|
Chachnama
''Chach Nama'' (; ; "Story of the Chach"), also known as the ''Fateh nama Sindh'' (; "Story of the Conquest of Sindh"), and as ''Tareekh al-Hind wa a's-Sind'' (; "History of Hind and Sind"), is a historical source for the history of Sindh. The text, which purports to be a Persian translation by `Ali Kufi (13th-century) of an undated, original Arabic text, has long been considered to be the story of the early 8th-century conquests by the Umayyad general Muhammad bin Qasim. The text is significant because it has been a source of colonial understanding of the origins of Islam and the Islamic conquests in the Indian subcontinent. It influenced the debate on the partition of British India and its narrative has been included in the state-sanctioned history textbooks of Pakistan. However, according to Manan Ahmed Asif, the text is in reality original, "not a work of translation". Asif asserts that the ''Chach Nama'' is a romantic work influenced by the 13th-century history, not a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rai Dynasty
The Rai dynasty (–632 CE) was a Buddhist dynasty that ruled the Sindh region. All that is known about the dynasty comes from the '' Chachnama'', a 13th-century Persian work about Sindhi history. Nothing particular is known about the first three kings—Rai Diwaji, Rai Sahiras I, and Rai Sahasi I. The fourth king, Rai Sahiras II, is said to have ruled over a vast prosperous area, including the seaport of Debal, divided into four provinces; he was killed in a conflict with the Sassanian King of Nimroz and lost territories around Makran. Rai Sahiras II was succeeded by Rai Sahasi II whose secretary, Chach, a Brahmin, usurped the throne after his death in connivance with Sohan Devi, the King's widow, and established the Brahmin dynasty. Sahasi II's relatives—Rai Mahrit, ruler of Chittor and Bachhera, the governor of Multan province—took on Chach, individually, but in vain. Background The Rais were a Sindhi family that reigned in the Sindh region for a period of 144 year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Dahir
Raja Dahir (663 – 712 CE) was the last Hindu ruler of Sindh (in present-day Pakistan). A Brahmin ruler, his kingdom was invaded in 711 CE by the Arab Umayyad Caliphate, led by Muhammad bin Qasim, where Dahir died. According to the Chach Nama, the Umayyad campaign against Dahir was due to a pirate raid off the Sindh coast that resulted in gifts to the Umayyad caliph from the king of Serendib (Old name of Sri Lanka) being stolen.Mirza Kalichbeg Fredunbeg: The Chachnamah, An Ancient History of Sind, Giving the Hindu period down to the Arab Conquest. Commissioners Press 1900, Section 18: "It is related that the king of Sarandeb* sent some curiosities and presents from the island of pearls, in a small fleet of boats by sea, for Hajjáj. He also sent some beautiful pearls and valuable jewels, as well as some Abyssinian male and female slaves, some pretty presents, and unparalleled rarities to the capital of the Khalífah. A number of Mussalman women also went with them with the objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
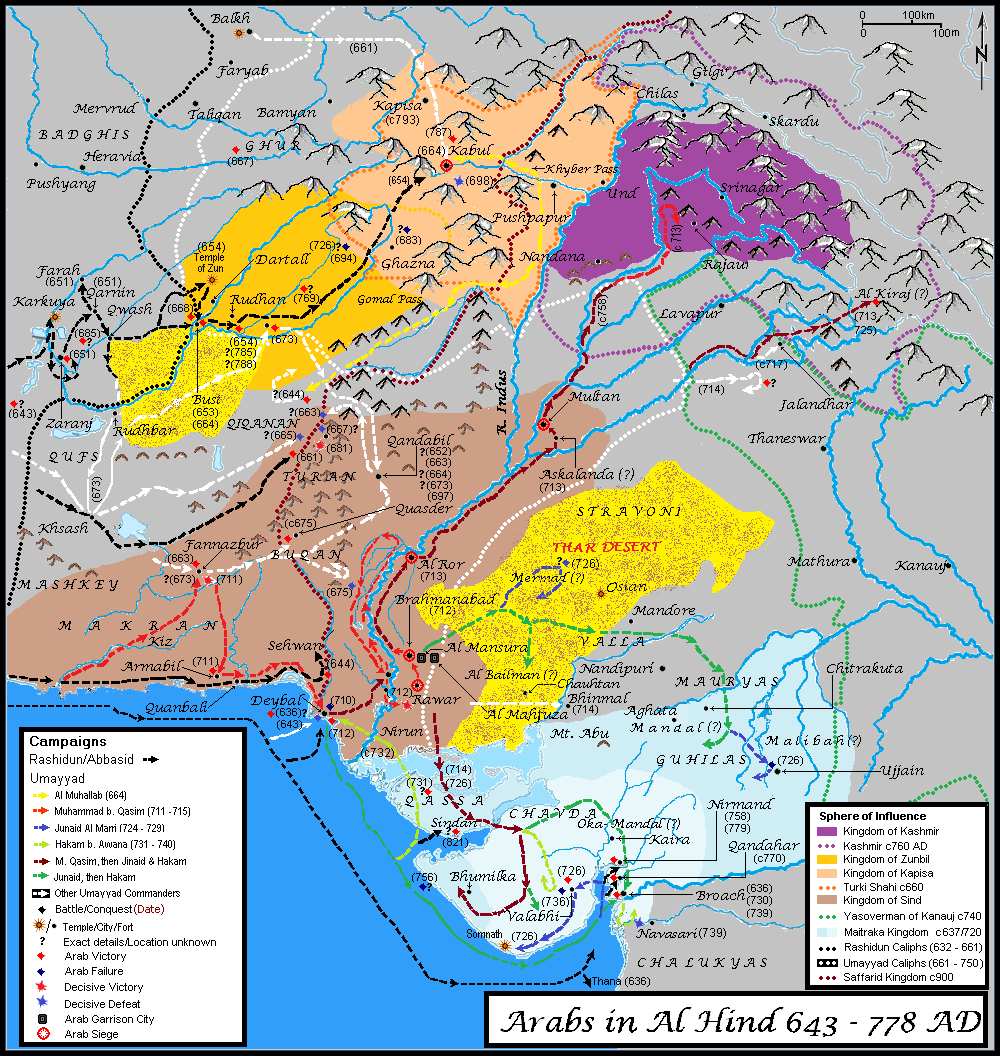
Arab-Sind War
The Umayyad conquest of Sindh took place in 711 AD and resulted in Sindh being incorporated as a province into the Umayyad Caliphate. The conquest resulted in the overthrow of the last Hindu dynasty of Sindh, the Brahmin dynasty, after the death of Raja Dahir. Background Although there was no connection between Arabia and Sindh, the war being started was due to events of piracy that plagued the Arabian Sea, at the time the Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate offered Raja Dahir protection and sovereignty if he would help him in quelling the piracy. Raja Dahir of Sindh had refused to return Arab rebels from SindhFredunbeg, Mirza Kalichbeg, "The Chachnama: An Ancient History of Sind", pp57 and '' Meds'' and others.Wink (2002), pg.164 ''Med'' pirates shipping from their bases at Kutch, Debal and Kathiawar during one of their raids had kidnapped Muslim women traveling from Sri Lanka to Arabia, thus providing a ''casus belli'' against Sindhi King Dahir. Raja Dahir expressed his inabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manan Ahmed Asif
Manan Ahmed Asif, also known as Manan Ahmed, is a Pakistani historian of South Asia and West Asia. He is an associate professor of history at Columbia University in New York City. He is the founder of the South Asia blog ''Chapati Mystery'' and co-founder oColumbia's Group for Experimental Methods in Humanistic Research Since 2021, he is co-executive editor of the Journal of the History of Ideas. Life and education Ahmed was born in 1971 in Lahore, Pakistan. At a young age, his family moved to Doha, Qatar, where his father worked as a migrant laborer. In the 8th grade, Ahmed and his family moved back to Lahore. Having grown up abroad, Ahmed initially struggled to reintegrate back into Pakistani culture, as his Arabic was more proficient than his Urdu. Ahmed graduated from Punjab University in Lahore with a BA in math and physics in 1991. In 1997, he graduated from Miami University in Ohio with a second BA with honors in history. At Miami, he completed two theses, one in art h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Bin Qasim
Muḥammad ibn al-Qāsim al-Thaqafī (; –) was an Arabs, Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (and Punjab, part of ancient Sindh), inaugurating the Umayyad campaigns in India. His military exploits led to the establishment of the Sind (caliphal province), Islamic province of Sindh, and the takeover of the region from the Brahmin dynasty of Sindh, Sindhi Brahman dynasty and its ruler, Raja Dahir, who was subsequently decapitated with his head sent to al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf in Basra. With the capture of the then-capital of Aror by Arab forces, Muhammad ibn al-Qasim became the first Muslims, Muslim to have successfully captured Indian land, which marked the beginning of Islamic rulers in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim rule in South Asia. Muhammad ibn al-Qasim belonged to the Banu Thaqif, an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe that is concentrated around the city of Taif in western Arabian Peninsula, Arabia. After the Muslim conq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam In India
Islam is India's Religion in India, second-largest religion, with 14.2% of the country's population, or approximately 172.2 million people, identifying as adherents of Islam in a 2011 census. India also has the Islam by country, third-largest number of Muslims in the world. The majority of India's Muslims are Sunni, with Shia making up around 15% of the Muslim population. Islam spread in Indian communities along the Arab coastal trade routes in Gujarat and in Malabar Coast shortly after the religion emerged in the Arabian Peninsula. Islam arrived in the inland of Indian subcontinent in the 7th century when the Arabs invaded and conquered Sindh and later arrived in Punjab and North India in the 12th century via the Ghaznavids and Ghurid dynasty, Ghurids conquest and has since become a part of India's Culture of India, religious and cultural heritage. The Barwada Mosque in Ghogha, Gujarat built before 623 CE, Cheraman Juma Mosque (629 CE) in Methala, Kerala and Palaiya Jumma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabi Bakhsh Khan Baloch
Nabi Bakhsh Khan Baloch (; 16 December 1917 – 6 April 2011) was a Sindhi research scholar, historian, sindhologist, educationist, linguist and writer. He predominantly wrote in Sindhi, but also in Urdu, English, Persian and Arabic. He has been described as the "moving library" of the Pakistani province of Sindh. The author of some 150 books, he contributed to many subjects and disciplines of knowledge, which include history, education, folklore, archeology, anthropology, musicology, Islamic culture and civilisation. He contributed two articles - on Sindh and Baluchistan - which appeared in the Fifteenth Edition of ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 1972. Baloch did pioneering work on the classic poets of Sindh, culminating in the ten-volume critical text of '' Shah Jo Risalo'', the poetic compendium of the Sufi poet of Sindh, Shah Abdul Latif Bhittai. He edited 42 volumes on Sindhi folklore, with scholarly prefaces in English, under the heading of the Folklore and Literature Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chach Of Alor
Chach ( 631–671 AD, ) was a Hindu Brahmin king of Sindh region of the Indian subcontinent in the mid-7th century AD. He was in service of the court of Rai Sahasi II and became a close confidate of the king and the queen. When Rai Sahasi died, he married the widowed queen and thus became ruler of Sindh. His ascend was challanged by Rai Sahasi's brother from Chittor, who claimed to be rightful successor of the kingdom. He marched to Sind but was killed by Chanch by stratagem. Thus Chanch became ruler of Sindh and laying foundation of a short-lived Brahmin dynasty of Sindh. Chach expanded the kingdom of Sindh and defeated those who objected to his ascend like Agham Lohana. His his successful efforts to subjugate surrounding monarchies and ethnic groups into an empire covering the entire Indus valley and beyond were recorded in the ''Chach Nama ''Chach Nama'' (; ; "Story of the Chach"), also known as the ''Fateh nama Sindh'' (; "Story of the Conquest of Sindh"), and as ''Tare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aror
Aror (or Alor or Arorkot) is the medieval name of the city of Rohri in Sindh, modern Pakistan. Aror once served as the capital of Sindh. History As Roruka, capital of the Sauvira Kingdom, it is mentioned as an important trading center in early Buddhist literature. In the Chachnamah, members of the Brahman group were noted in the city of Aror. Little is known about the city's history prior to the Arab invasion in the 8th century CE. Sauvīra was an ancient kingdom of the lower Indus Valley. Aror was the capital of the Rai dynasty and then the Brahman dynasty that once ruled northern Sindh. Aror is the ancestral town of the Arora community. In 711, Aror was captured by the army of Umayyad general Muhammad ibn al-Qasim. In 962 it was hit by a massive earthquake that changed the course of the Indus River The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain spring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin Dynasty Of Sindh
The Brahmin dynasty (), also known as the Chacha dynasty or Silaij dynasty, was a Sindhi Hindu dynasty that ruled the Sindh region, after usurping and overthrowing the Buddhist Rai dynasty of Sindh. Most of the information about its existence comes from the ''Chach Nama'', a historical account of the Chach-Brahmin dynasty. The members of the dynasty continued to administer parts of Sindh under the Umayyad Caliphate's Caliphal province of Sind after it Umayyad conquest of Sindh, fell in 712. These rulers include Hullishāh and Shishah. History The dynasty was founded by a Brahmin named Chach of Aror after he married the widow of Rai Sahasi II and usurped the Buddhist Rai dynasty. His claim was further secured by the killing of Rai Sahasi II's brother. The casus belli for the Ummayad invasion was Sindhi pirates seizing tribute sent from the king of Serendib to the Ummayad Caliph. For the campaign Caliph Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan granted a large army to the governor Al-Hajjaj ibn Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the Demographics of Pakistan, second-largest province by population after Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is bordered by the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan to the west and north-west and Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab to the north. It shares an India-Pakistan border, International border with the Indian states of Gujarat and Rajasthan to the east; it is also bounded by the Arabian Sea to the south. Sindh's landscape consists mostly of alluvial plains flanking the Indus River, the Thar Desert of Sindh, Thar Desert in the eastern portion of the province along the India–Pakistan border, international border with India, and the Kirthar Mountains in the western portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Baladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī () was a 9th-century West Asian historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al-Mutawakkil. He travelled in Syria and Iraq, compiling information for his major works. His full name was Ahmad Bin Yahya Bin Jabir Al-Baladhuri (), Balazry Ahmad Bin Yahya Bin Jabir Abul Hasan or Abi al-Hassan Baladhuri. Biography Al Baladhuri's ethnicity has been described as Persian by his contemporaries including Ibn Nadim, but some scholars have surmised that he was of Arab descent solely since he spent most of his life in Baghdad. Baladhuri was a Persian speaker who translated Persian works to Arabic. Nonetheless, his sympathies seem to have been strongly with the Arabs, for Masudi refers to one of his works in which he rejects Baladhuri's condemnation of non-Arab nationalism Shu'ubiyya. He is certainly not the first Persian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |