|
CfA Redshift Survey
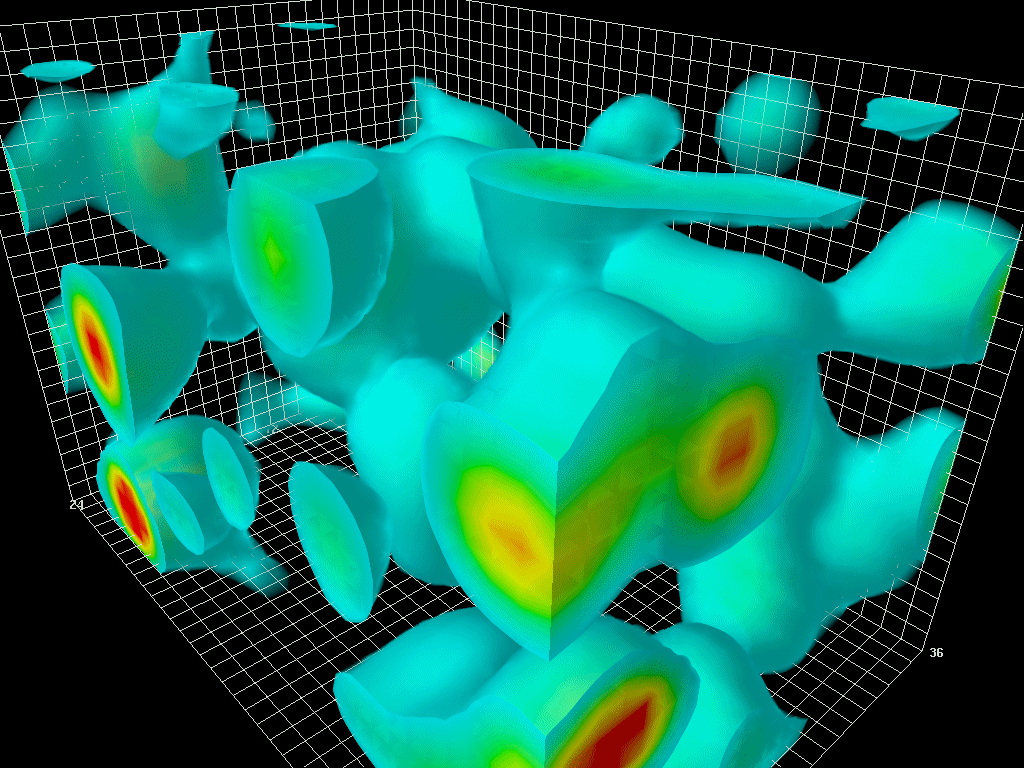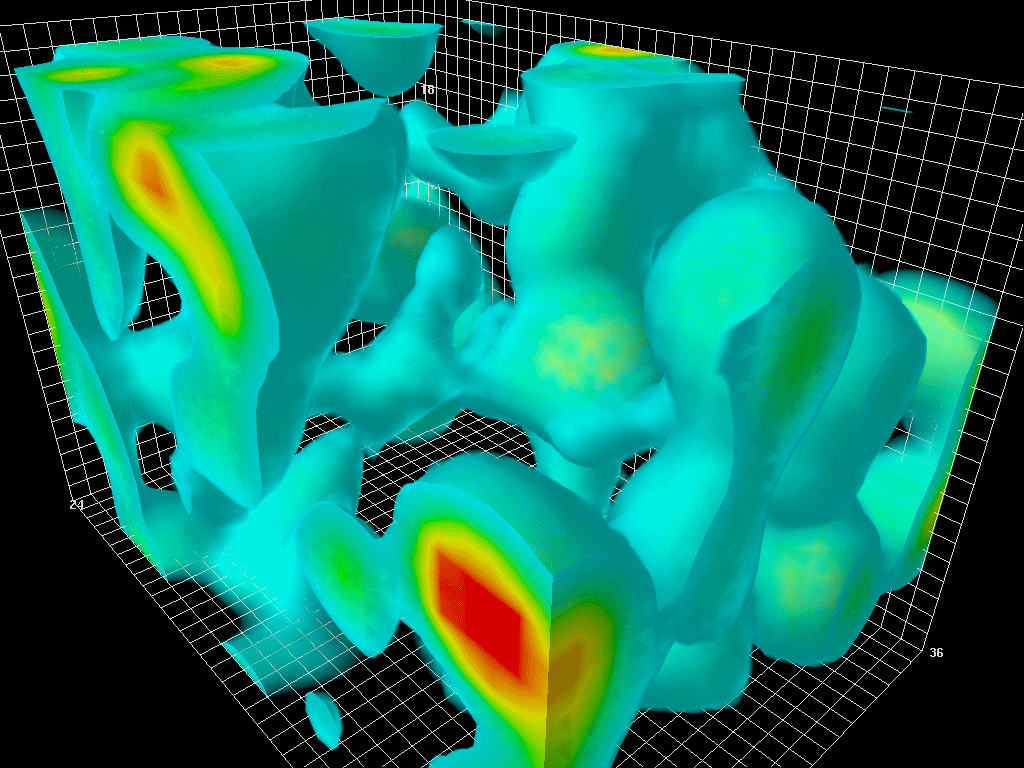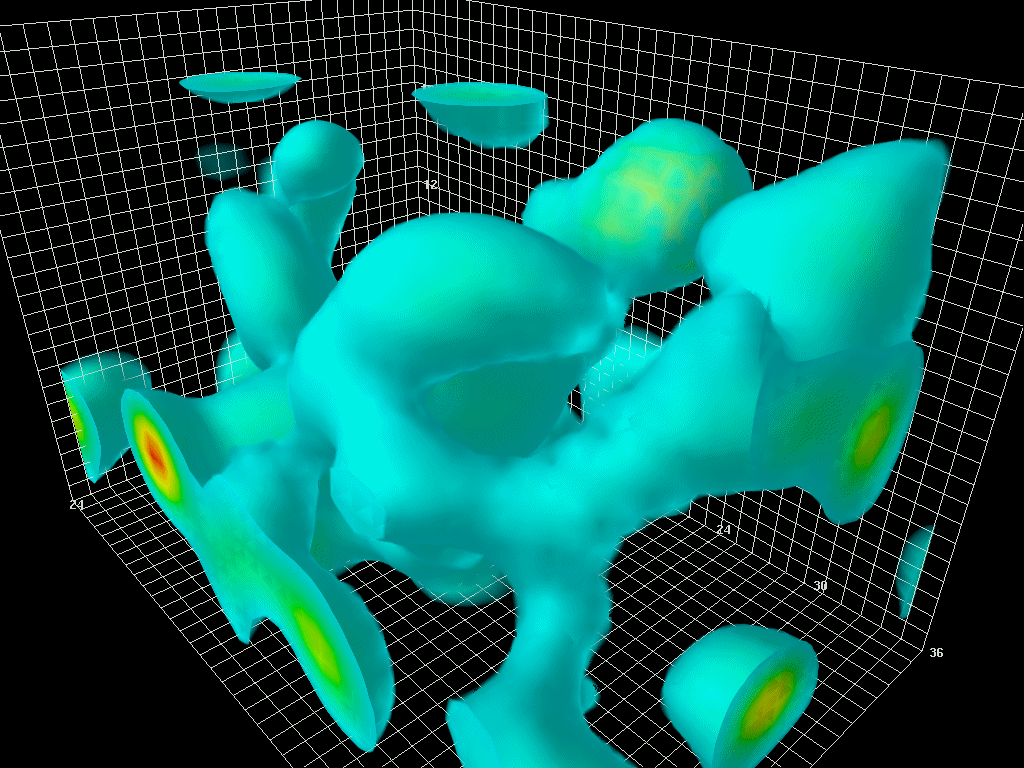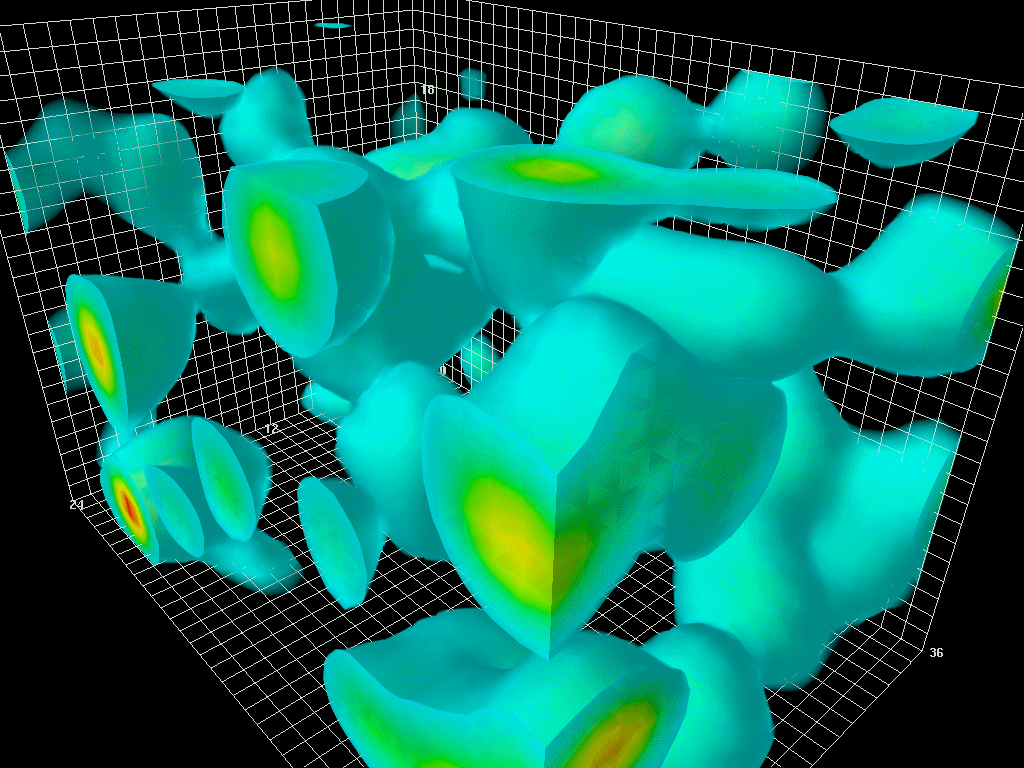
The Center for Astrophysics (CfA) Redshift Survey was the first attempt to map the large-scale structure of the universe. The first survey began in 1977 with the objective of calculating the velocities of the brighter galaxies in the nearby universe by measuring their redshifts at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The redshift is the relative increase in the wavelength emitted by a light source, in this case a galaxy, moving away from an observer from which its speed and then, using Hubble's Law, its distance can be calculated. A 3-dimensional map of that part of the Universe could thus be produced. This initial data collection was completed by 1982. The second survey (CfA2) was started in 1985 by John Huchra and Margaret Geller and measured the redshifts of 18,000 bright galaxies in the Northern sky by 1995. Data from the second CfA survey showed that galaxies were not evenly distributed but clustered on the spherical surfaces of empty " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center For Astrophysics
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Jay County, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin ** Center (community), Wisconsin * Center Township (other) * Centre Township (other) * Centre Avenue (other) * Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon) * Centre-Val de Loire, formerly Centre, France * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large-scale Structure Of The Cosmos
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these objects has had time to reach the Solar System and Earth since the beginning of the cosmological expansion. There may be 2 trillion galaxies in the observable universe, although that number was reduced in 2021 to only several hundred billion based on data from ''New Horizons''. Assuming the universe is isotropic, the distance to the edge of the observable universe is roughly the same in every direction. That is, the observable universe is a spherical region centered on the observer and is unique for every unique observational position. The word ''observable'' in this sense does not refer to the capability of modern technology to detect light or other information from an object, or whether there is anything to be detected. It refers to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observational Astronomy
Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical models. It is the practice and study of observing celestial objects with the use of telescopes and other astronomical instruments. As a science, the study of astronomy is somewhat hindered in that direct experiments with the properties of the distant universe are not possible. However, this is partly compensated by the fact that astronomers have a vast number of visible examples of stellar phenomena that can be examined. This allows for observational data to be plotted on graphs, and general trends recorded. Nearby examples of specific phenomena, such as variable stars, can then be used to infer the behavior of more distant representatives. Those distant yardsticks can then be employed to measure other phenomena in that neighborhood, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Inflation
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation, is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the early universe. The inflationary epoch lasted from seconds after the conjectured Big Bang singularity to some time between and seconds after the singularity. Following the inflationary period, the universe continued to expand, but at a slower rate. The acceleration of this expansion due to dark energy began after the universe was already over 7.7 billion years old (5.4 billion years ago). Inflation theory was developed in the late 1970s and early 80s, with notable contributions by several theoretical physicists, including Alexei Starobinsky at Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Alan Guth at Cornell University, and Andrei Linde at Lebedev Physical Institute. Alexei Starobinsky, Alan Guth, and Andrei Linde won the 2014 Kavli Prize "for pioneering the theory of cosmic inflation." It was developed further in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Fluctuation
In quantum physics, a quantum fluctuation (also known as a vacuum state fluctuation or vacuum fluctuation) is the temporary random change in the amount of energy in a point in space, as prescribed by Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. They are minute random fluctuations in the values of the fields which represent elementary particles, such as electric and magnetic fields which represent the electromagnetic force carried by photons, W and Z fields which carry the weak force, and gluon fields which carry the strong force. Vacuum fluctuations appear as virtual particles, which are always created in particle-antiparticle pairs. Since they are created spontaneously without a source of energy, vacuum fluctuations and virtual particles are said to violate the conservation of energy. This is theoretically allowable because the particles annihilate each other within a time limit determined by the uncertainty principle so they are not directly observable. The uncertainty p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of The Universe
In physical cosmology, the age of the universe is the time elapsed since the Big Bang. Astronomers have derived two different measurements of the age of the universe: a measurement based on direct observations of an early state of the universe, which indicate an age of billion years as interpreted with the Lambda-CDM concordance model as of 2018; and a measurement based on the observations of the local, modern universe, which suggest a younger age. The uncertainty of the first kind of measurement has been narrowed down to 20 million years, based on a number of studies which all show similar figures for the age and which include studies of the microwave background radiation by the ''Planck'' spacecraft, the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe and other space probes. Measurements of the cosmic background radiation give the cooling time of the universe since the Big Bang, and measurements of the expansion rate of the universe can be used to calculate its approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Collapse
Gravitational collapse is the contraction of an astronomical object due to the influence of its own gravity, which tends to draw matter inward toward the center of gravity. Gravitational collapse is a fundamental mechanism for structure formation in the universe. Over time an initial, relatively smooth distribution of matter will collapse to form pockets of higher density, typically creating a hierarchy of condensed structures such as clusters of galaxies, stellar groups, stars and planets. A star is born through the gradual gravitational collapse of a cloud of interstellar matter. The compression caused by the collapse raises the temperature until thermonuclear fusion occurs at the center of the star, at which point the collapse gradually comes to a halt as the outward thermal pressure balances the gravitational forces. The star then exists in a state of dynamic equilibrium. Once all its energy sources are exhausted, a star will again collapse until it reaches a new equilibr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
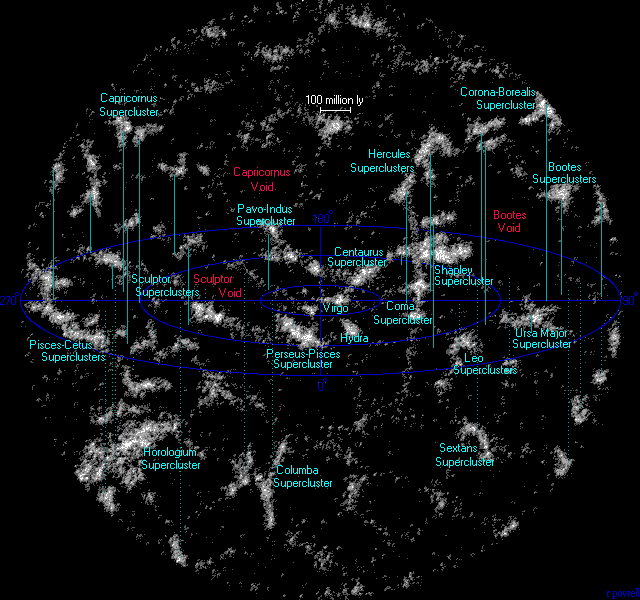
Supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster."Earth's new address: 'Solar System, Milky Way, Laniakea '''' The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the |
Redshift Survey
In astronomy, a redshift survey is a survey of a section of the sky to measure the redshift of astronomical objects: usually galaxies, but sometimes other objects such as galaxy clusters or quasars. Using Hubble's law, the redshift can be used to estimate the distance of an object from Earth. By combining redshift with angular position data, a redshift survey maps the 3D distribution of matter within a field of the sky. These observations are used to measure detailed statistical properties of the large-scale structure of the universe. In conjunction with observations of early structure in the cosmic microwave background, these results can place strong constraints on cosmological parameters such as the average matter density and the Hubble constant. Generally the construction of a redshift survey involves two phases: first the selected area of the sky is imaged with a wide-field telescope, then galaxies brighter than a defined limit are selected from the resulting images as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Wall (astronomy)
The Great Wall (also called Coma Wall), sometimes specifically referred to as the CfA2 Great Wall, is an immense galaxy filament. It is one of the largest known superstructures in the observable universe. This structure was discovered c. 1989 by a team of American astronomers led by Margaret J. Geller and John Huchra while analyzing data gathered by the second CfA Redshift Survey of the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA). Characteristics The term "Great" has been added to distinguish it as an even larger type compared to standard galaxy walls. Great walls are so rare that only five or possibly six (if the disputed Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall is counted) of them have been discovered to date. The CfA2 Great Wall has the maximum dimensions of either 500 million or 750 million light years depending on the figure and the reference used. It is 200 million light years in width and about 16 million light years in thickness. Its nearest point is about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Geller
Margaret J. Geller (born December 8, 1947) is an American astrophysicist at the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian. Her work has included pioneering maps of the nearby universe, studies of the relationship between galaxies and their environment, and the development and application of methods for measuring the distribution of matter in the universe. Career Geller made pioneering maps of large-scale structure in the universe. Geller received a Bachelor of Arts degree in Physics at the University of California, Berkeley (1970) and a Ph.D. in Physics from Princeton (1974). Geller completed her doctoral dissertation, titled "Bright galaxies in rich clusters: a statistical model for magnitude distributions", under the supervision of James Peebles. Although Geller was thinking about studying solid state physics in graduate school, Charles Kittel suggested she go to Princeton to study astrophysics. After research fellowships at the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |