|
Chachapoya
The Chachapoyas, also called the "Warriors of the Clouds", were a culture of the Andes living in the cloud forests of the southern part of the Department of Amazonas of present-day Peru. The Inca Empire conquered their civilization shortly before the Spanish conquest in the 16th century. At the time of the arrival of the ''conquistadores'', the Chachapoyas were one of the many nations ruled by the Incas, although their incorporation had been difficult due to their constant resistance to Inca troops. Since the Incas and conquistadors were the principal sources of information on the Chachapoyas, little first-hand or contrasting knowledge of the Chachapoyas has been found. Writings by the major chroniclers of the time, such as Inca Garcilaso de la Vega, were based on fragmentary, second-hand accounts. Much of what is known about the Chachapoya culture is based on archaeological evidence from ruins, pottery, tombs, and other artifacts. Spanish chronicler Pedro Cieza de León note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chachapoya Language
The Chachapoyas, also called the "Warriors of the Clouds", were a culture of the Andes living in the cloud forests of the southern part of the Amazonas (Peruvian department), Department of Amazonas of present-day Peru. The Inca Empire conquered their civilization shortly before the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, Spanish conquest in the 16th century. At the time of the arrival of the ''conquistadores'', the Chachapoyas were one of the many nations ruled by the Incas, although their incorporation had been difficult due to their constant resistance to Inca troops. Since the Incas and conquistadors were the principal sources of information on the Chachapoyas, little first-hand or contrasting knowledge of the Chachapoyas has been found. Writings by the major chroniclers of the time, such as Inca Garcilaso de la Vega, were based on fragmentary, second-hand accounts. Much of what is known about the Chachapoya culture is based on archaeological evidence from ruins, pottery, tombs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Amazonas, Peru
Amazonas () is a department and region in northern Peru bordered by Ecuador on the north and west, Cajamarca on the west, La Libertad on the south, and Loreto and San Martín on the east. Its capital is the city of Chachapoyas. With a landscape of steep river gorges and mountains, Amazonas is the location of Kuelap, a huge stone fortress enclosing more than 400 stone structures; it was built on a mountain about 3,000 meters high, starting about 500 AD and was occupied to the mid-16th century. It is one of Peru's major archeological sites. Geography The department of Amazonas consists of regions covered by rainforests and mountain ranges. The rainforest zone predominates (72.93%) and it extends to the north over its oriental slope, up to the border with Ecuador in the summits of the Cordillera del Cóndor. The mountain range zone is located in the southern provinces of the Amazonas Region and it only includes 27.07% of its whole territorial surface. One of the factors th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazonas (Peruvian Department)
Amazonas () is a department and Regional Government of Amazonas, region in northern Peru bordered by Ecuador on the north and west, Department of Cajamarca, Cajamarca on the west, Department of La Libertad, La Libertad on the south, and Department of Loreto, Loreto and Department of San Martín, San Martín on the east. Its capital is the city of Chachapoyas, Peru, Chachapoyas. With a landscape of steep river gorges and mountains, Amazonas is the location of Kuelap, a huge stone fortress enclosing more than 400 stone structures; it was built on a mountain about 3,000 meters high, starting about 500 AD and was occupied to the mid-16th century. It is one of Peru's major archeological sites. Geography The department of Amazonas consists of regions covered by rainforests and mountain ranges. The rainforest zone predominates (72.93%) and it extends to the north over its oriental slope, up to the border with Ecuador in the summits of the Cordillera del Cóndor. The mountain range zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chachapoyas, Peru
Chachapoyas () is a city in northern Peru at an elevation of 2,335 meters (7,661 ft). The city has a population of 32,026 people (2017 Peru Census, 2017). Situated in the mountains far from the Peruvian coast, Chachapoyas remains fairly isolated from other regions of Peru. It is served by buses to Chiclayo and Cajamarca, and flights to domestic locations from Chachapoyas Airport. The city of Chachapoyas is the capital of the Amazonas (Peruvian department), Amazonas Region. It was founded on September 5, 1538, by the Spanish conquistador Alonso de Alvarado "and his twenty". Local agriculture includes sugar cane, orchid and coffee growing. Chachapoyas' transitional location between the arid Cordillera Occidental (Peru), Cordillera Occidental and Cordillera Blanca, Cordillera Central and the rainy, rainforested Cordillera Oriental (Peru), Cordillera Oriental, allow it to receive generally moderate annual precipitation without experiencing the copiously excessive, tropical-rainfore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Conquest Of The Inca Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, also known as the Conquest of Peru, was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military skirmishes, 168 Spaniards, Spanish soldiers under conquistador Francisco Pizarro, along with his brothers in arms and their Indigenous peoples of South America, indigenous Indian auxiliaries, allies, captured the last Sapa Inca, Atahualpa, at the Battle of Cajamarca in 1532. It was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory in 1572 and colonization of the region as the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest of the Inca Empire (called "Tahuantinsuyu" or "Tawantinsuyu" in Quechuan languages, Quechua, meaning "Realm of the Four Parts"), led to spin-off campaigns into present-day Chile and Colombia, as well as expeditions to the Amazon basin, Amazon Basin and surrounding rainforest. When the Spanish arrived at the borders of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua Languages
Quechua (, ), also called (, 'people's language') in Southern Quechua, is an indigenous language family that originated in central Peru and thereafter spread to other countries of the Andes. Derived from a common ancestral " Proto-Quechua" language, it is today the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with the number of speakers estimated at 8–10 million speakers in 2004,Adelaar 2004, pp. 167–168, 255. and just under 7 million from the most recent census data available up to 2011. Approximately 13.9% (3.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechua language. Although Quechua began expanding many centuries before the Incas, that previous expansion also meant that it was the primary language family within the Inca Empire. The Spanish also tolerated its use until the Peruvian struggle for independence in the 1780s. As a result, various Quechua languages are still widely spoken today, being co-official in many regions and the most spoken language in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18th parallel south, 18°S and 20th parallel south, 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from south to north through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depression (geology), depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, Mérida, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano, Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Intermediate Period
This is a chart of cultural periods of Peru and the Andean Region developed by John Rowe and Edward Lanning and used by some archaeologists studying the area. An alternative dating system was developed by Luis Lumbreras and provides different dates for some archaeological finds. Most of the cultures of the Late Horizon and some of the cultures of the Late Intermediate joined the Inca Empire by 1493, but the period ends in 1532 because that marks the fall of the Inca Empire after the Spanish conquest of Peru, Spanish conquest. Most of the cut-off years mark either an end of a severe drought or the beginning of one. These marked a shift of the most productive farming to or from the mountains and tended to mark the end of one culture and the rise of another. The more recent findings concerning the Norte Chico civilization are not included on this list, as it was compiled before the site at Caral was investigated in detail. See also * Andean civilizations, Ancient Peru * Ama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
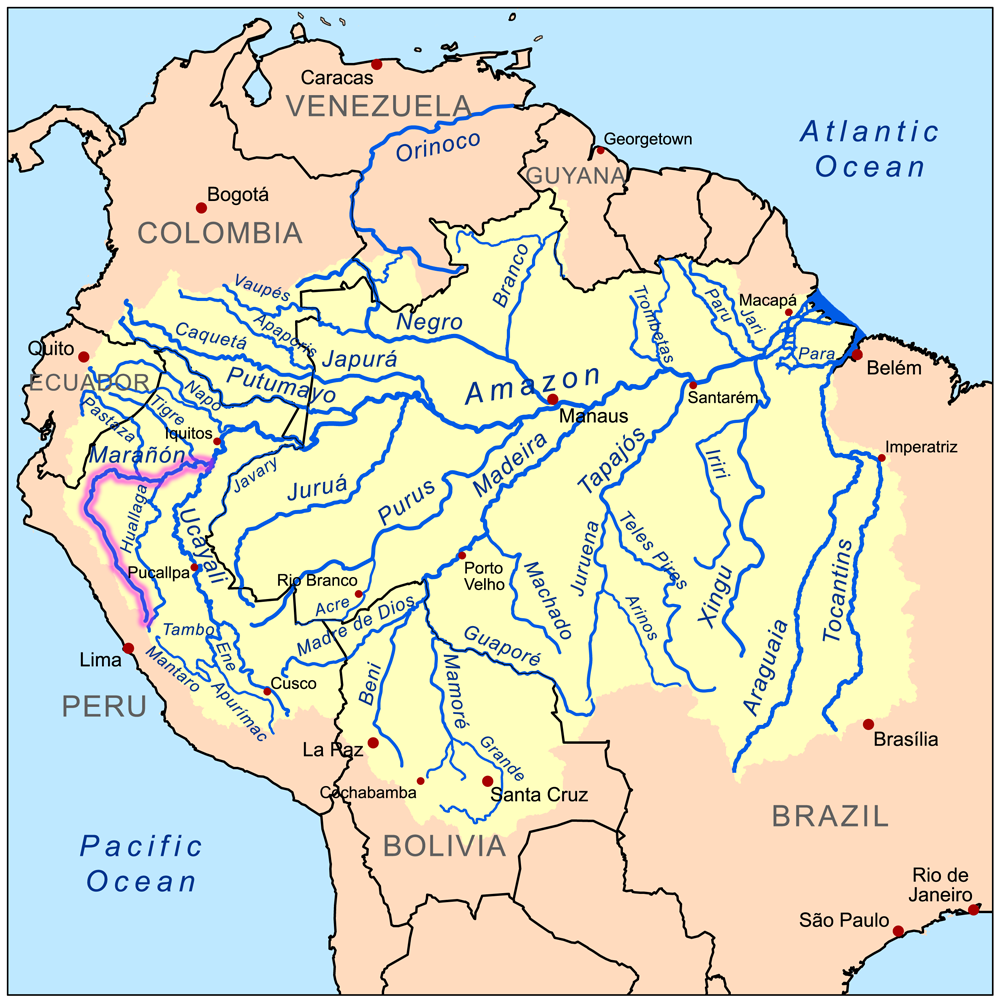
Marañón River
The Marañón River (, , ) is the principal or mainstem source of the Amazon River, arising about 160 km (100 miles) to the northeast of Lima, Peru, and flowing northwest across plateaus 3,650 m (12,000 feet) high, it runs through a deeply eroded Andean valley, along the eastern base of the Cordillera of the Andes, as far as 5° 36′ southern latitude; from where it makes a great bend to the northeast, and cuts through the jungle Ande in its midcourse, until at the Pongo de Manseriche it flows into the flat Amazon basin. Although historically, the term "Marañón River" often was applied to the river all the way to the Atlantic Ocean, nowadays the Marañón River is generally thought to end at the confluence with the Ucayali River, after which most cartographers label the ensuing waterway the Amazon River. As the Marañón passes through high jungle in its midcourse, it is marked by a series of unnavigable rapids and falls. The Marañón was the subject of a landmark legal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. Peru is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, with habitats ranging from the arid plains of the Pacific coastal region in the west, to the peaks of the Andes mountains extending from the north to the southeast of the country, to the tropical Amazon basin rainforest in the east with the Amazon River. Peru has Demographics of Peru, a population of over 32 million, and its capital and largest city is Lima. At , Peru is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 19th largest country in the world, and the List of South American countries by area, third largest in South America. Pre-Columbian Peru, Peruvian territory was home to Andean civilizations, several cultures during the ancient and medieval periods, and has one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moyobamba
Moyobamba () or Muyupampa ( Quechua ''muyu'' circle, ''pampa'' large plain, "circle plain") is the capital city of the San Martín Region in northern Peru. Called "Santiago of eight valleys of Moyobamba" or "Maynas capital". There are 50,073 inhabitants, according to the 2017 census. Some 3,500 species of orchids are native to the area, which has led to the city's nickname of ''The City of Orchids''. The city is the capital of both Moyobamba Province and Moyobamba District. The city is linked by road with Tarapoto to the southeast, Rioja to the west and Bagua to the northwest. Roads connect Moyobamba to the Pacific coast by way of Bagua and Olmos to the north and Cajamarca to the southwest. History The first colonies were from the Chachapoyas culture, but the modern city of Moyobamba was established by Juan Pérez de Guevara on 25 July 1540, who named it ''Santiago de los Ocho Valles de Moyobamba'' (Santiago of the eight Moyobamba Valleys). It was founded on the site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca civilisation rose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Portuguese explorer Aleixo Garcia was the first European to reach the Inca Empire in 1524. Later, in 1532, the Spanish Empire, Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire, and by 1572 Neo-Inca State, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andes, Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru with what are now western Ecuador, western and south-central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and Incas in Central Chile, a large portion of modern- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |