|
Capitán Oriel Lea Plaza Airport
Capitán Oriel Lea Plaza Airport is an airport serving Tarija, the capital of the Tarija Department of Bolivia. The airport is in the southeastern section of the city, which is within a basin of the Cordillera Central mountain range. There is distant mountainous terrain in all quadrants. The Tarija non-directional beacon (Ident: TJA) and VOR-DME (Ident: TAR) are located on the field. The runway length includes a displaced threshold on Runway 31. Airlines and destinations See also * Transport in Bolivia * List of airports in Bolivia References External linksTarija Airportat OpenStreetMap OpenStreetMap (abbreviated OSM) is a free, Open Database License, open geographic database, map database updated and maintained by a community of volunteers via open collaboration. Contributors collect data from surveying, surveys, trace from Ae ...Capitan Oriel Lea Plaza Airportat OurAirports *at FallingRain * * Airports in Tarija Department Tarija {{bolivia-airport- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarija, Bolivia
Tarija or San Bernardo de la Frontera de Tarixa is a city in southern Bolivia. Founded in 1574, Tarija is the largest city and capital and municipality within the Tarija Department, with an airport ( Capitán Oriel Lea Plaza Airport, (TJA)) offering regular service to primary Bolivian cities, as well as a regional bus terminal with domestic and international connections. Its climate is semi-arid ( BSh) with generally mild temperatures in contrast to the harsh cold of the Altiplano (e.g., La Paz) and the year-round humid heat of the Amazon Basin (e.g., Santa Cruz de la Sierra). Tarija has a population of 234,442. History The name of ''Tarija'' is said to come from Francisco de Tarija or Tarifa. This group did not include anyone by the name of Francisco de Tarija. Similar-sounding toponyms exist for surrounding places, such as Tariquia and Taxara. In 1826 the citizens of Tarija voted to become part of Bolivia. In 1807, Tarija had become separated from Upper Peru to become par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
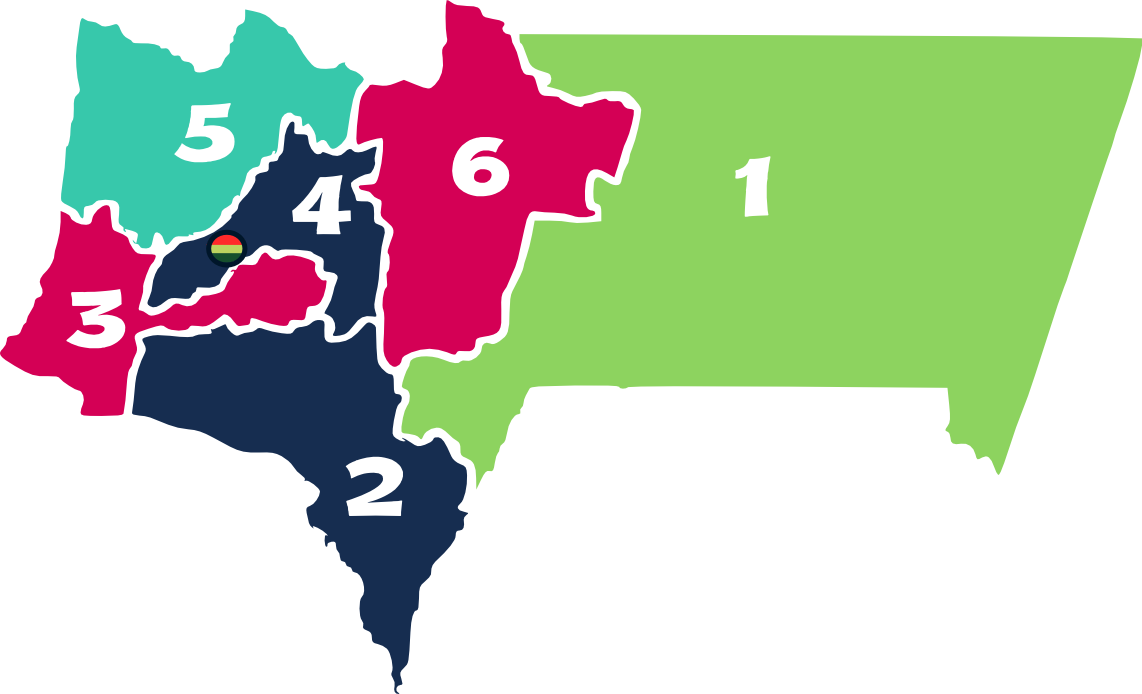
Tarija Department
Tarija () is a department in Bolivia. It is located in south-eastern Bolivia bordering with Argentina to the south and Paraguay to the east. According to the 2024 census, it has a population of 534,348 inhabitants. It has an area of . The city of Tarija is the capital of the department. Subdivisions The department is divided into five provinces and one autonomous region: # Gran Chaco Province (autonomous region) # Aniceto Arce Province # José María Avilés Province # Cercado Province # Eustaquio Méndez Province # Burdett O'Connor Province Notable places in Tarija include: * Villamontes in the department's oil-producing eastern scrubland. Villamontes has recorded the hottest temperature ever in Bolivia, , several times, most recently on 29 October 2010. * Bermejo, a border town adjoining Aguas Blancas, Argentina * Yacuiba, a border town with Argentina. The Department of Tarija is renowned for its mild, pleasant climate, and comprises one of the country's foremost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, warm valleys, high-altitude Andean plateaus, and snow-capped peaks, encompassing a wide range of climates and biomes across its regions and cities. It includes part of the Pantanal, the largest tropical wetland in the world, along its eastern border. It is bordered by Brazil to the Bolivia-Brazil border, north and east, Paraguay to the southeast, Argentina to the Argentina-Bolivia border, south, Chile to the Bolivia–Chile border, southwest, and Peru to the west. The seat of government is La Paz, which contains the executive, legislative, and electoral branches of government, while the constitutional capital is Sucre, the seat of the judiciary. The largest city and principal industrial center is Santa Cruz de la Sierra, located on the Geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordillera Central (Bolivia)
The Cordillera Central is a Bolivian mountain range that divides the three river basins in the country and also has the second highest peaks in Bolivia. It is rich in minerals and starts in the north with Chawpi Urqu and the three Palumanis that were in the south up to Zapaleri, forming a border with Chile and Argentina. The Cordillera Central is divided into three sections: * The northern section or Cordillera Real, with Chawpi Urqu and Palumani, also taking into account the most significant of Bolivia that you find near La Paz, Illimani, Illampu, Janq'u Uma, Mururata, and Huayna Potosí, all of which are more than 6,000 meters high. This section is famous because the highest meteorological observatory in the world can be found on Chacaltaya. Some of the highest ski slopes in the world can be found here also. * The central section contains Sumaq Urqu, with the Potosí mountain range and the ''Paso de Condor'' rail station, both situated at an elevation of 4,288 meters. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-directional Beacon
A non-directional beacon (NDB) or non-directional radio beacon is a radio beacon which does not include directional information. Radio beacons are radio transmitters at a known location, used as an aviation or marine navigational aid. NDB are in contrast to directional radio beacons and other navigational aids, such as low-frequency radio range, VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) and tactical air navigation system (TACAN). NDB signals Ground conductivity, follow the curvature of the Earth, so they can be received at much greater distances at lower altitudes, a major advantage over VOR. However, NDB signals are also affected more by atmospheric conditions, mountainous terrain, coastal refraction and electrical storms, particularly at long range. The system, developed by United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) Captain Albert Francis Hegenberger, was used to fly the world's first instrument approach on May 9, 1932. Types of NDBs NDBs used for aviation are standardised by the Internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VOR-DME
In radio navigation, a VOR/DME is a radio beacon that combines a VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) with a distance-measuring equipment (DME). The VOR allows the receiver to measure its Bearing (navigation), bearing to or from the beacon, while the DME provides the slant distance between the receiver and the station. Together, the two measurements allow the receiver to compute a position fix. The VOR system was first introduced in the 1930s, but did not enter significant commercial use until the early 1950s. It became much more practical with the introduction of low-cost Solid state (electronics), solid state receivers in the 1960s. DME was a modification of World War II-era navigation systems like Gee-H (navigation), Gee-H, and began development in 1946. Like VOR, it only became practical with the introduction of solid state receivers during the 1960s. In 1948, the United States Congress directed civilian and military aviation to standardize on VOR/DME equipment. However, the milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displaced Threshold
A displaced threshold or DTHR is a runway threshold located at a point other than the physical beginning or end of the runway. The portion of the runway behind a displaced threshold may be used for takeoff in either direction and landings from the opposite direction. After landing at the other end, the landing aircraft may use the area behind the displaced threshold for roll out.Aircraft Information Manual 2013, Chapter 2-3-3 h (2) Section 3. Airport Marking Aids and Signs /ref> Most often, the offset threshold is in place to give arriving aircraft clearance over an obstruction, while still allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boliviana De Aviación
Boliviana de Aviación (shortened in Spanish for ''Empresa Pública Nacional Estratégica Boliviana de Aviación'' "Bolivian National Strategic Aviation Public Company") and stylized as BoA, is the flag carrier airline of Bolivia and is wholly owned by the country's government. Founded in October 2007 and headquartered in Cochabamba, it operates most of its domestic network out of its primary hub at Jorge Wilstermann International Airport while its international services operate out Viru Viru International Airport in Santa Cruz de la Sierra. It is the largest airline in Bolivia and sixth largest in South America, in terms of fleet size and passengers carried. Boliviana de Aviación operates a fleet consisting of Airbus and Boeing aircraft and a regional fleet of Bombardier CRJ-200s. It currently flies to 21 destinations in 8 countries in the Americas together with a transatlantic extension to Madrid in Spain. The airline was established as a state-owned enterprise under th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jorge Wilstermann International Airport
Jorge Wilstermann International Airport (, ) is a high elevation international airport serving Cochabamba, the capital of the Cochabamba Department of Bolivia. The facility is named after Jorge Wilstermann, an early Bolivian commercial aviator. The airport used to be the main base of operations for Bolivia's former flag carrier Lloyd Aéreo Boliviano and currently serves as the main domestic hub for Boliviana de Aviación due to its geographical location at the center of Bolivia. History The airport was born with a single 2649 meter post office and a terminal on Guillermo Killman Avenue. In 1988, as an expansion plan, due to the fact that the old terminal was becoming more and more crowded and a longer runway was needed for more modern and larger aircraft, a new 3798 meter runway was created and put into operation in 1990, and a new air terminal was inaugurated years later in 1997, with the old terminal becoming a cargo terminal that currently houses a Boliviana de Aviacion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Alto International Airport
El Alto International Airport () is an international airport serving La Paz, Bolivia. It is located in the city of El Alto, west of La Paz. At an elevation of , it is the highest international airport in the world, the seventh highest commercial airport in the world and the highest commercial airport outside of China. The airport has been in service since the first half of the 20th century, but was modernized in the late 1960s, when its runway was lengthened and a new passenger terminal with modern facilities was built. The new airport was inaugurated in 1965. El Alto airport was a primary hub for the former Lloyd Aéreo Boliviano, Bolivia's flag carrier which ceased operations in 2007. It serves also as a focus city for Boliviana de Aviación, Bolivia's flag carrier and state-owned airline. History Bolivia is characterized by an extremely varied terrain including rugged mountains, high plateaus, low valleys and tropical forests; this topography has had a negative effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viru Viru International Airport
Viru Viru International Airport in Santa Cruz de la Sierra is Bolivia's largest international airport. Viru Viru handles domestic, regional, and international flights from Bolivia, North America, South America and Europe and serves as a focus city for Bolivia's biggest airline Boliviana de Aviación. The airport is able to handle widebody aircraft including the Boeing 747-400. History The idea of having an airport in the city of Santa Cruz de la Sierra was conceived in 1965 by General René Barrientos, former president of Bolivia, with the intention of creating an intercontinental airport. Shortly thereafter, construction of the airport began until it was completed and inaugurated in 1983, to replace the obsolete El Trompillo Airport. Upon its inauguration, Viru Viru became a main gateway for international flights. Lloyd Aéreo Boliviano used Viru Viru as a hub before ceasing operations in 2008. On 1 March 1997, the government of Bolivia entered into a 25-year contract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yacuiba Airport
Yacuiba Airport (, ) is an airport located north of Yacuiba, a city in the Tarija Department of Bolivia. The runway is in a north–south aligned valley, with rising terrain to the east, and the Cordillera Central mountains to the west. The Yacuiba non-directional beacon (Ident: YAC) is located on the field. Airlines and destinations Accidents, Disasters, and incidents * On 4 February 1964, a Douglas C-47 Skytrain operated by Lloyd Aéreo Boliviano crashed shortly after takeoff killing two. * 20 October 1973, A Boeing 737 operated by Aerolíneas Argentinas was highjacked and landed at Yacuiba where 38 passengers were released. * 2 June 1980, A Fairchild F-27 operated by Lloyd Aéreo Boliviano crashed while on Approach to the airport killing all 13 people on board. * 17 January 2003, A British Aerospace Jetstream operated by Servicio Aéreo Vargas España crashed shortly into trees while attempting to take off, no one was killed. See also * Transport in Bolivia * List of ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |