|
Cattle Grid In Israel
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are called cows and mature male cattle are bulls. Young female cattle are called heifers, young male cattle are oxen or bullocks, and castrated male cattle are known as steers. Cattle are commonly raised for meat, for dairy products, and for leather. As draft animals, they pull carts and farm implements. Cattle are considered sacred animals within Hinduism, and it is illegal to kill them in some Indian states. Small breeds such as the miniature Zebu are kept as pets. Taurine cattle are widely distributed across Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus are found mainly in India and tropical areas of Asia, America, and Australia. Sanga cattle are found primarily in sub-Saharan Africa. These types, sometimes classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleckvieh
The Fleckvieh (, ) is a List of cattle breeds, breed of dual-purpose cattle suitable for both dairy cattle, milk and beef cattle, meat production. It originated in Central Europe in the 19th century from cross-breeding of local stock with Simmental (cattle), Simmental cattle imported from Switzerland. Today, the worldwide population is 41 million animals. History The Fleckvieh originated in the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Bavaria from cross-breeding of local stock with Simmental (cattle), Simmental cattle imported from Switzerland from about 1830. The Simmental had good dairy cattle, milk-producing and Working animal, draught qualities, and the resulting crosses were triple-purpose animals with milk, meat, and draught capabilities. The Fleckvieh is now a dual-purpose breed; it may be used for the production of beef or milk, or be crossed with dairy breeds or with beef breeds. It is reported from several European countries, including Austria, Belgium, Germany, the Nethe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle Slaughter In India
Cattle slaughter in India refers to the slaughter and consumption of Bovinae, bovine species in India. A controversial phenomenon due to cattle's status as adored and respected beings to adherents of Dharmic religions like Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism. Though it is an acceptable source of meat in Abrahamic religions such as Islam in India, Islam, Christianity in India, Christianity, and Indian Jews, Judaism, most Indian people, Indian citizens abstain from consuming beef due to cattle's high regard in Dharma, Dharmic divinity. The association reflects the importance of cows in Hindu and Jain culture and spirituality, as cattle have been an integral part of rural Livelihood, livelihoods as an economic necessity across Hindu, Jain, and Buddhist societies, along with council-hoods in India. Cattle slaughter has also been opposed by various Indian religions because of the ethical principle of Ahimsa (non-violence) & the belief in the unity of all life. Legislation agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Norman Language
Anglo-Norman (; ), also known as Anglo-Norman French, was a dialect of Old Norman that was used in Kingdom of England, England and, to a lesser extent, other places in Great Britain and Ireland during the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman period. Origin The term "Anglo-Norman" harks back to the time when the language was regarded as being primarily the regional dialect of the Norman settlers. Today the generic term "Anglo-French" is used instead to reflect not only the broader origin of the settlers who came with William the Conqueror, but also the continued influence of Parisian French from the House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet period onwards. According to some linguists, the name Insular French might be more suitable, because "Anglo-Norman" is constantly associated with the notion of a mixed language based on English and Norman. According to some, such a mixed language never existed. Other sources, however, indicate that such a language did exist, and that it was the language desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Genome
The genome of a female Hereford cow was published in 2009. It was sequenced by the Bovine Genome Sequencing and Analysis Consortium, a team of researchers led by the National Institutes of Health and the U.S. Department of Agriculture. It was part of an effort to improve livestock breeding and at the time was one of the largest genomes ever sequenced. Genome The size of the bovine genome is 2.7 Gb (2.7 billion base pairs). It contains approximately 35,092 genes of which 14,000 are common to all mammalian species. Bovines share 80 percent of their genes with humans; cows are less similar to humans than rodents (humans and rodents belong to the clade of Supraprimates) and dogs (humans and dogs belong to the clade of Boreoeutheria). They also have about 1,000 genes shared with dogs and rodents but not identified in humans. The charting of key DNA differences, also known as haplotypes, between several varieties of cattle could allow scientists to understan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
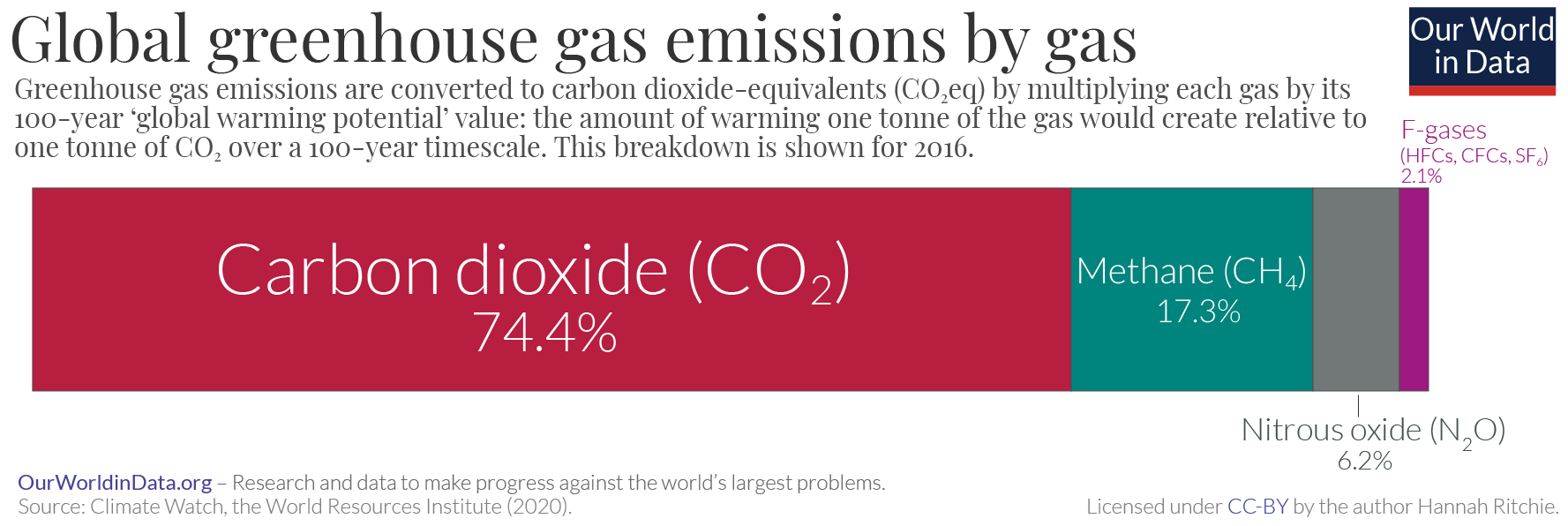
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan. (subscription required) Although the terms "Indian subcontinent" and "South Asia" are often also used interchangeably to denote a wider region which includes, in addition, Bhutan, the Maldives, Nepal and Sri Lanka, the "Indian subcontinent" is more of a geophysical term, whereas "South Asia" is more geopolitical. "South Asia" frequently also includes Afghanistan, which is not considered part of the subcontinent even in extended usage.Jim Norwine & Alfonso González, ''The Third World: states of mind and being'', pages 209, Taylor & Francis, 1988, Quote: ""The term "South Asia" also signifies the Indian Subcontinent""Raj S. Bhopal, ''Ethnicity, race, and health in multicultural societies'', pages 33, Oxford University Press, 2007, ; Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Iran
Western Iran consists of Armenian Highlands, northern Zagros and the rich agricultural area of the Khuzestan Plain in the south. It includes the provinces of Kordestan, Kermanshah Province, Kermanshah, Ilam Province, Ilam, Lorestan, and Hamadan Province, Hamadan. Some references also count West Azerbaijan Province and Khuzestan Province to this region. The major cities are Sanandaj, Kermanshah, Ilam, Iran, Ilam, Khorramabad, Hamadan, sometimes Urmia and Ahvaz. Climate *Humid continental climate in the north. *Hot-summer Mediterranean climate in the north. *BSk, cold semi-arid climate in the Zagros mountains. *Humid continental climate, Warm summer continental climate all over the central mountain ranges. *BWh, Hot desert climate in Khuzestan. See also * Northern Iran * Southern Iran * Eastern Iran * Central Iran * Northwestern Iran References {{Reflist Subdivisions of Iran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in Western AsiaGasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. p. 5: "... today the term ''Levantine'' can describe shared cultural products, such as Levantine cuisine or Levantine archaeology". .Steiner & Killebrew, p9: "The general limits ..., as defined here, begin at the Plain of 'Amuq in the north and extend south until the Wâdī al-Arish, along the northern coast of Sinai. ... The western coastline and the eastern deserts set the boundaries for the Levant ... The Euphrates and the area around Jebel el-Bishrī mark the eastern boundary of the northern Levant, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius''; or ; pl.: aurochs or aurochsen) is an extinct species of Bovini, bovine, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of the largest herbivores in the Holocene; it had massive elongated and broad horns that reached in length. The aurochs was part of the Pleistocene megafauna. It probably evolved in Asia and migrated west and north during warm interglacial periods. The oldest-known aurochs fossils date to the Middle Pleistocene. The species had an expansive range spanning from Western Europe and North Africa to the Indian subcontinent and East Asia. The distribution of the aurochs progressively contracted during the Holocene due to habitat loss and hunting, with the last known individual dying in the Jaktorów forest in Poland in 1627. There is a long history of interaction between aurochs and humans, including archaic hominins like Neanderthals. The aurochs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cattle Breeds
Over 1000 breeds of cattle are recognized worldwide, some of which adapted to the local climate, others which were bred by humans for specialized uses. Cattle breeds fall into two main types, which are regarded as either two closely related species, or two subspecies of one species. ''Bos indicus'' (or '' Bos taurus indicus'') cattle, commonly called zebu, are adapted to hot climates and originated in the tropical parts of the world such as India, Sub-saharan Africa, China, and Southeast Asia. ''Bos taurus'' (or '' Bos taurus taurus''), typically referred to as "taurine" cattle, are generally adapted to cooler climates and include almost all cattle breeds originating from Europe and northern Asia. In some parts of the world further species of cattle are found (both as wild and domesticated animals), and some of these are related so closely to taurine and indicus cattle that interspecies hybrids have been bred. Examples include the Dwarf Lulu cattle of the mountains of Nepal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and dependent territories in Africa, African countries and territories that are situated fully in that specified region, the term may also include polities that only have part of their territory located in that region, per the definition of the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations (UN). This is considered a non-standardised geographical region with the number of countries included varying from 46 to 48 depending on the organisation describing the region (e.g. United Nations, UN, World Health Organization, WHO, World Bank, etc.). The Regions of the African Union, African Union (AU) uses a different regional breakdown, recognising all 55 member states on the continent—grouping them into five distinct and standard regions. The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |