|
Catherine Downes
Catherine Downes () was an English antiquarian and archaeologist, who excavated a Roman villa near Warminster, Wiltshire, in 1786. Downes is a significant figure in the early history of archaeology, since she was one of the first women antiquarians to excavate a Roman site; the other was Frances Stackhouse Acton. Downes is also one of the earliest recorded women who contributed to the work of the Society of Antiquaries of London. Pit Mead Roman villa Downes initially learnt of the find by a farmworker through an article in the ''Salisbury Journal,'' she then employed an assistant and gained permission to excavate. The site was located at a place called Pit Mead, just outside Warminster, on land owned by Lord Weymouth. The investigations revealed four mosaics, a bath house and a range of finds. The finds included pottery, coins, bone and metal objects and an ivory bodkin. The mosaic illustrated by Downes and Basire was removed from the site and taken to Longleat, as of 2021 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pit Mead Roman Villa Mosaic, Illustration By Catherine Downes
Pit or PIT may refer to: Structure * Ball pit, a recreation structure * Casino pit, the part of a casino which holds gaming tables * Trapping pit, pits used for hunting * Pit (motor racing), an area of a racetrack where pit stops are conducted * Trading pit, a part of a trading floor where open outcry takes place * Pit cave, a natural cave containing a vertical shaft * Mine (mining) ** Open-pit mine, surface extraction of rock or minerals ** Coal mine or pit Science and technology * Pit, an excavation on metallic surface caused by pitting corrosion * Pit, one of many indentations used to store data on a compact disc * Pit, a seed inside a fruit; for example a cherry pit * Pit (nuclear weapon), the core of an implosion weapon * Powered industrial truck, a US legal term * Programmable interval timer, a computing device * Pulsed inductive thruster, a device used in spacecraft propulsion * Pit (botany), a part of plant cell walls which allows the exchange of fluids * Pyrena, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daines Barrington
Daines Barrington, FRS, FSA (1727/2814 March 1800) was an English lawyer, antiquary and naturalist. He was one of the correspondents to whom Gilbert White wrote extensively on natural history topics. Barrington served as a Vice President of the Royal Society and wrote on a range of topics related to the natural sciences including early ideas and scientific experimentation on the learning of songs by young birds. He designed a standard format for the collection of information about weather, the flowering of plants, the singing of birds and other annual changes that was also used by Gilbert White. He also wrote on child geniuses including Mozart, who at the age of nine had visited England. Early life and legal career Barrington was the fourth son of John Barrington, 1st Viscount Barrington. He matriculated at The Queen's College, Oxford, in 1745, but never graduated. In the same year he was admitted to the Inner Temple, and was called to the bar in 1750. He subsequently held va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century English Women
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women Illustrators
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men. Throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Warminster
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Women Archaeologists
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *'' Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Death Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetusta Monumenta
''Vetusta Monumenta'' is the title of a published series of illustrated antiquarian papers on ancient buildings, sites and artefacts, mostly those of Britain, published at irregular intervals between 1718 and 1906 by the Society of Antiquaries of London. The folio-sized papers, usually written by members of the society, were first published individually, and then later in collected volumes. Publication The full title is ''Vetusta monumenta quae ad Rerum Britanicarum memoriam conservandam Societas Antiquariorum Londini sumptu suo edenda curavit'', but the volumes are normally simply cited as ''Vetusta Monumenta''. There were various reprints of both individual papers and collected volumes, and the plates were often published separately from the text. According to the HOLLIS database at Harvard: "The seven volumes are dated 1747, 1789, 1796, 1815, 1835, 1883 and 1906 (for the fourth part of vol. 7). The plates for vol. 1 were published between 1718 and 1747; plates for vol. 2 wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Basire
James Basire (1730–1802 London), also known as James Basire Sr., was a British engraver. He is the most significant of a family of engravers, and noted for his apprenticing of the young William Blake. Early life His father was Isaac Basire (1704–1768), a cartographer, his son (1769–1822) and grandson (1796–1869) were also named James; these four generations of Basires were all engravers. Their longevity produced overlapping careers, which has led to difficulties in attribution of some works. Career A member of the Society of Antiquaries, James Basire specialized in prints depicting architecture. His studio was on Great Queen Street in London. His appointment as engraver to the society, as were all three generations, and much of his finest work is found in '' Vetusta Monumenta''. A major piece was his copperplate for ''Field of the Cloth of Gold'', an exquisitely detailed translation of a watercolour by Edward Edwards; this oversize historical print was issued on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
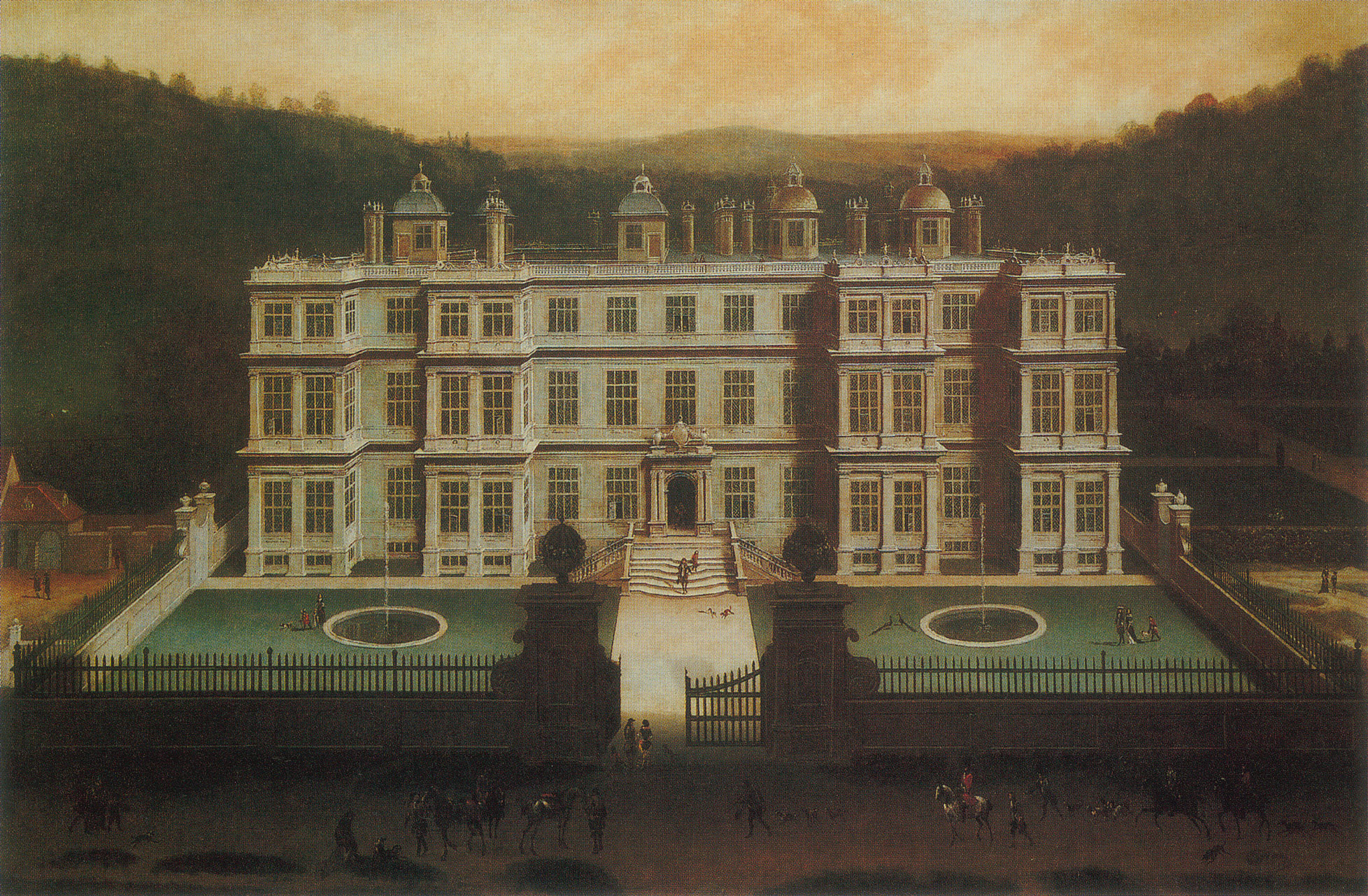
Longleat
Longleat is an English stately home and the seat of the Marquesses of Bath. A leading and early example of the Elizabethan prodigy house, it is adjacent to the village of Horningsham and near the towns of Warminster and Westbury in Wiltshire, and Frome in Somerset. The Grade I listed house is set in of parkland landscaped by Capability Brown, with of let farmland and of woodland, which includes a Center Parcs holiday village. It was the first stately home to open to the public, and the Longleat estate has the first safari park outside Africa and other attractions including a hedge maze. The house was built by Sir John Thynne and designed mainly by Robert Smythson, after Longleat Priory was destroyed by fire in 1567. It took 12 years to complete and is widely regarded as one of the finest examples of Elizabethan architecture in Britain. It continues to be the seat of the Thynn family, who have held the title of Marquess of Bath since 1789; the eighth and present Marque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English People
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language, a West Germanic language, and share a common history and culture. The English identity is of Anglo-Saxon origin, when they were known in Old English as the ('race or tribe of the Angles'). Their ethnonym is derived from the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples who migrated to Great Britain around the 5th century AD. The English largely descend from two main historical population groups the West Germanic tribes (the Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians) who settled in southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Romans, and the partially Romanised Celtic Britons already living there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons. Nat Commun 7, 10326 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10326 Collectively known as the Anglo-Saxons, they founded what was to become the Kingdom of England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_1938.jpg)

.jpg)