|
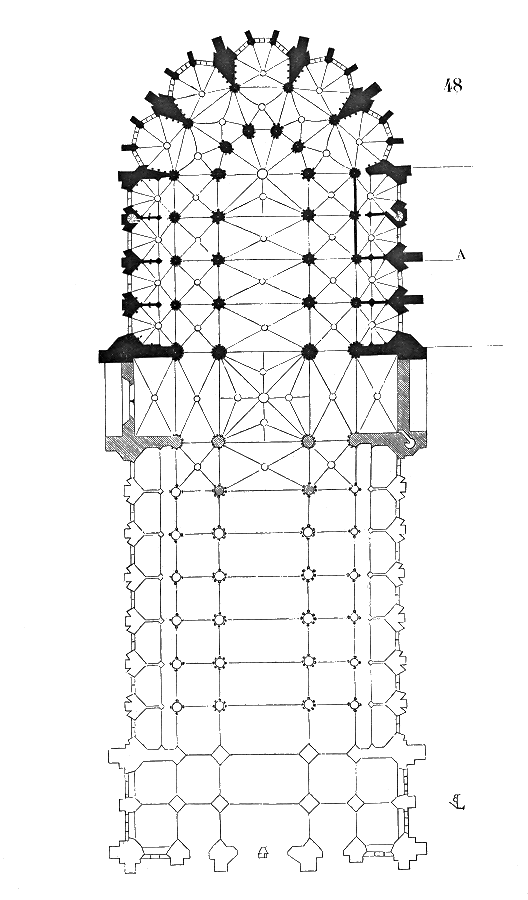
Cathédrale Saint-Étienne De Toulouse
Toulouse Cathedral () is a Roman Catholic church located in the city of Toulouse, France. The cathedral is a national monument, and is the seat of the Archbishop of Toulouse. It has been listed since 1862 as a ''monument historique'' by the French Ministry of Culture. cathédrale Saint-Etienne History The Romanesque cathedral The cathedral is said to have been built atop the foundations of a chapel constructed in the 3rd century by Saint Saturnin, sent to Christianize the Gauls and martyred in Toulouse. It is said to have been reconstructed by Saint Exuperius, Bishop of Toulouse, one hundred and fifty years later. This first documented cathedral is recorded at the beginning of the 5th century, but nothing remains of the original building. A Romanesque cathedral was constructed on the same site beginning in about 1078. The Romanesque structure was smaller than the present church; it was probably about twenty meters wide and 85 meters long. It probably had a massive west front w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and from Paris. It is the List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, fourth-largest city in France after Paris, Marseille and Lyon, with 511,684 inhabitants within its municipal boundaries (2022); its Functional area (France), metropolitan area has a population of 1,513,396 inhabitants (2022). Toulouse is the central city of one of the 22 Métropole, metropolitan councils of France. Between the 2014 and 2020 censuses, its metropolitan area was the third fastest growing among metropolitan areas larger than 500,000 inhabitants in France. Toulouse is the centre of the European aerospace industry, with the headquarters of Airbus, the SPOT (satellites), SPOT satellite system, ATR ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monument Historique
() is a designation given to some national heritage sites in France. It may also refer to the state procedure in France by which national heritage protection is extended to a building, a specific part of a building, a collection of buildings, a garden, a bridge, or other structure, because of their importance to France's architectural and historical cultural heritage. Both public and privately owned structures may be listed in this way, as well as movable objects. there were 44,236 monuments listed. The term "classification" is reserved for designation performed by the French Ministry of Culture for a monument of national-level significance. Monuments of lesser significance may be "inscribed" by various regional entities. Buildings may be given the classification (or inscription) for either their exteriors or interiors. A monument's designation could be for a building's décor, its furniture, a single room, or even a staircase. An example is the classification of the déco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narbonne Cathedral
Narbonne Cathedral (''Cathédrale Saint-Just-et-Saint-Pasteur de Narbonne'') is a Roman Catholic church located in the town of Narbonne, France. The cathedral is a national monument and dedicated to Saints Justus and Pastor. It was the seat of the Archbishop of Narbonne until the Archbishopric was merged into the Diocese of Carcassonne under the Concordat of 1801. (The title, however, passed to the Archbishop of Toulouse.) The church was declared a minor basilica in 1886. It is now a co-cathedral of the Diocese of Carcassonne and Narbonne, as it has been since 2006. The building, begun in 1272, is noted for being unfinished. History The cathedral is situated in the heart of the present city of Narbonne, but in the Middle Ages was located by the city wall. This placement was due to a long history of the site as a place of worship. In 313, just after the Edict of Milan, a Constantinian basilica was erected on approximately the same spot as the present cathedral. Ruined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayonnant
Rayonnant was a very refined style of Gothic Architecture which appeared in France in the 13th century. It was the defining style of the High Gothic period, and is often described as the high point of French Gothic architecture."Encylclopaedia Britannica" on-line, ""Rayonnant" (by subscription) retrieved April 2024 French architects turned their attention from building cathedrals of greater size and height towards bringing greater light into the cathedral interiors and adding more extensive decoration. The architects made the vertical columns and supports thinner, made extensive use of pinnacles and moldings. They combined the triforium gallery and the clerestory into single space and filled it with stained glass. They made extensive use of moldings and bar tracery to decorate the exteriors and interiors. The most prominent features of the Rayonnant style were the enormous rose windows installed in the transepts and facades, made possible by the use of bar tracery. The desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Gothic
High Gothic was a period of Gothic architecture in the 13th century, from about 1200 to 1280, which saw the construction of a series of refined and richly decorated cathedrals of exceptional height and size. It appeared most prominently in France, largely thanks to support given by King Louis IX (), also known as Saint Louis."High Gothic", Encyclopaedia Britannica on-line (by subscription) retrieved February 2024 The goal of High Gothic architects was to bring the maximum possible light from the stained glass windows, and to awe the church goers with lavish decoration. High Gothic is often described as the high point of the Gothic style. High Gothic was a period, rather than a specific style; during the High Gothic period, the Rayonnant style was predominant. Notable High Gothic cathedrals in the Rayonnant style included Reims Cathedral, Amiens Cathedral, Bourges Cathedral, Chartres Cathedral, and Beauvais Cathedral. The Innovations during the High Gothic period included the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertrand De L'Isle-Jourdain (bishop Of Toulouse)
Bertrand de L'Isle-Jourdain (1227–1286) was the bishop of Toulouse from 1270 until his death. Bertrand was a son of Bernard Jordan, the lord of L'Isle-Jourdain, and Indie, an illegitimate daughter of Count Raymond V of Toulouse. He was born after the death of his father in 1227. In accordance with his father's will, he was given to the cathedral of Toulouse to be raised by the church. He was serving the cathedral as provost when Bishop Raymond du Fauga died on 19 October 1270.Odette Pontal"De la défense à la pastorale de la foi: les épiscopats de Foulque, Raymond du Fauga et Bertrand de l'Isle-Jourdain à Toulouse" ''Cahiers de Fanjeaux'' 20 (1985): 175–197, at 192–193. Bertrand was unanimously elected to succeed Raymond. He was ordained a priest two days before his consecration as bishop. He joined the Order of Saint Augustine.Patrice Cabau"Les évêques de Toulouse (IIIe–XIVe siècles) et les lieux de leur sépulture: seconde partie" ''Mémoires de la Société ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Toulouse
The count of Toulouse (, ) was the ruler of Toulouse during the 8th to 13th centuries. Originating as vassals of the Frankish kings, the hereditary counts ruled the city of Toulouse and its surrounding county from the late 9th century until 1270. The counts and other family members were also at various times counts of Quercy, Rouergue, Albi, and Nîmes, and sometimes margraves (military defenders of the Holy Roman Empire) of Septimania and Provence. Count Raymond IV founded the Crusader state of Tripoli, and his descendants were also counts there. They reached the zenith of their power during the 11th and 12th centuries, but after the Albigensian Crusade the county fell to the kingdom of France, nominally in 1229 and '' de facto'' in 1271. Later the title was revived for Louis Alexandre, Count of Toulouse, a bastard of Louis XIV (1678–1737). History Carolingian era During the youth of young Louis the Pious his tutor, Torson (sometimes Chorso or Choson), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern French Gothic
Southern French Gothic, or Meridional Gothic (), is a specific and militant style of Gothic architecture developed in the South of France, especially in the Toulouse region. It arose in the early 13th century following the victory of the Catholic church over the Cathars, as the church sought to re-establish its authority in the region. As a result, church buildings typically present features drawn from military architecture. Taking into account the Cathars' criticism of the Catholic Church, Southern French Gothic is simpler and less ornate than northern French Gothic, and further differs in that the construction material is typically brick rather than stone. Over time, the style came to influence secular buildings as well as churches and spread beyond the area where Catharism had flourished. Origins During the rise of Catharism, the luxury of the Roman Catholic Church faced constant criticism by the Cathar ecclesiastics. After the political eradication of the Cathar aristocracy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |