|
Cancer Of Unknown Primary Origin
Cancer of unknown primary origin (CUP) is a cancer that is determined to be at the metastasis, metastatic stage at the time of diagnosis, but a primary tumor cannot be identified. A diagnosis of CUP requires a clinical picture consistent with metastatic disease and one or more biopsy results inconsistent with a tumor cancer. CUP is found in about 3 to 5% of all people diagnosed with invasive cancer, and carries a poor prognosis in most (80 to 85%) of those circumstances. The other 15 to 20% of people, however, have localized or small metastatic sites at the time of diagnosis, and is associated with a relatively long survival with appropriate treatment. The worldwide incidence of CUP is estimated to be 2-15 cases per 100,000 person years and this incidence is declining as advances are made in diagnostic imaging, molecular markers and other cancer diagnostic tests such that it is easier to find a primary tumor. Risk factors for CUP are similar to other types of cancers and include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's Etymology, etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is focused on the diagnosis of cancer in a person, therapy (e.g., surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities), monitoring of patients after treatment, palliative care of people with advanced-stage cancers, Ethics, ethical questions surrounding cancer care, Screening (medicine), screening of patients, and the study of cancer treatments through clinical research. An oncologist typically focuses on a specialty area in cancer treatment, such as surgery, Radiation therapy, radiation, gynecology, gynecologic oncology, geriatrics, geriatric oncology, pediatrics, pediatric oncology, and various organ-specific disciplines (breast, brain, liver, among others). The exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Examination
A pelvic examination is the physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs. It is frequently used in gynecology for the evaluation of symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract, such as pain, bleeding, discharge, urinary incontinence, or trauma (e.g. sexual assault). It can also be used to assess a woman's anatomy in preparation for procedures. The exam can be done awake in the clinic and emergency department, or under anesthesia in the operating room. The most commonly performed components of the exam are 1) the external exam, to evaluate the vulva 2) the internal exam with palpation (commonly called the ''bimanual exam'') to examine the uterus, ovaries, and structures adjacent to the uterus (adnexae) and 3) the internal exam using a speculum to visualize the vaginal walls and cervix. During the pelvic exam, sample of cells and fluids may be collected to screen for sexually transmitted infections or cancer (the Pap test). Some clinici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
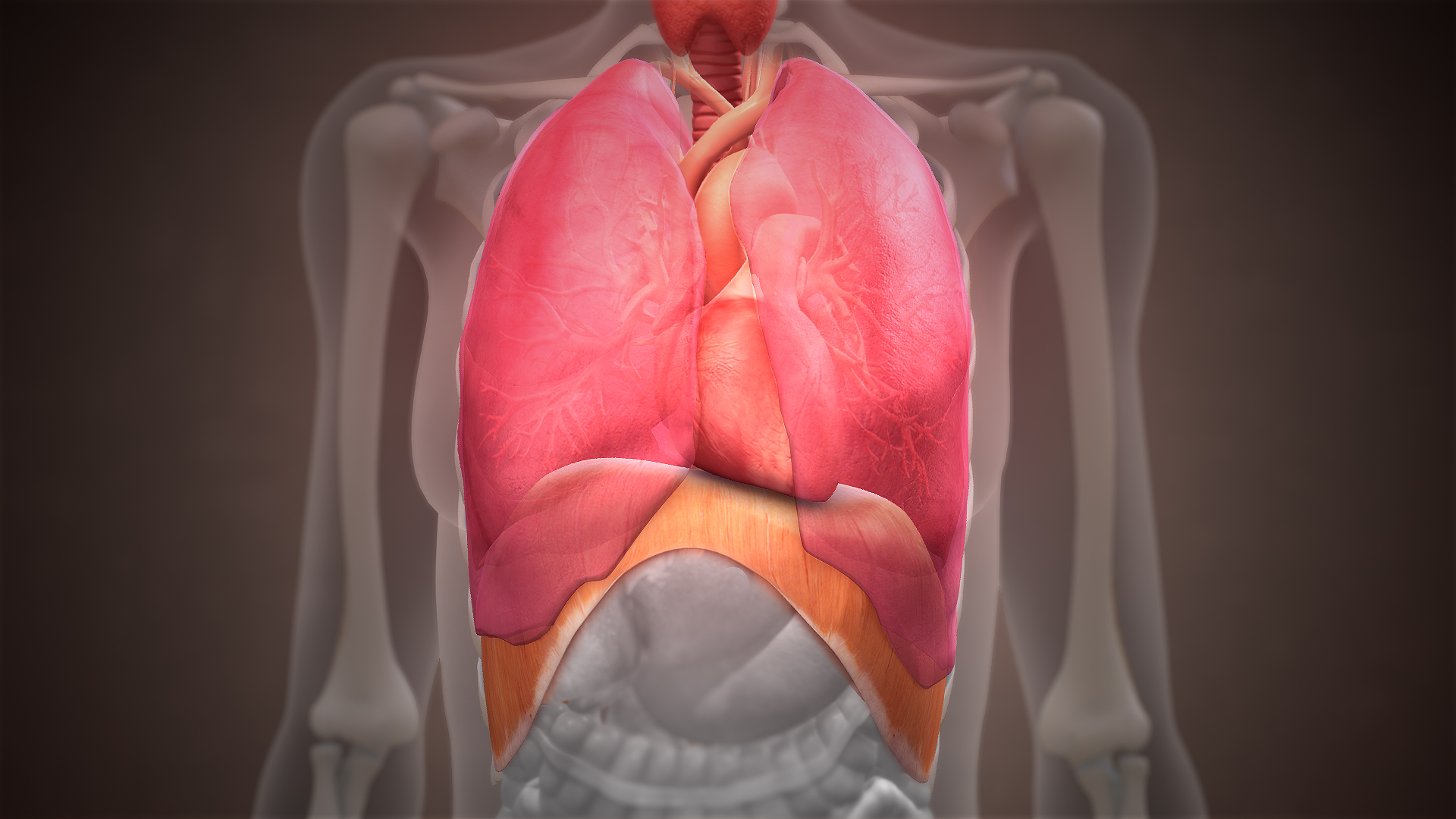
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm (; ), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply to any frequency range, including ultrasound. Ultrasonic devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on the mathematical properties of String instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
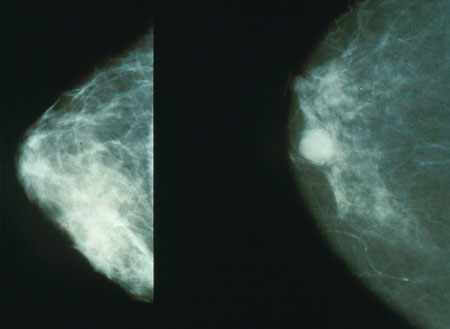
Mammogram
Mammography (also called mastography; DICOM modality: MG) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses, microcalcifications, asymmetries, and distortions. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D ( tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In clinical practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made and the words are usually treated as synonymous. Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels is known as lymphangitis. Infectious lymphadenitis affecting lymph nodes in the neck is often called scrofula. Lymphadenopathy is a common and nonspecific sign. Common causes include infections (from minor causes such as the common cold and post-vaccination swelling to serious ones such as HIV/AIDS), autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Lymphadenopathy is frequently idiopathic and self-limiting. Causes Lymph node enlargement is recognized as a common sign of infectious, autoimmune, or malignant disease. Examples may include: * Reactive: acute infection (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cell (biology), cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Cell Tumor
A germ cell tumor (GCT) is a neoplasm derived from primordial germ cells. Germ-cell tumors can be cancerous or benign. Germ cell tumors typically originate from the gonads (ovary and testis), but can arise in other areas of the body. Extragonadal GCTs are thought to result from abnormal migration of germ cell precursors during development of the embryo. Classification GCTs are classified by their histology, regardless of location in the body. However, as more information about the genetics of these tumors become available, they may be classified based on specific gene mutations that characterize specific tumors. They are broadly divided in two classes: * The germinomatous or seminomatous germ-cell tumors (GGCT, SGCT) include only germinoma and its synonyms dysgerminoma and seminoma. * The nongerminomatous or nonseminomatous germ-cell tumors (NGGCT, NSGCT) include all other germ-cell tumors, pure and mixed. The two classes reflect an important clinical difference. Compare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
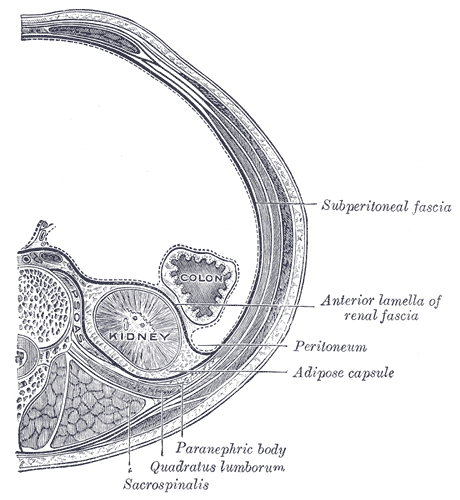
Retroperitoneal Space
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the spatium, anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal. This is different from organs that are not retroperitoneal, which have peritoneum on their posterior side and are suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity. The retroperitoneum can be further subdivided into the following: *Perirenal (or perinephric) space *Anterior pararenal (or paranephric) space *Posterior pararenal (or paranephric) space Retroperitoneal structures Structures that lie behind the peritoneum are termed "retroperitoneal". Organs that were once suspended within the abdominal cavity by mesentery but migrated posterior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ;: mediastina) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, mainly the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the vagus nerve, vagus, phrenic nerve, phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pulmonary pleurae, pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the Spine (anatomy), spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |