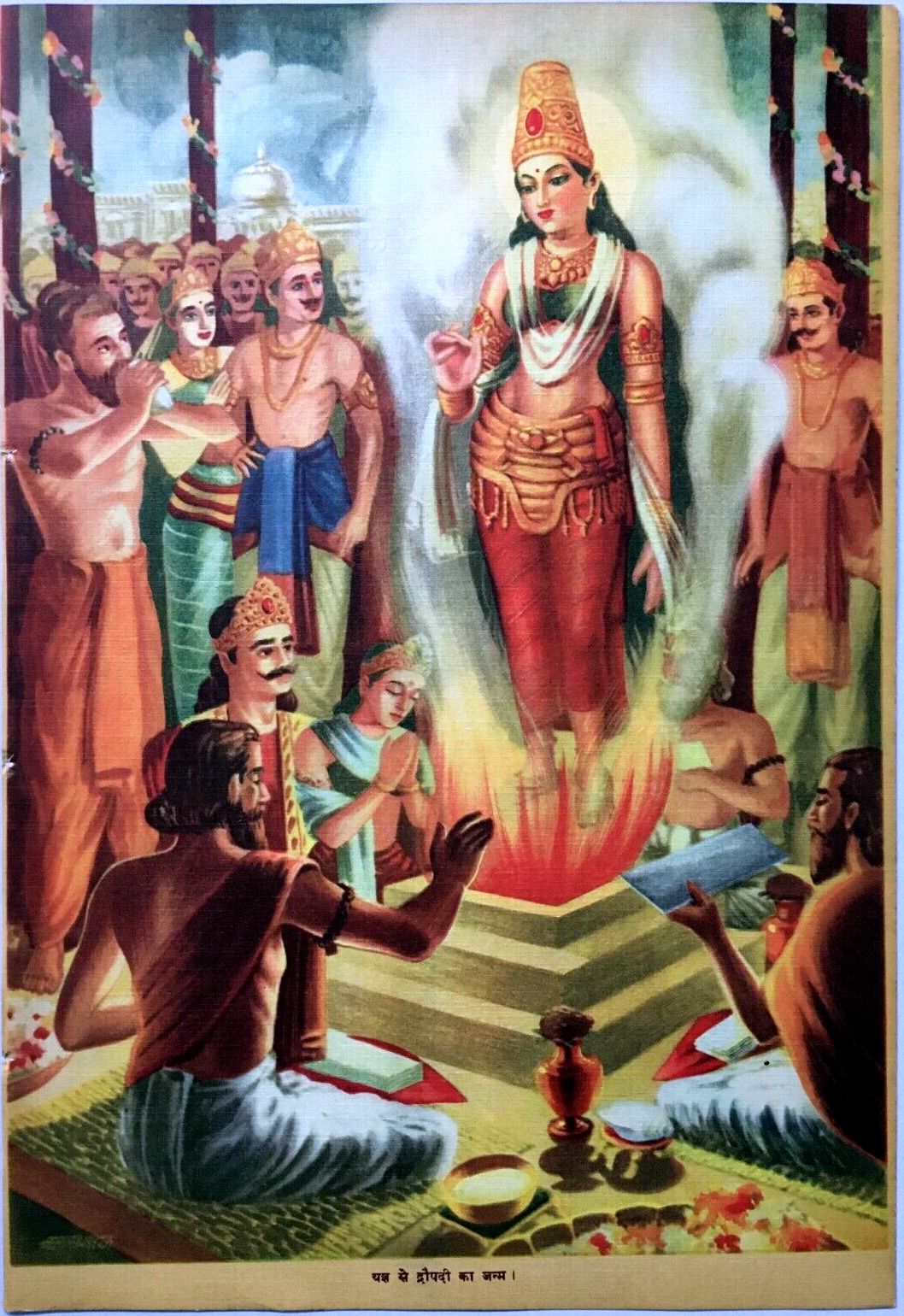
Draupadi
Draupadi (), also referred to as Krishnā, Panchali and Yajnaseni, is the central heroine of the Indian epic poetry, ancient Indian epic ''Mahabharata''. In the epic, she is the princess of Panchala Kingdom, who later becomes the empress of Kuru kingdom, Kuru Kingdom. She is the Polyandry, common wife of the five Pandava brothers—Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—and is renowned for her beauty, courage, devotion, intelligence and rhetorical skills. She is also described as ''sakhi''—a close friend—of the god Krishna. Draupadi, along with her twin brother Dhrishtadyumna, emerges fully grown from a ''yajna'' (fire sacrifice) organized by King Drupada of Panchala. Draupadi’s marriage is determined through a ''svayamvara'' (self-choice ceremony), structured as an archery contest of great difficulty. Arjuna succeeds in the challenge and wins her hand. However, their mother, Kunti, unknowingly instructs her sons to share whatever they had brought home, resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandavas
The Pandavas (Sanskrit: पाण्डव, aɳɖɐʋᵊ IAST: Pāṇḍava) is a group name referring to the five legendary brothers, Yudhishtira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva, who are central figures of the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. They are acknowledged as the sons of Pandu, the King of Kuru, but were fathered by different '' Devas'' (gods) due to Pandu's cursed inability to naturally sire children. In the epic, the Pandavas married Draupadi, the princess of Panchala, and founded the city of Indraprastha after the Kuru Kingdom was split to avoid succession disputes. After the split, the other part of the kingdom was ruled by their cousins, the Kauravas. However, the Pandavas lost their kingdom to Duryodhana (eldest and king of the Kauravas) when Yudhishthira gambled it away during a game of dice. The bet Yudhishtira agreed to was that the Pandavas would hand the kingdom over to the Kauravas and go into exile for 12 followed by an year in hiding. After this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penguin Books
Penguin Books Limited is a Germany, German-owned English publishing, publishing house. It was co-founded in 1935 by Allen Lane with his brothers Richard and John, as a line of the publishers the Bodley Head, only becoming a separate company the following year."About Penguin – company history" , Penguin Books. Penguin revolutionised publishing in the 1930s through its inexpensive paperbacks, sold through Woolworths (United Kingdom), Woolworths and other stores for Sixpence (British coin), sixpence, bringing high-quality fiction and non-fiction to the mass market. Its success showed that large audiences existed for several books. It also affected modern British popular culture significantly through its books concerning politics, the arts, and science. Penguin Books is now an imprint (trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parikshit
Parīkṣit (, ) was a Kuru king who reigned during the Middle Vedic period (12th–9th centuries BCE). Along with his son and successor, Janamejaya, he played a decisive role in the consolidation of the Kuru state, the arrangement of Vedic hymns into collections, and the development of the orthodox srauta ritual, transforming the Kuru realm into the dominant political and cultural center of northern Iron Age India. He also appears as a figure in later legends and traditions. According to the legendary accounts in Mahabharata and the Puranas, he succeeded his granduncle Yudhishthira to the throne of Hastinapur. Introduction "Listen to the good praise of the King belonging to all people, who, (like) a god, is above men, (listen to the praise) of Parikṣit! - 'Parikṣit has just now made us peaceful dwelling; darkness has just now run to its dwelling.' The Kuru householder, preparing (grains) for milling, speaks (thus) with his wife. — 'What shall I bring you, sour milk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |