|
Chatyr-Köl
Chatyr-Köl (, ) is an endorheic alpine lake in the Tian Shan mountains in At-Bashy District of Naryn Province, Kyrgyzstan; it lies in the lower part of Chatyr-Köl Depression near the Torugart Pass border crossing into China. The name of the lake means “Celestial Lake” in Kyrgyz language, Kyrgyz (literally "Roof Lake"). Climate The mean annual temperature in the lake basin is , with mean temperature of in January, and in July. The maximum temperature in summer is , and the minimum one in winter is . Some 88-90% of the lake basin's 208–269 mm of annual precipitation falls in summer. From October to end of April the lake surface freezes, the ice becoming as much as 0.25-1.5 m thick. Hydrology The water of Chatyr Kul Lake is yellowish-green with water transparency of up to . The mineralization of the lake ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 milligrams per liter (chloride, hydrocarbonate, sodium and magnesium type of mineralization). The salinity of the lake is 2 ppt. Mineral sourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naryn Province
Naryn Region is the largest Regions of Kyrgyzstan, region of Kyrgyzstan. It is located in the east of the country and borders with Chüy Region in the north, Issyk-Kul Region in the northeast, Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China in the southeast, Osh Region in the southwest, and Jalal-Abad Region in the west. Its capital is Naryn. Its total area is . The resident population of the region was 292,140 as of January 2021. The main highway runs from the Chinese border at Torugart Pass north to Balykchy on Issyk-Kul, Lake Issyk-Kul. It is known as the location of Song-Köl, Lake Song-Köl, Chatyr-Köl, Lake Chatyr-Köl, and Tash Rabat. The population of Naryn oblast is 99% Kyrgyz. The economy is dominated by animal herding (sheep, horses, yaks), with wool and meat as the main products. Mining of various minerals developed during the Soviet era has largely been abandoned as uneconomical. It boasts mountains, alpine pastures, and Song Köl Lake which during summer mont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naryn Region
Naryn Region is the largest region of Kyrgyzstan. It is located in the east of the country and borders with Chüy Region in the north, Issyk-Kul Region in the northeast, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China in the southeast, Osh Region in the southwest, and Jalal-Abad Region in the west. Its capital is Naryn. Its total area is . The resident population of the region was 292,140 as of January 2021. The main highway runs from the Chinese border at Torugart Pass north to Balykchy on Lake Issyk-Kul. It is known as the location of Lake Song-Köl, Lake Chatyr-Köl, and Tash Rabat. The population of Naryn oblast is 99% Kyrgyz. The economy is dominated by animal herding (sheep, horses, yaks), with wool and meat as the main products. Mining of various minerals developed during the Soviet era has largely been abandoned as uneconomical. It boasts mountains, alpine pastures, and Song Köl Lake which during summer months attracts large herds of sheep and horses with their h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
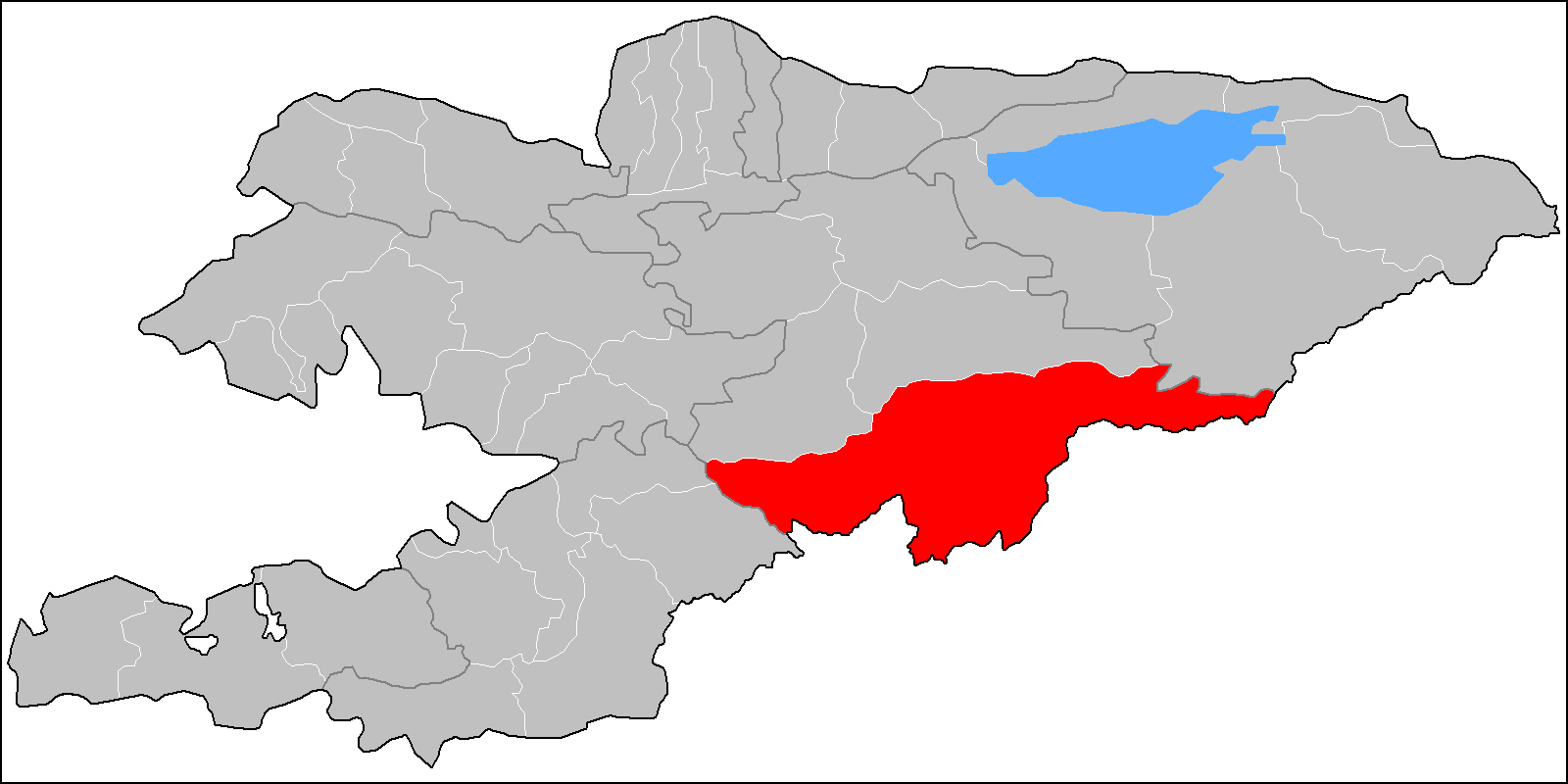
Karatal-Japyryk Nature Reserve
The Karatal-Japyryk Nature Reserve (, ) is a nature reserve in Naryn Region of Kyrgyzstan. Established in 1994, it currently covers 36,393 hectares. It was established for the conservation of unique nature complexes, protection of rare and threatened species of flora and fauna of Central Tien-Shan, and maintain regional environmental balance. The main section of the nature reserve is situated in the Ak-Talaa and Naryn districts, south of the lake Song-Köl. It covers the basins of the rivers Karatal and Japyryk, which are tributaries of the Kajyrty ( Naryn basin). In 1998 sections of the lakes Song-Köl (3,400 ha land, 5,200 ha water) and Chatyr-Köl Chatyr-Köl (, ) is an endorheic alpine lake in the Tian Shan mountains in At-Bashy District of Naryn Province, Kyrgyzstan; it lies in the lower part of Chatyr-Köl Depression near the Torugart Pass border crossing into China. The name of the lak ... (3,200 ha land, 3,954 ha water) were added to the Karatal-Japyryk Nature Reserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torugart Pass
Torugart Pass (, , ; ; ) is a mountain pass in the Tian Shan mountain range near the border between the Naryn Region of Kyrgyzstan and the Xinjiang Autonomous Region of China. It is one of two border crossings between Kyrgyzstan and China, the other being Erkeshtam, some to the southwest. The scenic lake Chatyr-Köl lies near the pass on the Kyrgyz side. The road to Naryn and then to Balykchy and Bishkek—stretching for some —is narrow and in winter often impassable due to heavy snowfall and frequent avalanches. On the Chinese side, the Torugart Port of Entry (吐尔尕特口岸), where travelers must clear for customs, is located about from the pass itself in Ulugqat County of the Kizilsu Kirghiz Autonomous Prefecture. Distances from the pass to major cities are: to Ulugqat, to Kashgar, to Artux and some to Ürümqi. The pass is also terminus of European route E125 and, under the new National Highway plans, the China National Highway 315, but neither a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tian Shan
The Tian Shan, also known as the Tengri Tagh or Tengir-Too, meaning the "Mountains of God/Heaven", is a large system of mountain ranges in Central Asia. The highest peak is Jengish Chokusu at high and located in Kyrgyzstan. Its lowest point is at the Turpan Depression, which is below sea level. The Tian Shan is sacred in Tengrism. Its second-highest peak is known as Khan Tengri, which can be translated as "Lord of the Spirits". At the 2013 Conference on World Heritage, the eastern portion of Tian Shan in western China's Xinjiang Region was listed as a World Heritage Site. The western portion in Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, and Uzbekistan was then listed in 2016. Geography Tian Shan with the ancient Silk Road The Tian Shan range is located north and west of the Taklamakan Desert and directly north of the Tarim Basin. It straddles the border regions of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan and Xinjiang in Northwest China. To the south, it connects with the Pamir Mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Lakes
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endorheic Lakes Of Asia
An endorheic basin ( ; also endoreic basin and endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water (e.g. rivers and oceans); instead, the water drainage flows into permanent and seasonal lakes and swamps that equilibrate through evaporation. Endorheic basins are also called closed basins, terminal basins, and internal drainage systems. Endorheic regions contrast with open lakes (exorheic regions), where surface waters eventually drain into the ocean. In general, water basins with subsurface outflows that lead to the ocean are not considered endorheic; but cryptorheic. Endorheic basins constitute local base levels, defining a limit of the erosion and deposition processes of nearby areas. Endorheic water bodies include the Caspian Sea, which is the world's largest inland body of water. Etymology The term ''endorheic'' derives from the French word , which combines ( 'within') and 'flow'. Endorheic lakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramsar Sites In Kyrgyzstan
Ramsar may refer to: * Places so named: ** Ramsar, Mazandaran, city in Iran ** Ramsar, Rajasthan, village in India * Eponyms of the Iranian city: ** Ramsar Convention, concerning wetlands, signed in Ramsar, Iran ** Ramsar site, wetland listed in accord with the Ramsar Convention * Others ** Ramsar Palace The Ramsar Palace or Marmar Palace is a historic royal residence in Iran. The palace is in Ramsar, Mazandaran, Ramsar, a city on the coast of the Caspian Sea. History The Ramsar Palace was established on a land of 60,000 square meters in 1937. T ..., a palace in Ramsar, Mazandaran See also * :Ramsar sites {{Disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Areas Of Kyrgyzstan
Importance is a property of entities that matter or make a difference. For example, World War II was an important event and Albert Einstein was an important person because of how they affected the world. There are disagreements in the academic literature about what type of difference is required. According to the causal impact view, something is important if it has a big causal impact on the world. This view is rejected by various theorists, who insist that an additional aspect is required: that the impact in question makes a value difference. This is often understood in terms of how the important thing affects the well-being of people. So in this view, World War II was important, not just because it brought about many wide-ranging changes but because these changes had severe negative impacts on the well-being of the people involved. The difference in question is usually understood counterfactually as the contrast between how the world is and how the world would have been withou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of Kyrgyzstan
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are fresh water and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions of oceans or large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Mapping Agency
The National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) is a combat support agency within the United States Department of Defense whose primary mission is collecting, analyzing, and distributing geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) to support national security. Founded in 1996 as the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA), it changed names in 2003. It is a member of the United States Intelligence Community. NGA headquarters, also known as NGA Campus East or NCE, is located at Fort Belvoir North Area in Springfield, Virginia. At , it is the third-largest government building in the Washington metropolitan area after the Pentagon and the Ronald Reagan Building. The agency also operates NGA Campus West, or NCW, in St. Louis, Missouri, and support and liaison offices worldwide. NGA also helps respond to natural and manmade disasters, helps with security planning for major events such as the Olympic Games, disseminates maritime safety information, and gathers data on climate change. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |