|
Carlisle Floyd
Carlisle Sessions Floyd (June 11, 1926September 30, 2021) was an American composer primarily known for his operas. These stage works, for which he wrote not only the music but also the librettos, typically engage with themes from the American South, particularly the Post-civil war South, the Great Depression and rural life. His best known opera, '' Susannah'', is based on a story from the Biblical Apocrypha, transferred to contemporary rural Tennessee, and written for a Southern dialect. It was premiered at Florida State University in 1955, with Phyllis Curtin in the title role. When it was staged at the New York City Opera the following year, the reception was initially mixed; some considered it a masterpiece, while others degraded it as a 'folk opera'. Subsequent performances led to an increase in ''Susannah'''s reputation and the opera quickly became among the most performed of American operas. In 1976, he became M. D. Anderson professor at the University of Houston. He c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Medal Of Arts
The National Medal of Arts is an award and title created by the United States Congress in 1984, for the purpose of honoring artists and Patronage, patrons of the arts. A prestigious American honor, it is the highest honor given to artists and arts patrons by the United States government. Nominations are submitted to the National Council on the Arts, the advisory committee of the National Endowment for the Arts (NEA), who then submits its recommendations to the White House for the President of the United States to award. The medal was designed for the NEA by sculptor Robert Graham (sculptor), Robert Graham. Laureates In 1983, prior to the official establishment of the National Medal of Arts, through the President's Committee on the Arts and Humanities, President Ronald Reagan awarded a medal to artists and arts patrons. Recipients of the National Medal of Arts The National Medal of Arts was first awarded in 1985. The ceremony was not held in 2021 or 2022 due to the COVID-19 pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern American English
Southern American English or Southern U.S. English is a regional dialect or collection of dialects of American English spoken throughout the Southern United States, primarily by White Southerners and increasingly concentrated in more rural areas. As of 2000s research, its conservative and innovative (linguistics), most innovative accents include southern Appalachian English, Appalachian and certain Texan English, Texan accents. Such research has described Southern American English as the largest Dialects of North American English, American regional accent group by number of speakers. More formal terms used within American linguistics include ''Southern White Vernacular English'' and ''Rural White Southern English''. However, more commonly in the United States, the variety is recognized as a Southern accent, which technically refers merely to the Southern accent (United States), dialect's sound system, often also simply called Southern. History A diversity of Older Southern Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divine grace, the priesthood of all believers, and the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. The five solae, five ''solae'' summarize the basic theological beliefs of mainstream Protestantism. Protestants follow the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began in the 16th century with the goal of reforming the Catholic Church from perceived Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies. The Reformation began in the Holy Roman Empire in 1517, when Martin Luther published his ''Ninety-five Theses'' as a reaction against abuses in the sale of indulgences by the Catholic Church, which purported to offer the remission of the Purgatory, temporal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Honor (Southern United States)
The traditional culture of the Southern United States has been called a "culture of honor", that is, a culture where people avoid intentionally offending others, and maintain a reputation for not accepting improper conduct by others. A theory as to why the American South had or may have had this culture is an assumed regional belief in retribution to enforce one's rights and deter predation against one's family, home, and possessions.Nisbett, R.E., & Cohen, D. (1996). ''Culture of honor: The psychology of violence in the South''. Boulder, CO: Westview Press. Background The "culture of honor" in the Southern United States is hypothesized by some social scientists to have its roots in the livelihoods of the settlers who first inhabited the region. Unlike those from the densely populated South East England and East Anglia, who settled in New England, the Southern United States was settled by herders from Scotland, Northern Ireland, Northern England, and the West Country. David Hackett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Hospitality
Southern hospitality is a phrase used in American English to describe a cultural stereotype of the Southern United States, with residents perceived to show kindness, warmth, and welcoming of visitors to their homes, or to the South in general. Origins Although Southerners from all walks of life have been perceived as friendly for centuries, some like the writer Anthony Szczesiul claim that Southern hospitality "first existed as a narrowly defined body of social practices among the antebellum planters classes". As such, the origin of the practice was intimately tied to slavery in the United States. One analysis notes: Over time however, the concept "developed into a discourse that stretches far beyond the image of the planter class", and the principles of Southern hospitality were eventually adopted by non-planter class and Southern African Americans as well, and incorporated into materials used to advertise destinations in the South to other African American tourists. The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of The Southern United States
The culture of the Southern United States, Southern culture, or Southern heritage, is a subculture of the United States. From its many cultural influences, Southern United States, the South developed its own unique customs, Southern American English, dialects, arts, Southern literature, literature, Southern US cuisine, cuisine, dance, and Country music, music. The combination of its unique history and the fact that many Southerners maintain—and even nurture—an identity separate from the rest of the country has led to it being one of the most studied and written-about regions of the United States. During the 1600s to mid-1800s, the central role of agriculture and slavery during the Thirteen Colonies, colonial period and Antebellum South, antebellum era economies made society stratified according to land ownership. This landed gentry made culture in the early Southern United States differ from areas north of the Mason–Dixon line and west of the Appalachian Mountains, Appalac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
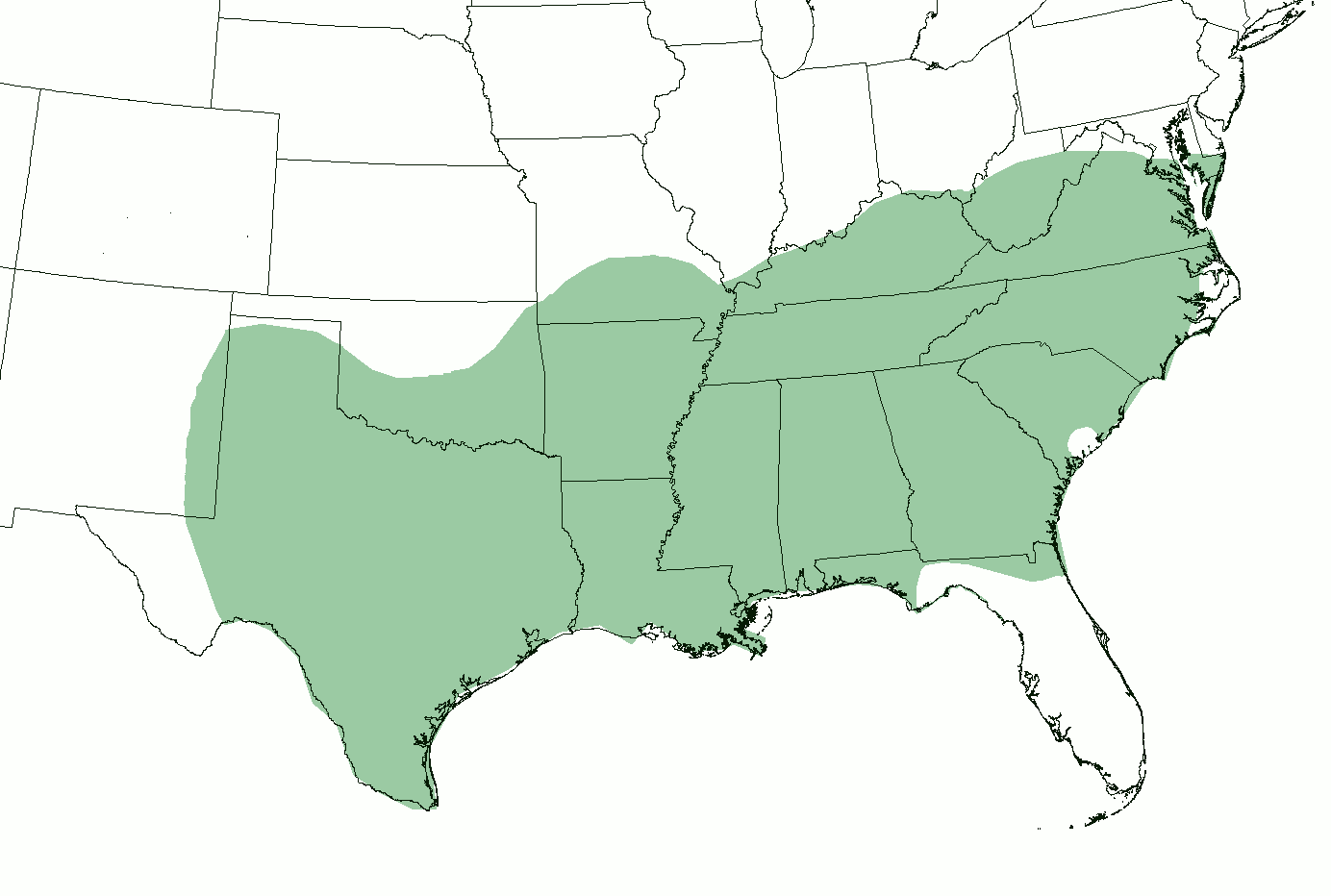
Southern United States
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, Dixieland, or simply the South) is List of regions of the United States, census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It is between the Atlantic Ocean and the Western United States, with the Midwestern United States, Midwestern and Northeastern United States to its north and the Gulf of Mexico and Mexico to its south. Historically, the South was defined as all states south of the 18th-century Mason–Dixon line, the Ohio River, and the Parallel 36°30′ north, 36°30′ parallel.The South . ''Britannica''. Retrieved June 5, 2021. Within the South are different subregions such as the Southeastern United States, Southeast, South Central United States, South Central, Upland South, Upper South, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolinas
The Carolinas, also known simply as Carolina, are the U.S. states of North Carolina and South Carolina considered collectively. They are bordered by Virginia to the north, Tennessee to the west, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the southwest. The Atlantic Ocean is to the east. Combining North Carolina's population of 10,439,388 and South Carolina's of 5,118,425, the Carolinas have a collective population of 15,557,813 as of 2020. If the Carolinas were a single state of the United States, it would be the List of U.S. states and territories by population, fifth-most populous state, behind California, Texas, Florida, and New York. The Carolinas were known as the Province of Carolina during America's early Colonial America, colonial period, from 1663 to 1712. Prior to that, the land was considered part of the Colony and Dominion of Virginia, from 1609 to 1663. The province was named ''Carolina'' to honor King Charles I of England. Carolina is taken from the Latin word for "Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother Charles Wesley were also significant early leaders in the movement. They were named ''Methodists'' for "the methodical way in which they carried out their Christian faith". Methodism originated as a Christian revival, revival movement within Anglicanism with roots in the Church of England in the 18th century and became a separate denomination after Wesley's death. The movement spread throughout the British Empire, the United States and beyond because of vigorous Christian mission, missionary work, and today has about 80 million adherents worldwide. Most List of Methodist denominations, Methodist denominations are members of the World Methodist Council. Wesleyan theology, which is upheld by the Methodist denominations, focuses on Sanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Public Radio
National Public Radio (NPR) is an American public broadcasting organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with its NPR West headquarters in Culver City, California. It serves as a national Radio syndication, syndicator to a network of more than List of NPR stations, 1,000 public radio stations in the United States. Funding for NPR comes from dues and fees paid by member stations, Underwriting spot, underwriting from corporate sponsors, and annual grants from the publicly funded Corporation for Public Broadcasting. Most of its member stations are owned by non-profit organizations, including public school districts, colleges, and universities. NPR operates independently of any government or corporation, and has full control of its content. NPR produces and distributes both news and cultural programming. The organization's flagship shows are two drive time, drive-time news broadcasts: ''Morning Edition'' and the afternoon ''All Things Considered'', both carried by most NPR me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Née
The birth name is the name of the person given upon their birth. The term may be applied to the surname, the given name or to the entire name. Where births are required to be officially registered, the entire name entered onto a births register or birth certificate may by that fact alone become the person's legal name. The assumption in the Western world is often that the name from birth (or perhaps from baptism or ''brit milah'') will persist to adulthood in the normal course of affairs—either throughout life or until marriage. Some possible changes concern middle names, diminutive forms, changes relating to parental status (due to one's parents' divorce or adoption by different parents), and changes related to gender transition. Matters are very different in some cultures in which a birth name is for childhood only, rather than for life. Maiden and married names The terms née (feminine) and né (masculine; both pronounced ; ), Glossary of French expressions in Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boosey & Hawkes
Boosey & Hawkes is a British Music publisher (sheet music), music publisher, purported to be the largest specialist classical music publisher in the world. Until 2003, it was also a major manufacturer of brass instrument, brass, string instrument, string and woodwind instrument, woodwind musical instruments. Formed in 1930 through the merger of two well-established British music businesses, Boosey & Hawkes controls the copyright to much major 20th-century music, including works by Leonard Bernstein, Benjamin Britten, Aaron Copland, Sergei Prokofiev, and Igor Stravinsky. It also publishes many prominent contemporary composers, including John Adams (composer), John Adams, Karl Jenkins, James MacMillan, Mark-Anthony Turnage, and Steve Reich. With subsidiaries in Berlin and New York City, New York, the company also sells sheet music via its online shop. History Pre-merger Boosey & Hawkes was founded in 1930 through the merger of two respected music companies, Boosey & Company a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |