|
Characteristic Based Product Configurator
A characteristic-based product configurator is a product configurator extension which uses a set of discrete variables, called characteristics (or features), to define all possible product variations. Characteristics There are two characteristic types: * binary variables, which describe the presence or not of a specific feature, * n-values variables, which describe a selection between n possible value for a specific product feature. Constraints The range of characteristic-value combinations is reduced by a variety of constraints that define which combinations can, cannot, and must occur alongside each other. These constraints can be reflective of technological or commercial constraints in the real world. The constraints can represent: * incompatibility: they indicate the mutual exclusivity between some product feature-values; * implication: they indicate the presence of a specific feature-value is constrained to the presence of another feature-value. Characteristic filter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Configurator
Mass customization makes use of flexible computer-aided systems to produce custom products. Such systems combine the low unit costs of mass production processes with the flexibility of individual customization. Mass customization is the new frontier in business for both manufacturing and service industries. At its core, is a tremendous increase in variety and customization without a corresponding increase in costs. At its limit, it is the mass production of individually customized goods and services. At its best, it provides strategic advantage and economic value. Product design strategy Mass customization is a product design strategy and is currently used with both delayed differentiation and modular design to enhance the value delivered to customers. Mass customization is the method of, "effectively postponing the task of differentiating a product for a specific customer until the latest possible point in the supply network". From a collaborative engineering perspective, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
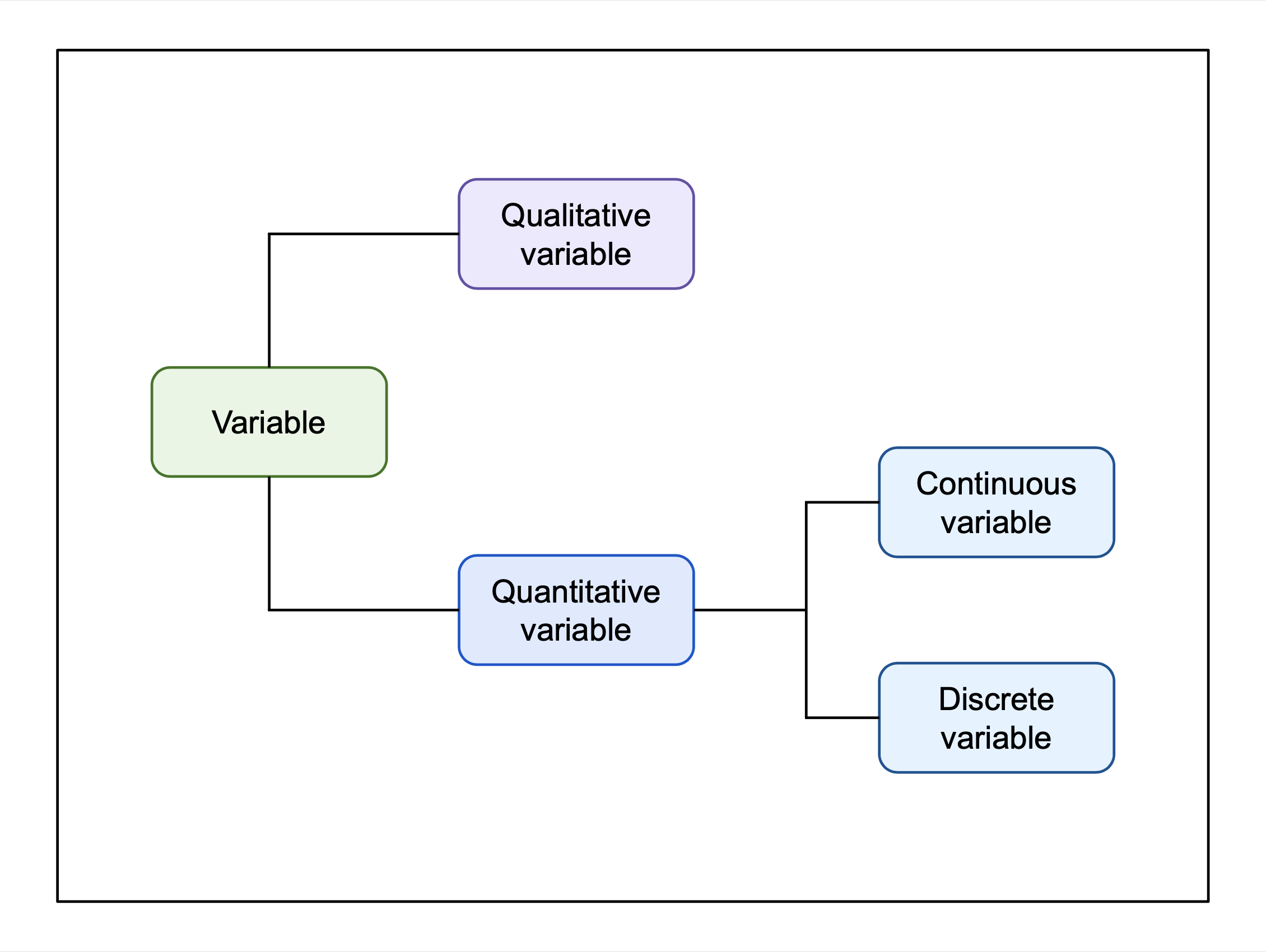
Discrete Variable
In mathematics and statistics, a quantitative variable may be continuous or discrete. If it can take on two real values and all the values between them, the variable is continuous in that interval. If it can take on a value such that there is a non-infinitesimal gap on each side of it containing no values that the variable can take on, then it is discrete around that value. In some contexts, a variable can be discrete in some ranges of the number line and continuous in others. In statistics, continuous and discrete variables are distinct statistical data types which are described with different probability distributions. Continuous variable A continuous variable is a variable such that there are possible values between any two values. For example, a variable over a non-empty range of the real numbers is continuous if it can take on any value in that range. Methods of calculus are often used in problems in which the variables are continuous, for example in continuous optimi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Variable
Binary data is data whose unit can take on only two possible states. These are often labelled as 0 and 1 in accordance with the binary numeral system and Boolean algebra. Binary data occurs in many different technical and scientific fields, where it can be called by different names including '' bit'' (binary digit) in computer science, ''truth value'' in mathematical logic and related domains and '' binary variable'' in statistics. Mathematical and combinatoric foundations A discrete variable that can take only one state contains zero information, and is the next natural number after 1. That is why the bit, a variable with only two possible values, is a standard primary unit of information. A collection of bits may have states: see binary number for details. Number of states of a collection of discrete variables depends exponentially on the number of variables, and only as a power law on number of states of each variable. Ten bits have more () states than three decimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Exclusivity
In logic and probability theory, two events (or propositions) are mutually exclusive or disjoint if they cannot both occur at the same time. A clear example is the set of outcomes of a single coin toss, which can result in either heads or tails, but not both. In the coin-tossing example, both outcomes are, in theory, collectively exhaustive, which means that at least one of the outcomes must happen, so these two possibilities together exhaust all the possibilities. However, not all mutually exclusive events are collectively exhaustive. For example, the outcomes 1 and 4 of a single roll of a six-sided die are mutually exclusive (both cannot happen at the same time) but not collectively exhaustive (there are other possible outcomes; 2,3,5,6). Logic In logic, two propositions \phi and \psi are mutually exclusive if it is not logically possible for them to be true at the same time; that is, \lnot (\phi \land \psi) is a tautology. To say that more than two propositions are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constraints
Constraint may refer to: * Constraint (computer-aided design), a demarcation of geometrical characteristics between two or more entities or solid modeling bodies * Constraint (mathematics), a condition of an optimization problem that the solution must satisfy * Constraint (mechanics), a relation between coordinates and momenta * Constraint (computational chemistry) * Constraint (information theory), the degree of statistical dependence between or among variables * ''Constraints'' (journal), a scientific journal * Constraint (database), a concept in relational database Particular types of constraint * Biological constraints, factors which make populations resistant to evolutionary change * Carrier's constraint on lung function in long thin animals * Finite domain constraint, in mathematical solution-finding * Integrity constraints in databases ** Check constraint ** Foreign key constraint * Specific types of mechanical constraints: ** First-class constraint and second-class cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Function
In mathematics, a Boolean function is a function whose arguments and result assume values from a two-element set (usually , or ). Alternative names are switching function, used especially in older computer science literature, and truth function (or logical function), used in logic. Boolean functions are the subject of Boolean algebra and switching theory. A Boolean function takes the form f:\^k \to \, where \ is known as the Boolean domain and k is a non-negative integer called the arity of the function. In the case where k=0, the function is a constant element of \. A Boolean function with multiple outputs, f:\^k \to \^m with m>1 is a vectorial or ''vector-valued'' Boolean function (an S-box in symmetric cryptography). There are 2^ different Boolean functions with k arguments; equal to the number of different truth tables with 2^k entries. Every k-ary Boolean function can be expressed as a propositional formula in k variables x_1,...,x_k, and two propositional formulas a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logical Operator
In logic, a logical connective (also called a logical operator, sentential connective, or sentential operator) is a logical constant. Connectives can be used to connect logical formulas. For instance in the syntax of propositional logic, the binary connective \lor can be used to join the two atomic formulas P and Q, rendering the complex formula P \lor Q . Common connectives include negation, disjunction, conjunction, implication, and equivalence. In standard systems of classical logic, these connectives are interpreted as truth functions, though they receive a variety of alternative interpretations in nonclassical logics. Their classical interpretations are similar to the meanings of natural language expressions such as English "not", "or", "and", and "if", but not identical. Discrepancies between natural language connectives and those of classical logic have motivated nonclassical approaches to natural language meaning as well as approaches which pair a classica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Of Materials
A bill of materials or product structure (sometimes bill of material, BOM or associated list) is a list of the raw materials, sub-assemblies, intermediate assemblies, sub-components, parts, and the quantities of each needed to manufacture an Product (business), end product. A BOM may be used for communication between manufacturing partners or confined to a single manufacturing plant. A bill of materials is often tied to a production order whose issuance may generate reservations for components in the bill of materials that are in stock and requisitions for components that are not in stock. The first Hierarchical database model, hierarchical databases were developed for automating bills of materials for manufacturing organizations in the early 1960s. At present, this BOM is used as a database to identify the many parts and their codes in automobile manufacturing companies. A BOM can also be visually represented by a Product structure modeling, product structure tree, although they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing Process Management
Manufacturing process management (MPM) is a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufactured. MPM differs from ERP/MRP which is used to plan the ordering of materials and other resources, set manufacturing schedules, and compile cost data. A cornerstone of MPM is the central repository for the integration of all these tools and activities aids in the exploration of alternative production line scenarios; making assembly lines more efficient with the aim of reduced lead time to product launch, shorter product times and reduced work in progress (WIP) inventories as well as allowing rapid response to product or product changes. * Production process planning ** Manufacturing concept planning ** Factory layout planning and analysis *** work flow simulation. *** walk-path assembly planning *** plant design optimization ** Mixed model line balancing. ** Workloads on multiple stations. ** Process simulation tools e.g. die press lines, manufacturi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |