|
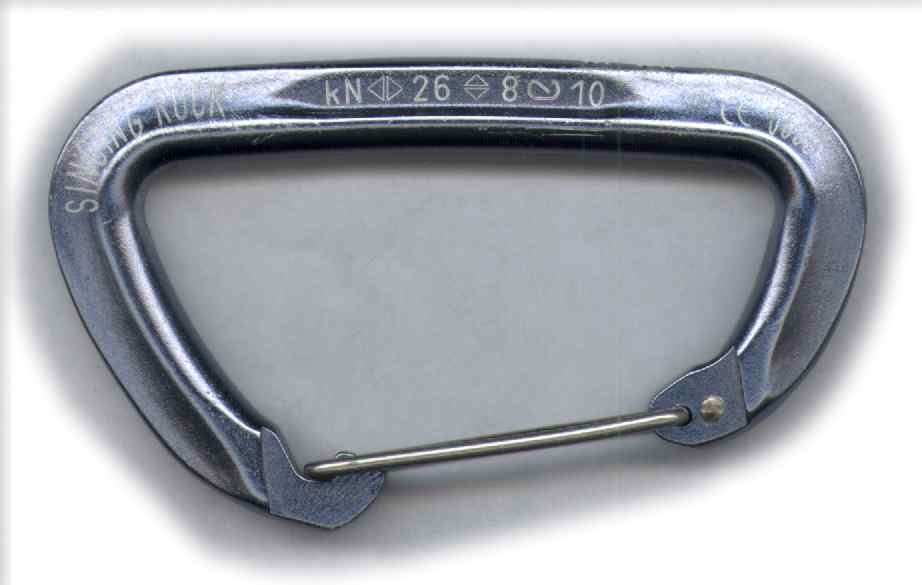
Carabiner
A carabiner or karabiner (), often shortened to biner or to crab, colloquially known as a (climbing) clip, is a specialized type of shackle, a metal loop with a spring-loaded gate used to quickly and reversibly connect components, most notably in safety-critical systems. The word comes from the German language, German , short for , meaning "carbine hook," as the device was used by carabiniers to attach their carbines to their belts. Use Carabiners are widely used in rope-intensive activities such as climbing, fall arrest systems, arboriculture, caving, sailing, hot air ballooning, hot-air ballooning, rope rescue, construction, industrial rope access, industrial rope work, window cleaning, whitewater rescue, and acrobatics. They are predominantly made from both steel and aluminium. Those used in sports tend to be of a lighter weight than those used in commercial applications and rope rescue. Often referred to as carabiner-style or as mini-carabiners, carabiner keyrings and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munter Hitch
The Munter hitch, also known as the Italian hitch, mezzo barcaiolo is a simple adjustable knot, commonly used by climbers, cavers, and rescuers to control friction in a life-lining or belay system. It is often mistakenly identified as the crossing hitch, however in the cross hitch the line does not return along its original path. To climbers, this hitch is also known as HMS, the abbreviation for the German term , meaning ''half clove hitch belay''. This technique can be used with a special "pear-shaped" HMS locking carabiner, or any locking carabiner wide enough to take two turns of the rope. In the late 1950s, three Italian climbers, Mario Bisaccia, Franco Garda and Pietro Gilardoni developed a new belay technique called the "Mezzo Barcaiolo" (MB) meaning; "a half of the knot, which is used by the sailors to secure a boat to a bollard in a harbor." The "MB" came to be known as the Munter hitch after Werner Munter, a Swiss mountain guide popularized its use in mountaineeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
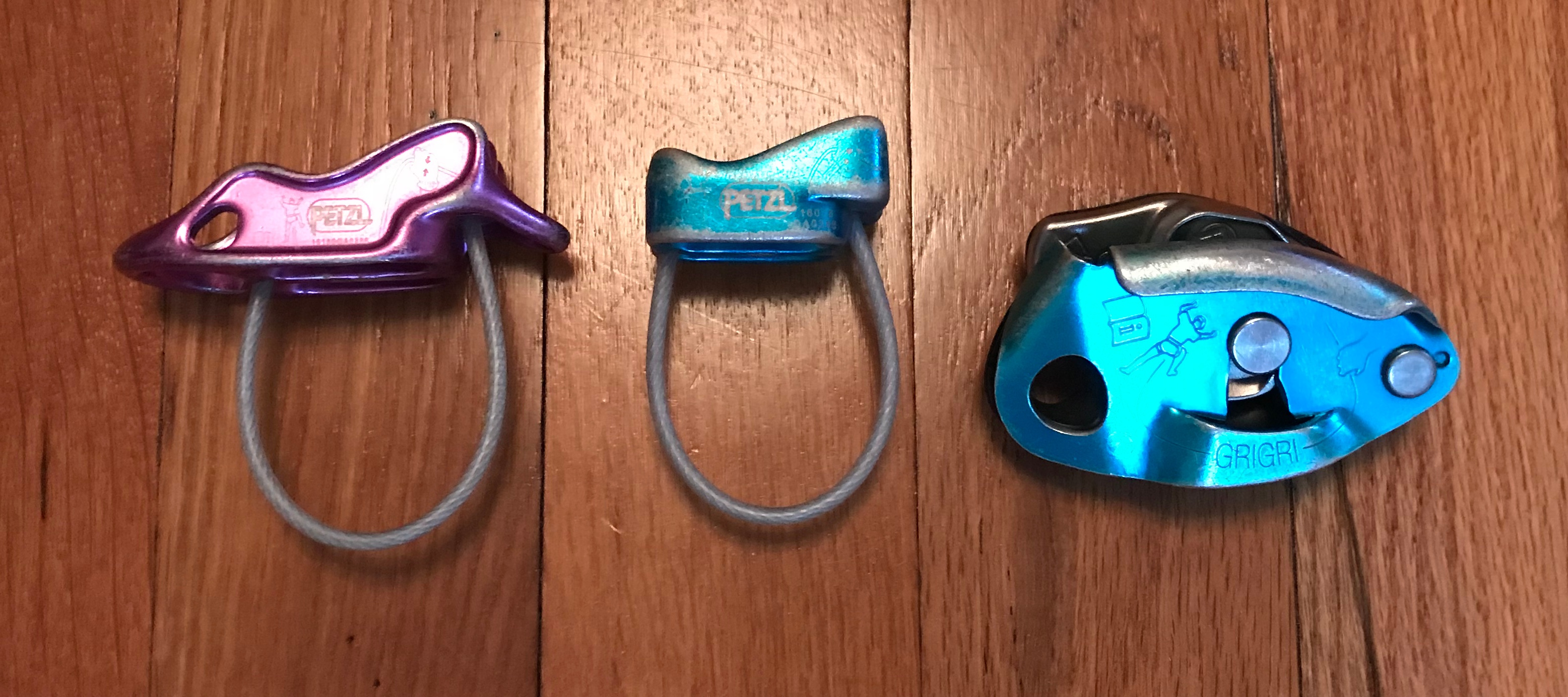
Belay Device
A belay device is a mechanical piece of climbing equipment used to control a rope during belaying. It is designed to improve belay safety for the climber by allowing the belayer to manage their duties with minimal physical effort. With the right belay device, a small, weak climber can easily arrest the fall of a much heavier partner. Belay devices act as a friction brake, so that when a climber falls with any slack in the rope, the fall is brought to a stop. Typically, when the rope is held outward, away from the body, it moves relatively freely, so the belayer can take up or pay out slack. When the rope is brought backward, to the side of the body, the rope is forced into tight bends and rubs against the device and/or against itself, allowing the belayer to arrest the descent of a climber in the case of a fall. This rubbing slows the rope, but also generates heat. Some types of belay devices can arrest a fall without the belayer taking any action, while others require the belay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threaded Sleeve
A maillon, maillon rapide or quick link is a metal link, similar to a carabiner. Maillons have a threaded sleeve which tightens over a thread, as opposed to a hinged gate like a carabiner, making them stronger, but more difficult to use. Like carabiners, maillons are available in a range of shapes and thicknesses (i.e., strengths), and often offer greater versatility over carabiners as their different shapes and lack of hinged gates allow them to be used in multi-directional load situations. The word ''maillon'' comes from the French language, meaning "link". Usage Maillons are used primarily in climbing and caving. In caving, they are used to make secure and vital connections such as those required when using single rope technique,http://www.cave-crag.co.uk/721/Maillon-Rapide-10mm-Semi-Circular.html or for attaching ropes to anchor points. In climbing, they are used to construct leave-in-place abseil anchors. Maillons can also be used for fastening harnesses with a dual attach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
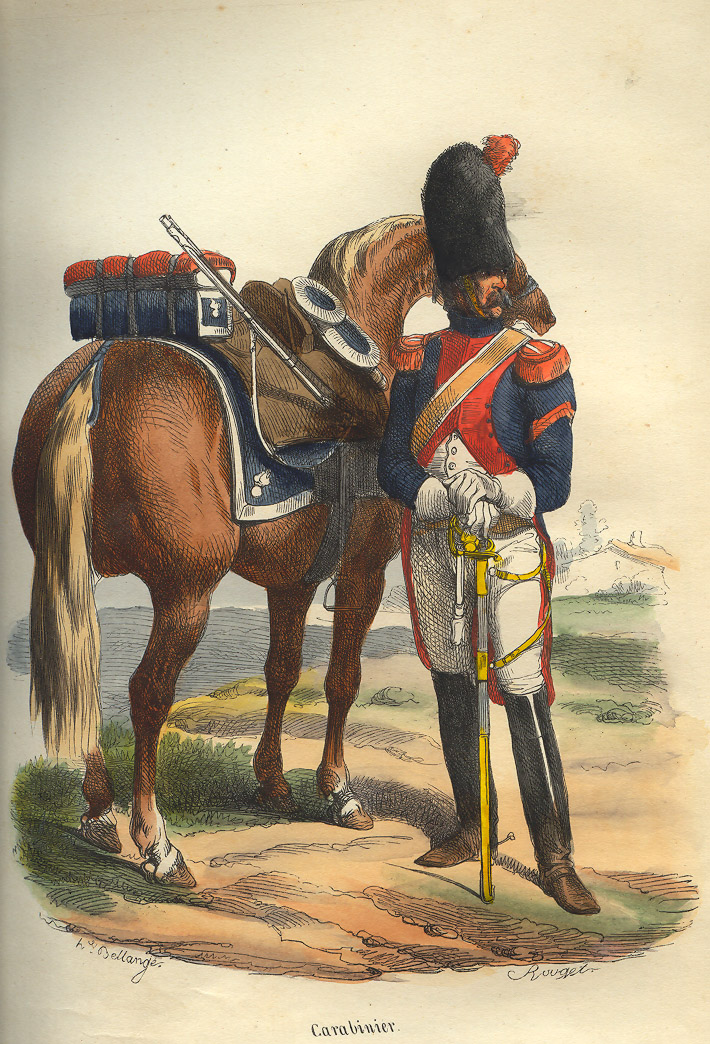
Carabinier
A carabinier (also sometimes spelled carabineer or carbineer) is in principle a soldier armed with a carbine, musket, or rifle, which became commonplace by the beginning of the Napoleonic Wars in Europe. The word is derived from the identical French language, French word ''wikt:carabinier#French, carabinier''. Historically, carabiniers were generally (but not always) Cavalry, horse soldiers. The carbine was considered a more appropriate firearm for a horseman than a full-length musket, since it was shorter in length, weighed less, and was easier to manipulate on horseback. Light infantry sometimes carried carbines because they are less encumbering when moving rapidly, especially through vegetation, but in most armies the tendency was to equip light infantry with longer-range weapons such as rifles rather than shorter-range weapons such as carbines. In Italy and Spain, carbines were considered suitable equipment for soldiers with policing roles, so the term ''carabinier'' evolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilonewton
The newton (symbol: N) is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). Expressed in terms of SI base units, it is 1 kg⋅m/s2, the force that accelerates a mass of one kilogram at one metre per second squared. The unit is named after Isaac Newton in recognition of his work on classical mechanics, specifically his second law of motion. Definition A newton is defined as 1 kg⋅m/s2 (it is a named derived unit defined in terms of the SI base units). One newton is, therefore, the force needed to accelerate one kilogram of mass at the rate of one metre per second squared in the direction of the applied force. The units "metre per second squared" can be understood as measuring a rate of change in velocity per unit of time, i.e. an increase in velocity by one metre per second every second. In 1946, the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) Resolution 2 standardized the unit of force in the MKS system of units to be the amount needed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Climbing
Lead climbing (or leading) is a technique in rock climbing where the 'lead climber' Glossary of climbing terms#clip in, clips their rope to the climbing protection as they ascend a pitch (climbing), pitch of the climbing route, while their 'second' (or 'belayer') remains at the base of the route belaying the rope to protect the 'lead climber' in the event that they fall. The term is used to distinguish between the two roles, and the greater effort and increased risk, of the role of the 'lead climber'. Leading a climb is in contrast with top roping a climb, where even though there is still a 'second' belaying the rope, the 'lead climber' faces little or no risk in the event of a fall and does not need to clip into any protection as the rope is already Anchor (climbing), anchored to the top of the route (i.e. if they fall off, they just hang from the rope). Leading a climbing route is a Rock climbing#Description, core activity in rock climbing, and most first ascents and first fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilonewton
The newton (symbol: N) is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). Expressed in terms of SI base units, it is 1 kg⋅m/s2, the force that accelerates a mass of one kilogram at one metre per second squared. The unit is named after Isaac Newton in recognition of his work on classical mechanics, specifically his second law of motion. Definition A newton is defined as 1 kg⋅m/s2 (it is a named derived unit defined in terms of the SI base units). One newton is, therefore, the force needed to accelerate one kilogram of mass at the rate of one metre per second squared in the direction of the applied force. The units "metre per second squared" can be understood as measuring a rate of change in velocity per unit of time, i.e. an increase in velocity by one metre per second every second. In 1946, the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) Resolution 2 standardized the unit of force in the MKS system of units to be the amount needed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
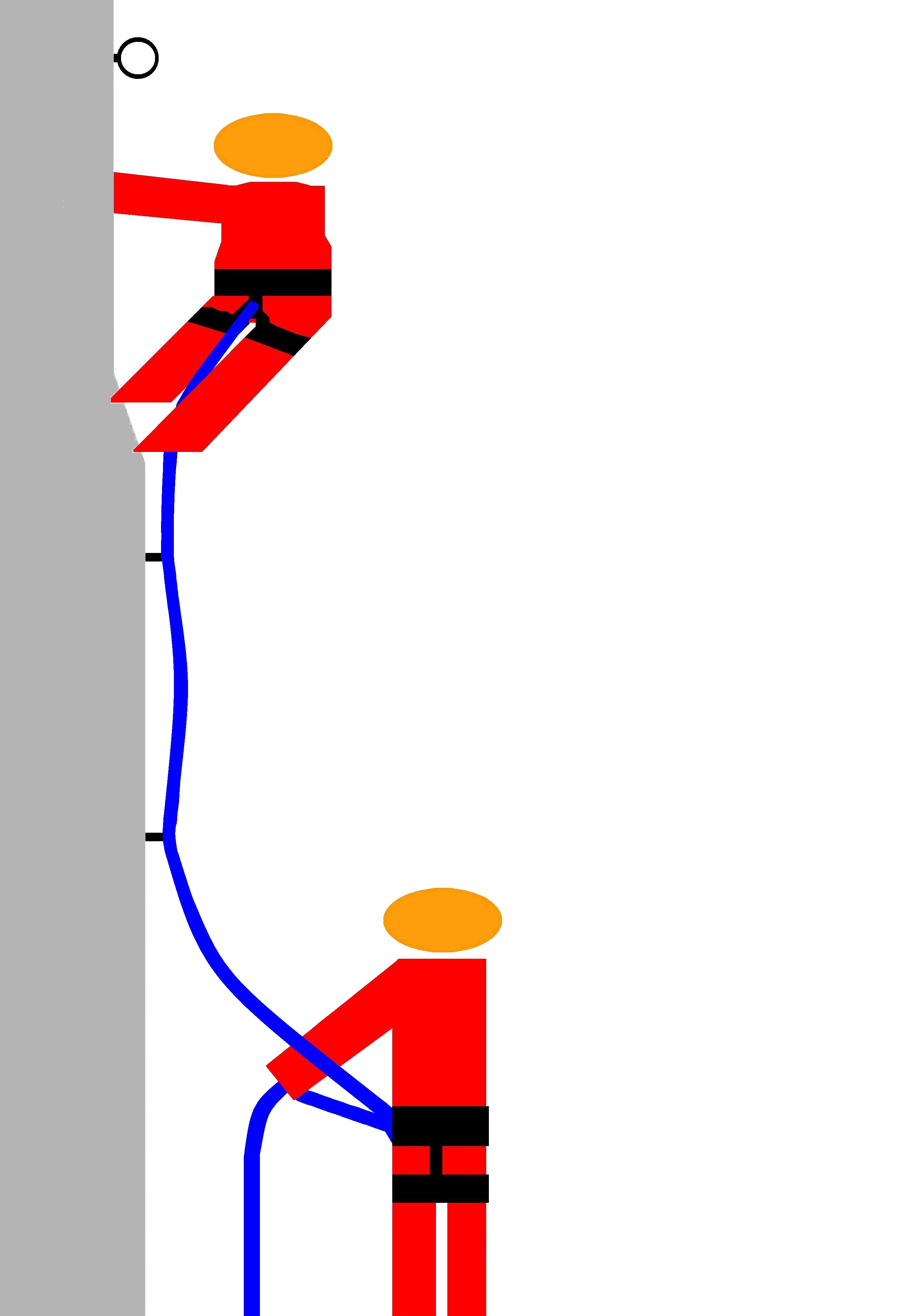
Belaying
In climbing and mountaineering, belaying comprises techniques used to create friction within a climbing protection system, particularly on a climbing rope, so that a falling climber does not fall very far. A climbing partner typically applies tension at the other end of the rope whenever the climber is not moving, and removes the tension from the rope whenever the climber needs more rope to continue climbing. The belay is the place where the belayer is anchored, which is typically on the ground, or on ledge (where it is also called a belay station) but may also be a hanging belay where the belayer themself is suspended from an anchor in the rock on a multi-pitch climbing, multi-pitch climb. Description Belaying is a critical part of climbing safety. Correct belaying methods allow a belayer to hold the entire weight of the climber with relatively little force and easily arrest falls. In its simplest form, a belay consists of a rope that runs from a climber to another person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbilical Cable
An umbilical cable or umbilical is a cable and/or hose that supplies required consumables to an apparatus, like a rocket, or to a person, such as a diver or astronaut. It is named by analogy with an umbilical cord. An umbilical can, for example, supply air and power to a pressure suit or hydraulic power, electrical power and fiber optics to subsea equipment and divers. Spaceflight applications Rockets Umbilicals connect a missile or space vehicle to ground support equipment on the launch pad before launch. Cables carry electrical power, communications, and telemetry, and pipes or hoses carry liquid propellants, cryogenic fluids, and pressurizing and purge gases. These are automatically disconnected shortly before or at launch. Umbilical connections are also used between rocket stages, and between the rocket and its spacecraft payload; these umbilicals are disconnected as stages are disconnected and discarded. Space suits Early space suits used in Project Gemini in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Supplied Diving
Surface-supplied diving is a mode of underwater diving using equipment supplied with breathing gas through a diver's umbilical from the surface, either from the shore or from a diving support vessel, sometimes indirectly via a diving bell. This is different from scuba diving, where the diver's breathing equipment is completely self-contained and there is no essential link to the surface. The primary advantages of conventional surface supplied diving are lower risk of drowning and considerably larger breathing gas supply than scuba, allowing longer working periods and safer decompression. Disadvantages are the absolute limitation on diver mobility imposed by the length of the umbilical, encumbrance by the umbilical, and high logistical and equipment costs compared with scuba. The disadvantages restrict use of this mode of diving to applications where the diver operates within a small area, which is common in commercial diving work. The copper helmeted free-flow standard di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot-air Balloon
A hot air balloon is a lighter-than-air aircraft consisting of a bag, called an envelope, which contains heated air. Suspended beneath is a gondola or wicker basket (in some long-distance or high-altitude balloons, a capsule), which carries passengers and a source of heat, in most cases an open flame caused by burning liquid propane. The heated air inside the envelope makes it buoyant, since it has a lower density than the colder air outside the envelope. As with all aircraft, hot air balloons cannot fly beyond the atmosphere. The envelope does not have to be sealed at the bottom, since the air inside the envelope is at about the same pressure as the surrounding air. In modern sport balloons the envelope is generally made from nylon fabric, and the inlet of the balloon (closest to the burner flame) is made from a fire-resistant material such as Nomex. Modern balloons have been made in many shapes, such as rocket ships and the shapes of various commercial products, though t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |