|
Chen Qun
Chen Qun (died 7 February 237), courtesy name Changwen, was a Chinese politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He initiated the Nine-rank system for civil service nomination in Wei. Following the death of the first Wei emperor Cao Pi, Chen Qun, along with Sima Yi and Cao Zhen, nominated Cao Pi's son, Cao Rui, to be the new emperor. Early life Chen Qun was born in the illustrious Chen family of Yingchuan Commandery (), which is around present-day Xuchang, Henan. His grandfather Chen Shi, father Chen Ji and uncle Chen Chen () all held high offices in the central government of the Eastern Han dynasty. As a child, he was already recognised as a talent by his grandfather Chen Shi, who told the elders in the clan, "This child will make our clan prosper!". When he was older, Kong Rong, a descendant of Confucius and close friend of his father Chen Ji, became friends with Chen Qun as well, thus making Chen Qun famous. In the days when Liu Bei wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Rui
Cao Rui () (204 or 205 – 22 January 239), courtesy name Yuanzhong, was the second emperor of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period. His parentage is in dispute: his mother, Lady Zhen, was Yuan Xi's wife, but she later remarried Cao Pi, the first ruler of Wei. Based on conflicting accounts of his age, Pei Songzhi calculated that, in order to be Cao Pi's son, Cao Rui could not have been 36 (by East Asian age reckoning) when he died as recorded, so the recorded age was in error; late-Qing scholars Lu Bi (卢弼) and Mao Guangsheng (冒广生) argued instead that Cao Rui was Yuan Xi's son. Cao Rui's reign was viewed in many different ways throughout Chinese history. He devoted many resources into building palaces and ancestral temples, and his reign saw the stalemate between his empire, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu become more entrenched. His building projects and his desire to have many concubines (who numbered in the thousands) greatly exhausted the imperial trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from AD 220 to 280 following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Jin dynasty (266–420), Western Jin dynasty. Academically, the periodisation begins with the establishment of Cao Wei in 220 and ends with the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280. The period immediately preceding the Three Kingdoms, from 184 to 220, was marked by chaotic infighting among warlords across China as Han authority collapsed. The period from 220 to 263 was marked by a comparatively stable arrangement between Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. This stability broke down with the conquest of Shu by Wei in 263, followed by the usurpation of Cao Wei by Jin in 266 and ultimately the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280. The Three Kingdoms period including the collapse of the Han was one of the most dangerous in Chinese history due to multiple plagues, widespread famines, and civil war. A n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xu Province
Xuzhou as a historical toponym refers to varied area in different eras. Ordinarily, it was a reference to the Nine Provinces which modern Xuzhou inherited. History Pre-Qin era Xuzhou or Xu Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China mentioned in Chinese historical texts such as the '' Tribute of Yu'', '' Erya'' and '' Rites of Zhou''. The '' Yu Gong'' 'Tribute of Yu''records: "The Sea, Mount Dai (ancient name of Mount Tai), and the Huai River served as the boundaries of Xuzhou." While the definition of Xuzhou is more brief in '' Erya'': "Where is located in the east of Ji River". Based on these descriptions, the ancient Xuzhou covered an area that roughly corresponds to the regions in modern southeastern Shandong (south of Mount Tai) and northern Jiangsu (north of the Huai River). Han dynasty In 106 BCE, during the reign of Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BCE) in the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE – 9 CE), China was divided into 13 administrative divisions or provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tao Qian (Han Dynasty)
Tao Qian () (132–194), courtesy name Gongzu, was a government official and warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He is best known for serving as the governor of Xu Province. Early life Tao Qian was born in Danyang Commandery (), which is around present-day Ma'anshan, Anhui. His father served as Chief of Yuyao (餘姚長) and died when Tao Qian was still young. As an orphan, he was well known for his daredevil attitude. At the age of 13, he sewed from silk a made-up banner while riding a bamboo horse with all the children from the village following his lead. The Administrator of Cangwu (蒼梧太守), Gan Gong (甘公), who was from the same county by birth, met Tao while travelling. Gan was deeply impressed by Tao's appearance and conversed with him. He was further impressed and agreed to have his daughter married to him. His wife was displeased and told him angrily, "This Tao kid is a ruffian; why offer him our daughter?" Gan Gong replied that Tao Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuzhou (ancient China)
Yuzhou or Yu Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China, later to become an administrative division around the reign of Emperor Wu (r. 141 BC - 87 BC) of the Western Han dynasty (206 BC-AD 9). History Pre-Qin dynasty Pre-Qin dynasty (221 BC–206 BC) historical texts such as the '' Yu Gong'' or ''Tribute of Yu'' chapter of the '' Book of History'', '' Erya'', '' Rites of Zhou'' and '' Lüshi Chunqiu'' all refer to the Nine Provinces. Yuzhou appears in all of these texts even though different names are provided for the Nine Provinces. The ''Rites of Zhou'' states that Yuzhou was Henan Province, while the ''Lüshi Chunqiu'' records: "Yuzhou was between the Yellow and Han rivers. That was where Zhou was located." Han dynasty In 106 BC during the reign of Emperor Wu of the Western Han dynasty (206 BC-AD 9), China was divided into thirteen administrative divisions (excluding the area under the central government's control), each governed by an Inspector (刺史). Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Bei
Liu Bei (, ; ; 161 – 10 June 223), courtesy name Xuande (), was a China, Chinese warlord in the late Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty who later became the founding Emperor of China, emperor of Shu Han, one of the Three Kingdoms of China. Despite early failings and lacking both the material resources and social status other warlords of his time commanded, he gathered support among Han loyalists who opposed Cao Cao, the warlord who controlled the Han central government and the figurehead Emperor Xian of Han, Emperor Xian, and led a popular movement to restore the Han dynasty. Liu Bei overcame a number of setbacks to carve out his own realm, which at its peak spanned present-day Sichuan, Chongqing, Guizhou, Hunan, and parts of Hubei, Yunnan, and Gansu. Bolstered by the cultural influence of the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' and its portrayal of Liu Bei as an exemplar of virtuous Confucianism, Confucian rule, Liu Bei is widely revered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
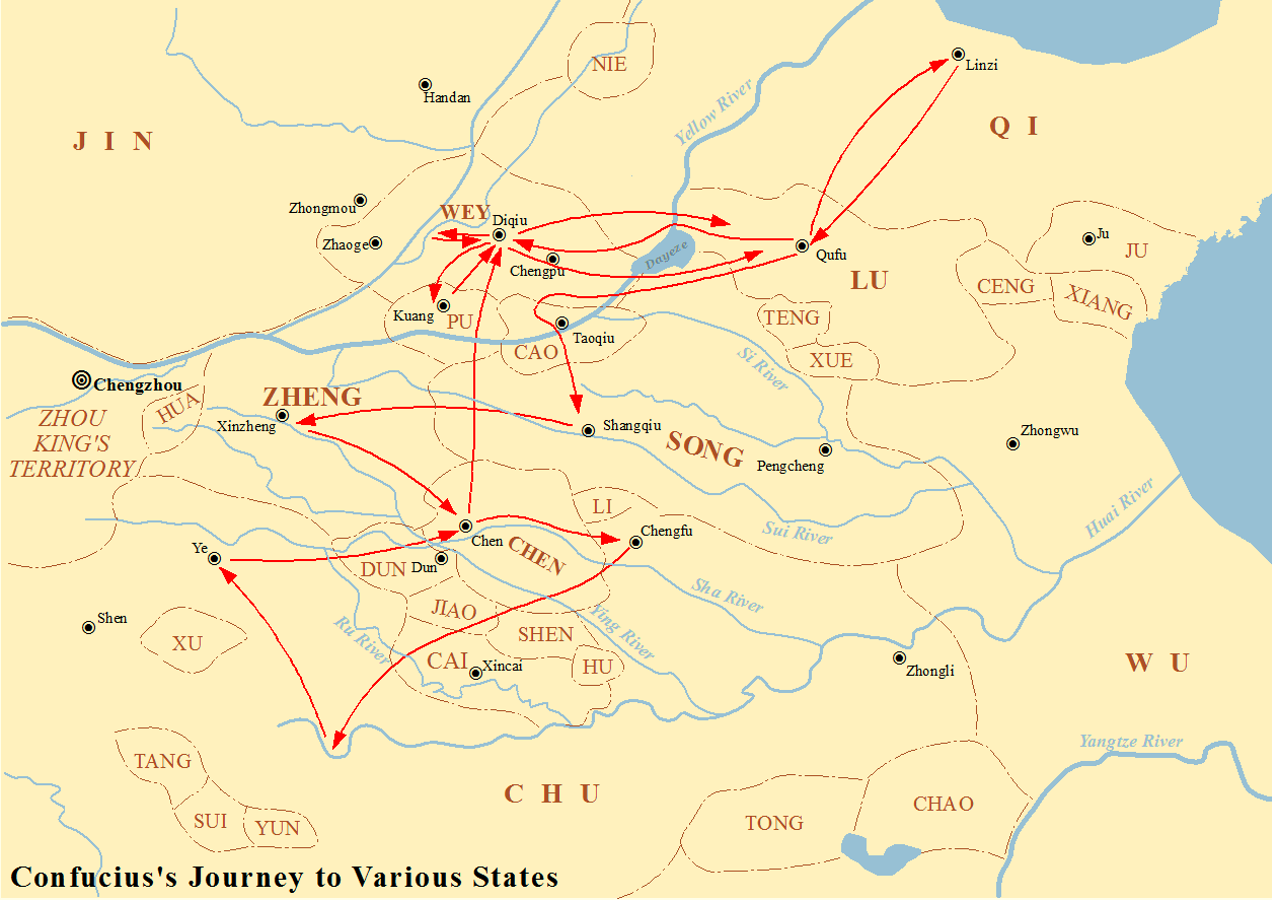
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kong Rong
Kong Rong () (151/153 – 26 September 208), courtesy name Wenju, was a Chinese poet, politician, and minor warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was a 20th generation descendant of Confucius. As he was once the Chancellor of Beihai State, he was also known as Kong Beihai. He was defeated by Yuan Tan in 196 and escaped to the capital Xuchang. For being a political opponent of Cao Cao and humiliating him on multiple occasions, Kong Rong was eventually put to death on various charges. Famed for his quick wits and elaborate literary style, Kong Rong was ranked among the Seven Scholars of Jian'an, a group of representative literati of his time. However, most of his works had been lost. Those that survived can be found in compilations from the Ming and Qing dynasties. A well-known story commonly used to educate children – even in contemporary times – on the values of courtesy and fraternal love involves a four-year-old Kong Rong giving u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Ji (Chen Shi's Son)
Chen Ji (129 – July 199According to the "Stele of Master Chen, Minister Herald of Later Han" by Handan Chun (recorded in volume 19 of ''Gu Wen Yuan''), Chen Ji died of illness, aged 71 (by East Asian reckoning), in the 6th month of the 4th year of the ''Jian'an'' era of Liu Xie's reign. This corresponds to 11 July to 9 August 199 on the Julian calendar. (《古文苑卷十九·後漢鴻臚陳君碑》邯鄲淳撰:不幸寢疾,年七十有一,建安四年六月卒。)), courtesy name Yuanfang, was an official and scholar who lived during the Eastern Han dynasty of China. Life Chen Ji was from Xu County (), Yingchuan Commandery (), which is present-day Xuchang, Henan. His father Chen Shi was a notable official who served from the reign of Emperor Huan ( 146–168) well into the early reign of Emperor Ling ( 168–189). Due to the Disasters of the Partisan Prohibitions in 166 and 169, Chen Ji did not enter government service and instead spent his time reading and writi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Shi (Han Dynasty)
Chen Shi (陳寔) (10416 September 186), courtesy name Zhonggong (仲弓), was an official of the Eastern Han dynasty of China. Life Chen Shi was the father of Chen Ji and the paternal grandfather of Chen Qun. As he was the mayor () of Taiqiu County (), he was also known as Chen Taiqiu (). He was the primogenitor of surname Chen () of Yingchuan () and the central figure of the Qingliu school () in the Yingchuan () region. Though he was raised at an impoverished family, he loved books and studies at early years. As he was the person of rightfulness, without prejudice and generous, he was held in high repute among the common people. However, as he objected to the eunuchs' abuse of power, he was prevented from holding government positions by the Disasters of Partisan Prohibitions. As he was prevented from government services, he lived a hermit life at his hometown. Whenever a civil lawsuit occurred, local residents invited him to preside over the case. Whenever consulted, Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yingchuan Commandery
Yingchuan Commandery ( zh, 潁川郡) was a Chinese commandery from the Warring States period to Tang dynasty, located in modern central Henan province. The name referred to the Ying River, which flowed through its territory. The commandery was established by the state of Qin after it conquered Hán. The seat was Yangdi (陽翟, modern Yuzhou, Henan), which, according to legend, was the capital of Yu the Great, and was the capital of the Warring States era State of Han. After the establishment of Hàn dynasty, it originally became Xin, King of Hán's fief. However, Xin was soon moved to Taiyuan, and the commandery was restored. In 2 AD, it administered 20 counties: Yangdi, Kunyang (昆陽), Yingyang (潁陽), Dingling (定陵), Changshe (長社), Xinji (新汲), Xiangcheng (襄城), Yan (郾), Jia (郟), Wuyang (舞陽), Yingyin (潁陰), Chonggao (崇高), Xu (許), Yanling (傿陵), Linying (臨潁), Fucheng (父城), Cheng'an (成安), Zhouchengxiu (周承休), Ya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Family Of Yingchuan
Chen or Ch'en may refer to: People *Chen (surname) (陳 / 陈), a common Chinese surname *Chen (singer) (born 1992), member of the South Korean-Chinese boy band EXO * Chen Chen (poet) (born 1989), Chinese-American poet * (), a Hebrew first name or surname: ** Hen Lippin (born 1965), former Israeli basketball player ** Chen Kugel (born 1962), Israeli pathologist who did an autopsy on Yahya Sinwar ** Chen Reiss (born 1979), Israeli operatic soprano ** Ronen Chen (born 1965), Israeli fashion designer Historical states *Chen (state) (c. 1045 BC–479 BC), a Zhou dynasty state in present-day Anhui and Henan *Chen (Thessaly), a city-state in ancient Thessaly, Greece * Chen Commandery, a commandery in China from Han dynasty to Sui dynasty *Chen dynasty (557–589), a Chinese southern dynasty during the Northern and Southern dynasties period Businesses and organizations * Council for Higher Education in Newark (CHEN) * Chen (), acronym in Hebrew for the Women's Army Corps (, ) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |