|
Castulo
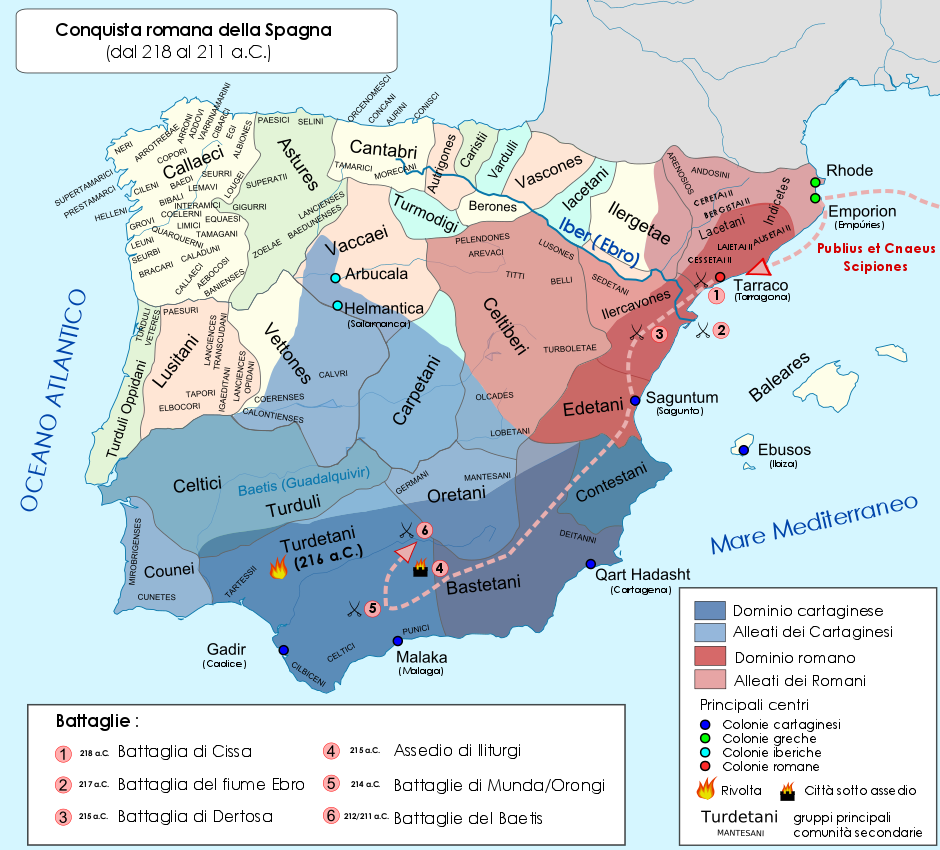
Castulo (Latin: ''Castulo''; Iberian: ''Kastilo'') was an Iberian town and bishopric (now Latin titular see located in the Andalusian province of Jaén, in south-central Spain, near modern Linares. History Evidence of human presence since the Neolithic period has been found there. It was the seat of the Oretani, an Iberian tribe which settled in the vicinity in the north of the Guadalquivir River beginning in the sixth century BC. According to tradition, a local princess named Himilce married Hannibal, gained the alliance of the city with the Carthaginian Empire. It probably is the place of the ancient Castax (). In 211 BC, Castulo was the site of Hasdrubal Barca's crushing victory over the Roman army with a force of roughly 40,000 Carthaginian troops plus local Iberian mercenaries. Thereafter the Romans made a pact with the residents of city — who then betrayed the Carthaginians — and they became foederati (allied people) of Rome. According to Livy, the inhab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of The Upper Baetis
The Battle of the Upper Baetis was a double battle, comprising the battles of Castulo and Ilorca, fought in 211 BC during the Second Punic War between a Carthaginian force led by Hasdrubal Barca (Hannibal's brother) and a Roman force led by Publius Cornelius Scipio and his brother Gnaeus. The immediate result was a Carthaginian victory in which both Roman brothers were killed. Before this defeat, the brothers had spent seven years (218–211 BC) campaigning against the Carthaginians in Hispania, thus limiting the resources available to Hannibal, who was simultaneously fighting the Romans in Italy. Background After the defeat of Hasdrubal Barca in the Battle of Dertosa in the spring of 215 BC, the Romans had secured their bases north of the Ebro. They then proceeded to win over some Iberian tribes in the region. Both the Romans and Carthaginians faced and put down Iberian tribal revolts. The Scipios received no reinforcement from Italy, where Hannibal had the Romans hard pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Illiturgis
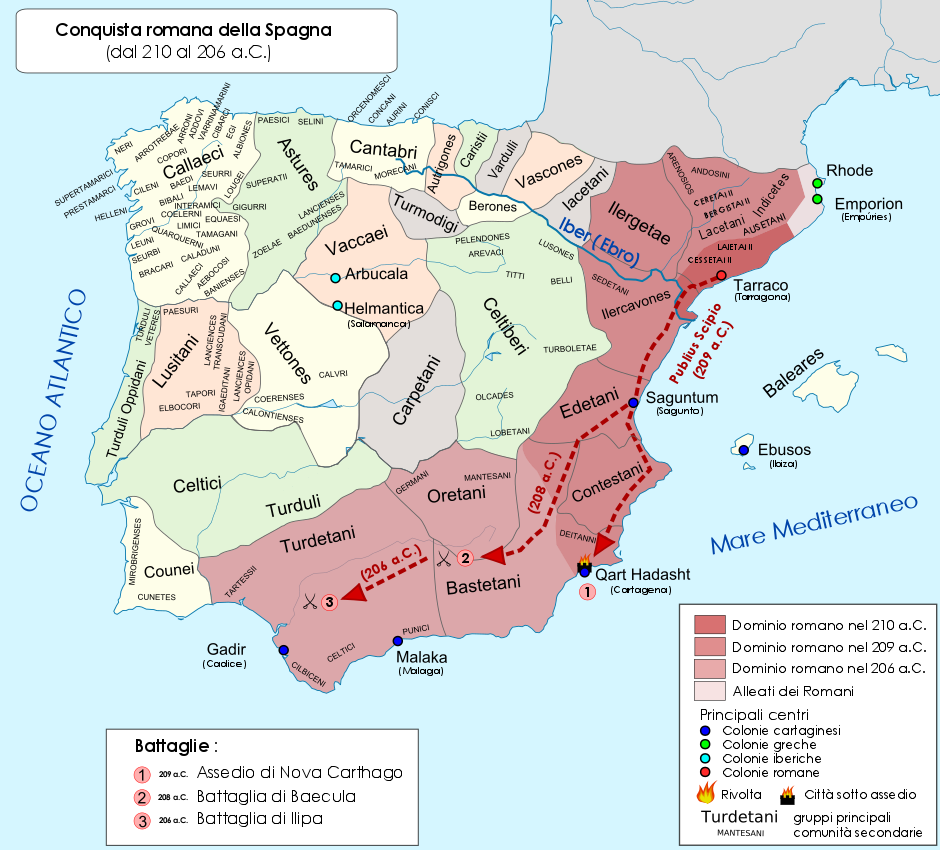
Illiturgis, also known as Iliturgi, was a city in Spain during antiquity, located on the road from Córdoba, Andalusia, Corduba to Castulo. Originally, it was located near the site of Mengíbar, but when it was destroyed the populace was relocated near present-day Andújar. It had the surname of ''Forum Julium'' during Roman Empire, Roman times. During the Second Punic War, it sided with the Romans, and was besieged by the Carthaginians. However, the sieges were raised. When the two Scipios, Publius Cornelius Scipio (consul 218 BC), Publius and Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus, Calvus, were overthrown, Illiturgis and Castulo sided with the Carthaginians. In addition, according to Roman sources, the citizens of Illiturgis are said to have executed the Romans who had fled to the city for refuge during the war. Scipio Africanus stormed the city in 206 BC and burnt the corpses of the slaughtered townspeople. (see below a detailed description of events during the Second Punic War). As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oretani
The Oretani or Oretanii (Greek: ''Orissioi'') were a pre-Roman ancient Iberian people (in the geographical sense) of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania) that lived in northeastern Andalusia, in the upper Baetis (Guadalquivir) river valley, eastern Marianus Mons (Sierra Morena), and the southern area of present-day La Mancha. Origins They could have been an Iberian tribe, a Celtic one, or a mixed Celtic and Iberian tribe or tribal confederacy (and hence related to the Celtiberians). The Mantesani/ Mentesani/ Mantasani of present-day La Mancha and the Germani (of Oretania) in eastern Marianus Mons (Sierra Morena) and west Jabalón river valley are sometimes included in the Oretani, but it is not certain if they were Oretani tribes. Territory Oretania, the country of the Oretani, was located in the eastern Sierra Morena, which included most of the province of Ciudad Real except its western end, the northern section of the province of Jaén, the western half of the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet ''Africanus'', literally meaning 'the African', but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa (Roman province), Africa. Scipio's conquest of Carthaginian Iberia culminated in the Battle of Ilipa in 206 BC against Hannibal's brother Mago Barca. Although considered a hero by the Roman people, primarily for his victories against Carthage, Scipio had many opponents, especially Cato the Elder, who hated him deeply. In 187 BC, he was tried in a show trial alongside his brother for bribes they supposedly received from the Seleucid king Antiochus III ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Linares, Jaén
Linares () is a Municipalities in Spain, municipality of Spain belonging to the Jaén (Spanish province), province of Jaén, Andalusia. It is the second-largest city in that province, with a population of 55,261 in the most recent census (2024). The altitude is and the total area of the municipality is . Overview Location Located in the west-central section of the province, the city of Linares is the second-largest city in the province after the capital, Jaén, Spain, Jaén. It is also the commercial capital of Sierra Morena, as well as the referential city in the surrounding areas. Geography The city territory is oriented in a northeast-southwest direction, with the altitude decreasing between the higher northern area of Sierra Morena; Paño Pico, at an elevation of 552 m is the highest area of the municipal territory; and the lowest area, the Guadalimar Valley in the southwestern section, has an altitude of 318 m. Geology Linares is located in the area where two of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War. Hannibal's father, Hamilcar Barca, was a leading Carthaginian general during the First Punic War. His younger brothers were Mago Barca, Mago and Hasdrubal Barca, Hasdrubal; his brother-in-law was Hasdrubal the Fair, who commanded other Carthaginian armies. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the Mediterranean Basin, triggered by the emergence of the Roman Republic as a great power with its defeat of Carthage in the First Punic War. Revanchism prevailed in Carthage, symbolized by the pledge that Hannibal made to his father to "never be a friend of Rome". In 218 BC, Hannibal attacked Saguntum (modern Sagunto, Spain), an ally of Rome, in Hispania, sparking the Second Punic War. Hannibal invaded Italy by Hannibal's crossing of the Alps, cross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Himilce
Imilce or Himilce was the Iberian wife of Hannibal Barca according to a number of historical sources. History Livy records that Hannibal married a woman from Castulo, a powerful Iberian city allied with Carthage., by Livy The Roman poet Silius Italicus identifies this woman as Imilce. Silius suggests a Greek origin for Imilce, but Gilbert Charles-Picard argued for a Punic heritage based on an etymology from the Semitic root m-l-k ('chief', 'king'). Silius also suggests the existence of a son,Silius Italicus, ''Punica'', III, 63-64 who is otherwise not attested by Livy, Polybius, or Appian. The son is thought to have been named Haspar or Aspar. According to Silius, during the Punic wars Hannibal tearfully sent Imilce and their son back to Carthage for their safety. Some historians have questioned the historicity of this event and suggested that it is an imitation of Pompey sending his wife away to Lucca for her safety during military conflict. Cultural depictions Imilce is ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iberians
The Iberians (, from , ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (among others, by Hecataeus of Miletus, Avienius, Herodotus and Strabo). Roman sources also use the term ''Hispani'' to refer to the Iberians. The term ''Iberian'', as used by the ancient authors, had two distinct meanings. One, more general, referred to all the populations of the Iberian peninsula without regard to ethnic differences ( Pre-Indo-European, Celts and non-Celtic Indo-Europeans). The other, more restricted ethnic sense and the one dealt with in this article, refers to the people living in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, which by the 6th century BC had absorbed cultural influences from the Phoenicians, Carthaginians and the Greeks. This pre-Indo-European cultural group spoke the Iberian language from the 7th to at least the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title (), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term '' mashiach'' () (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.3 billion Christians around the world, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the Americas, about 26% live in Europe, 24% live in sub-Saharan Afric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—once part of the Byzantine Empire� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in 753 BC through the reign of Augustus in Livy's own lifetime. He was on good terms with members of the Julio-Claudian dynasty and was a friend of Augustus. Livy encouraged Augustus’s young grandnephew, the future emperor Claudius, to take up the writing of history. Life Livy was born in Patavium in northern Italy, now modern Padua, probably in 59 BC. At the time of his birth, his home city of Patavium was the second wealthiest on the Italian peninsula, and the largest in the province of Cisalpine Gaul (northern Italy). Cisalpine Gaul was merged into Italy proper during his lifetime and its inhabitants were given Roman citizenship by Julius Caesar. In his works, Livy often expressed his deep affection and pride for Patavium, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Foederati
''Foederati'' ( ; singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the '' socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign states, client kingdoms or barbarian tribes to which the empire provided benefits in exchange for military assistance. The term was also used, especially under the empire, for groups of barbarian mercenaries of various sizes who were typically allowed to settle within the empire. Roman Republic In the early Roman Republic, ''foederati'' were tribes that were bound by a treaty (''foedus'' ) to come to the defence of Rome but were neither Roman colonies nor beneficiaries of Roman citizenship (''civitas''). Members of the Latini tribe were considered blood allies, but the rest were federates or '' socii''. The friction between the treaty obligations without the corresponding benefits of Romanity led to the Social War between the Romans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |