|
Central Solomon Languages
The Central Solomon languages are the four Papuan languages spoken in the state of Solomon Islands. The four languages are, listed from northwest to southeast, *Bilua language, Bilua of Vella Lavella and Ghizo Island, Ghizo islands, *Touo language, Touo (also known as ''Baniata)'' of Rendova Island, *Lavukaleve language, Lavukaleve of the Russell Islands, and *Savosavo language, Savosavo of Savo Island. Classification The four Central Solomon languages were identified as a Language family, family by Wilhelm Schmidt (linguist), Wilhelm Schmidt in 1908. The languages are at best distantly related, and evidence for their relationship is meager. Dunn and Terrill (2012) argue that the lexical evidence vanishes when Oceanic loanwords are excluded. Ross (2005) and Pedrós (2015), however, accept a connection, based on similarities among pronouns and other grammatical forms. Pedrós (2015) suggests, tentatively, that the branching of the family is as follows. ;Central Solomons *Lavukal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, to the northeast of Australia. It is directly adjacent to Autonomous Region of Bougainville, Bougainville, a part of Papua New Guinea to the west, Australia to the southwest, New Caledonia and Vanuatu to the southeast, Fiji, Wallis and Futuna, and Tuvalu to the east, and Nauru and the Federated States of Micronesia to the north. It has a total area of 28,896 square kilometres (11,157 sq mi), and a population of 734,887 according to the official estimates for mid-2023. Its capital and largest city, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), Solomon Islands archipelago, which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
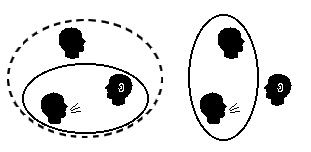
Clusivity
In linguistics, clusivity is a grammatical distinction between ''inclusive'' and ''exclusive'' first-person pronouns and verbal morphology, also called ''inclusive " we"'' and ''exclusive "we"''. Inclusive "we" specifically includes the addressee, while exclusive "we" specifically excludes the addressee; in other words, two (or more) words that both translate to "we", one meaning "you and I, and possibly someone else", the other meaning "me and some other person or persons, but not you". While imagining that this sort of distinction could be made in other persons (particularly the second) is straightforward, in fact the existence of second-person clusivity (you vs. you and they) in natural languages is controversial and not well attested. While clusivity is not a feature of the English language, it is found in many languages around the world. The first published description of the inclusive-exclusive distinction by a European linguist was in a description of languages of Peru in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Papuan Languages
The East Papuan languages is a defunct proposal for a family of Papuan languages spoken on the islands to the east of New Guinea, including New Britain, New Ireland, Bougainville, Solomon Islands, and the Santa Cruz Islands. There is no evidence that these languages are related to each other, and the Santa Cruz languages are no longer recognized as Papuan. All but two of the starred languages below ( Yélî Dnye and Sulka) make a gender distinction in their pronouns. Several of the heavily Papuanized Austronesian languages of New Britain do as well. This suggests a pre-Austronesian language area in the region. History of the proposal The East Papuan languages were proposed as a family by linguist Stephen Wurm (1975) and others. However, their work was preliminary, and there is little evidence that the East Papuan languages actually have a genetic relationship. For example, none of these fifteen languages marked with asterisks below share more than 2–3% of their basic vocab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Solomon Languages
The Central Solomon languages are the four Papuan languages spoken in the state of Solomon Islands. The four languages are, listed from northwest to southeast, *Bilua language, Bilua of Vella Lavella and Ghizo Island, Ghizo islands, *Touo language, Touo (also known as ''Baniata)'' of Rendova Island, *Lavukaleve language, Lavukaleve of the Russell Islands, and *Savosavo language, Savosavo of Savo Island. Classification The four Central Solomon languages were identified as a Language family, family by Wilhelm Schmidt (linguist), Wilhelm Schmidt in 1908. The languages are at best distantly related, and evidence for their relationship is meager. Dunn and Terrill (2012) argue that the lexical evidence vanishes when Oceanic loanwords are excluded. Ross (2005) and Pedrós (2015), however, accept a connection, based on similarities among pronouns and other grammatical forms. Pedrós (2015) suggests, tentatively, that the branching of the family is as follows. ;Central Solomons *Lavukal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm Ross (linguist)
Malcolm David Ross (born 1942) is an Australian linguist. He is the emeritus professor of linguistics at the Australian National University. Ross is best known among linguists for his work on Austronesian and Papuan languages, historical linguistics, and language contact (especially metatypy). He was elected as a Fellow of the Australian Academy of the Humanities in 1996. Career Ross served as the Principal of Goroka Teachers College in Papua New Guinea from 1980 to 1982, during which time he self-statedly become interested in local languages, and began to collect data on them. In 1986, he received his PhD from the ANU under the supervision of Stephen Wurm, Bert Voorhoeve and Darrell Tryon. His dissertation was on the genealogy of the Oceanic languages of western Melanesia, and contained an early reconstruction of Proto Oceanic. Malcolm Ross introduced the concept of a linkage, a group of languages that evolves via dialect differentiation rather than by tree-like spli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Greenhill
Simon James Greenhill is a New Zealand scientist who works on the application of quantitative methods to the study of cultural evolution and human prehistory. He is well known for creating and building various linguistics databases, including the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database, TransNewGuinea.org, Pulotu, and many others. In addition to Austronesian, he has contributed to the study of the phylogeny of many language families, including Dravidian and Sino-Tibetan. He is a graduate of University of Auckland, New Zealand. The title of his 2008 doctoral thesis is ''The archives of history: a phylogenetic approach to the study of language''. Greenhill is currently a scientist affiliated with the Australian National University in Canberra, Australia, and the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History in Jena Jena (; ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in Germany and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen C
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or " protomartyr") of the Christian Church. The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ( ); related names that have found some currency or significance in English include Stefan (pronounced or in English), Esteban (often pronounced ), and the Shakespearean Stephano ( ). Origins The name "Stephen" ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ger Reesink
Gerard P. Reesink (more commonly known as Ger Reesink) is a Dutch linguist who specializes in Papuan languages. Education He studied psychology at Utrecht University. He obtained his PhD in linguistics at the University of Amsterdam, where he completed his dissertation ''Structures and their functions in Usan, a Papuan language of Papua New Guinea''. Research In the 1990s, he researched the languages of the Bird's Head Peninsula as part of ''The Irian Jaya Studies: Program for Interdisciplinary Research'' (ISIR), which resulted in publications such as ''A grammar of Hatam'' (1999) and ''Languages of the eastern Bird's Head'' (2002). He also dealt with Papuan-Austronesian language contact in eastern Indonesia. Publications * '' West Papuan languages'' (2006) * ''East Nusantara as a linguistic area (2008)'' * ''Genetic and linguistic coevolution in northern Island Melanesia'' (2008) ;Pacific Linguistics Pacific Linguistics was established in 1963 as a non-profit publisher at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temotu Languages
The Temotu languages, named after Temotu Province of the Solomon Islands, are a branch of Oceanic languages proposed in Ross & Næss (2007) to unify the Reefs – Santa Cruz languages with Utupua and Vanikoro, each a group of three related languages. Utupua and Vanikoro were formerly classified together as the Utupua–Vanikoro languages or Eastern Outer Islands languages (see ). History of classification The Reefs-Santa Cruz languages had previously been considered Papuan, but Ross & Næss (2007) established that their closest relatives were the Utupua–Vanikoro languages, previously thought to be Central–Eastern Oceanic. However, Roger Blench (2014) argues that the aberrancy of Utupua and Vanikoro, which he considers to be separate branches that do not group with each other, is due to the fact that they are actually non-Austronesian languages. Blench (2014) doubts that Utupua and Vanikoro are closely related, and argues that thus they should not be grouped together. Sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SVO Word Order
SVO may refer to: * Association football clubs in Germany: ** SVO Germaringen ** SV Oberachern * Silver vanadium oxide battery (SVO battery) * San Jose Chamber of Commerce, a chamber of commerce in San Jose, California, United States, known as the Silicon Valley Organization (SVO) from 2017–2021 * Saturn Valley Online, an ''EarthBound'' MMORPG * SVO, save opportunity in baseball statistics * Sheremetyevo International Airport, of three major airports serving Moscow, Russia (IATA Airport Code: SVO) * Servicios Aeronáuticos de Oriente, former Mexican charter airline (ICAO code: SVO) * Small Veblen ordinal, a large countable ordinal * Social value orientations, a psychological construct * Sparse voxel octree, an algorithm for computer graphics rendering * Special Vehicle Operations, a subsidiary of Ford Motor Company ** Ford Mustang SVO, a car developed by Ford's SVO USA ** EA Falcon SVO, a sedan by Ford's SVO Australia * Special military operation (), a euphemism for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SOV Word Order
SOV may refer to: * SOV, a former ticker symbol for Sovereign Bank * SOV, a legal cryptocurrency created by the Sovereign Currency Act of 2018 of the Republic of the Marshall Islands * SOV, the National Rail station code for Southend Victoria railway station, Southend-on-Sea, England * SO Voiron, a French rugby union club * Schedule of values * Shot-on-video film * Single-occupancy vehicle * Subject–object–verb, used in linguistic typology * Symphony Orchestra Vorarlberg, an Austrian orchestra * Share of voice * Sorin Ovidiu Vântu, a Romanian business man * Store of value A store of value is any commodity or asset that would normally retain purchasing power into the future and is the function of the asset that can be saved, retrieved and exchanged at a later time, and be predictably useful when retrieved. The most ... * Strenght of victory, the combined record of all teams beaten in a schedule in the NFL {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |