|
Chemical Space
Chemical space is a concept in cheminformatics referring to the property space spanned by all possible molecules and chemical compounds adhering to a given set of construction principles and boundary conditions. It contains millions of compounds which are readily accessible and available to researchers. It is a library used in the method of molecular docking. Theoretical spaces A chemical space often referred to in cheminformatics is that of potential pharmacologically active molecules. Its size is estimated to be in the order of 1060 molecules. There are no rigorous methods for determining the precise size of this space. The assumptions used for estimating the number of potential pharmacologically active molecules, however, use the Lipinski rules, in particular the molecular weight limit of 500. The estimate also restricts the chemical elements used to be Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Sulfur. It further makes the assumption of a maximum of 30 atoms to stay below 500 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Molecule
Virtual may refer to: * Virtual image, an apparent image of an object (as opposed to a real object), in the study of optics * Virtual (horse), a thoroughbred racehorse * Virtual channel, a channel designation which differs from that of the actual radio channel (or range of frequencies) on which the signal travels * Virtual function, a programming function or method whose behaviour can be overridden within an inheriting class by a function with the same signature * Virtual machine, the virtualization of a computer system * Virtual meeting, or web conferencing * Virtual memory, a memory management technique that abstracts the memory address space in a computer * Virtual particle, a type of short-lived particle of indeterminate mass * Virtual reality (virtuality), computer programs with an interface that gives the user the impression that they are physically inside a simulated space * Virtual world, a computer-based simulated environment populated by many users who can create a persona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Space (evolution)
In evolutionary biology, sequence space is a way of representing all possible sequences (for a protein, gene or genome). The sequence space has one dimension per amino acid or nucleotide in the sequence leading to highly dimensional spaces. Most sequences in sequence space have no function, leaving relatively small regions that are populated by naturally occurring genes. Each protein sequence is adjacent to all other sequences that can be reached through a single mutation. It has been estimated that the whole functional protein sequence space has been explored by life on the Earth. Evolution by natural selection can be visualised as the process of sampling nearby sequences in sequence space and moving to any with improved fitness over the current one. Representation A sequence space is usually laid out as a grid. For protein sequence spaces, each residue in the protein is represented by a dimension with 20 possible positions along that axis corresponding to the possible amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Design
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the invention, inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic compound, organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic effect, therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and electric charge, charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on molecular modelling, computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is sometimes referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
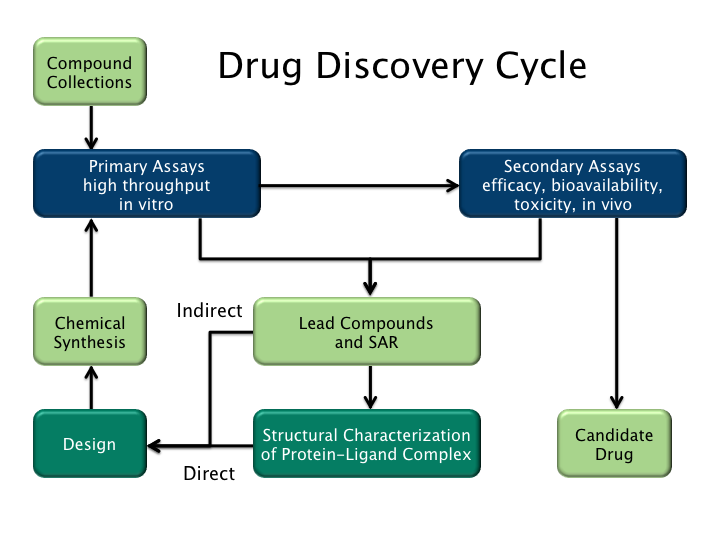
Drug Discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology, and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered. Historically, drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous discovery, as with penicillin. More recently, chemical libraries of synthetic small molecules, natural products, or extracts were screened in intact cells or whole organisms to identify substances that had a desirable therapeutic effect in a process known as classical pharmacology. After sequencing of the human genome allowed rapid cloning and synthesis of large quantities of purified proteins, it has become common practice to use high throughput screening of large compounds libraries against isolated biological targets which are hypothesized to be disease-modifying in a process known as reverse pharmacology. Hits from these screens are then tested in cells and then in animals for efficacy. Modern drug discovery i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Property
Molecular properties include the chemical properties, physical properties, and structural properties of molecules, including drugs. Molecular properties typically do not include pharmacological or biological properties of a chemical compound. See also * Biological activity * Chemical property * Chemical structure * Lipinski's rule of five, describing molecular properties of drugs * Physical property A physical property is any property of a physical system that is measurable. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momentary states. A quantifiable physical property is called ''physical ... * QSAR, quantitative structure-activity relationship References Physical quantities Molecules {{chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheminformatics
Cheminformatics (also known as chemoinformatics) refers to the use of physical chemistry theory with computer and information science techniques—so called "'' in silico''" techniques—in application to a range of descriptive and prescriptive problems in the field of chemistry, including in its applications to biology and related molecular fields. Such '' in silico'' techniques are used, for example, by pharmaceutical companies and in academic settings to aid and inform the process of drug discovery, for instance in the design of well-defined combinatorial libraries of synthetic compounds, or to assist in structure-based drug design. The methods can also be used in chemical and allied industries, and such fields as environmental science and pharmacology, where chemical processes are involved or studied. History Cheminformatics has been an active field in various guises since the 1970s and earlier, with activity in academic departments and commercial pharmaceutical rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology (chemistry)
In chemistry, topology provides a way of describing and predicting the molecular structure within the constraints of three-dimensional (3-D) space. Given the determinants of chemical bonding and the Chemical property, chemical properties of the atoms, topology provides a model for explaining how the atoms ethereal wave functions must fit together. Molecular topology is a part of mathematical chemistry dealing with the algebraic description of chemical compounds so allowing a unique and easy characterization of them. Topology is insensitive to the details of a scalar field, and can often be determined using simplified calculations. Scalar fields such as electron density, Erwin Madelung, Madelung field, covalent field and the electrostatic potential can be used to model topology.Brown, David; Topology and Chemistry; Structural Chemistry Volume 13, Numbers 3–4, 339–355, Each scalar field has its own distinctive topology and each provides different information about the nature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford at the Department_of_Physics_and_Astronomy,_University_of_Manchester , University of Manchester based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden experiments, Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of () for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about for uranium. These dimensions are much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrons
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry () is the relationships between the masses of reactants and Product (chemistry), products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of mass; the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products, so the relationship between reactants and products must form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated. This is illustrated in the image here, where the unbalanced equation is: : : However, the current equation is imbalanced. The reactants have 4 hydrogen and 2 oxygen atoms, while the product has 2 hydrogen and 3 oxygen. To balance the hydrogen, a coefficient of 2 is added to the product H2O, and to fix the imbalance of oxygen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |