|
Cancer In Cats
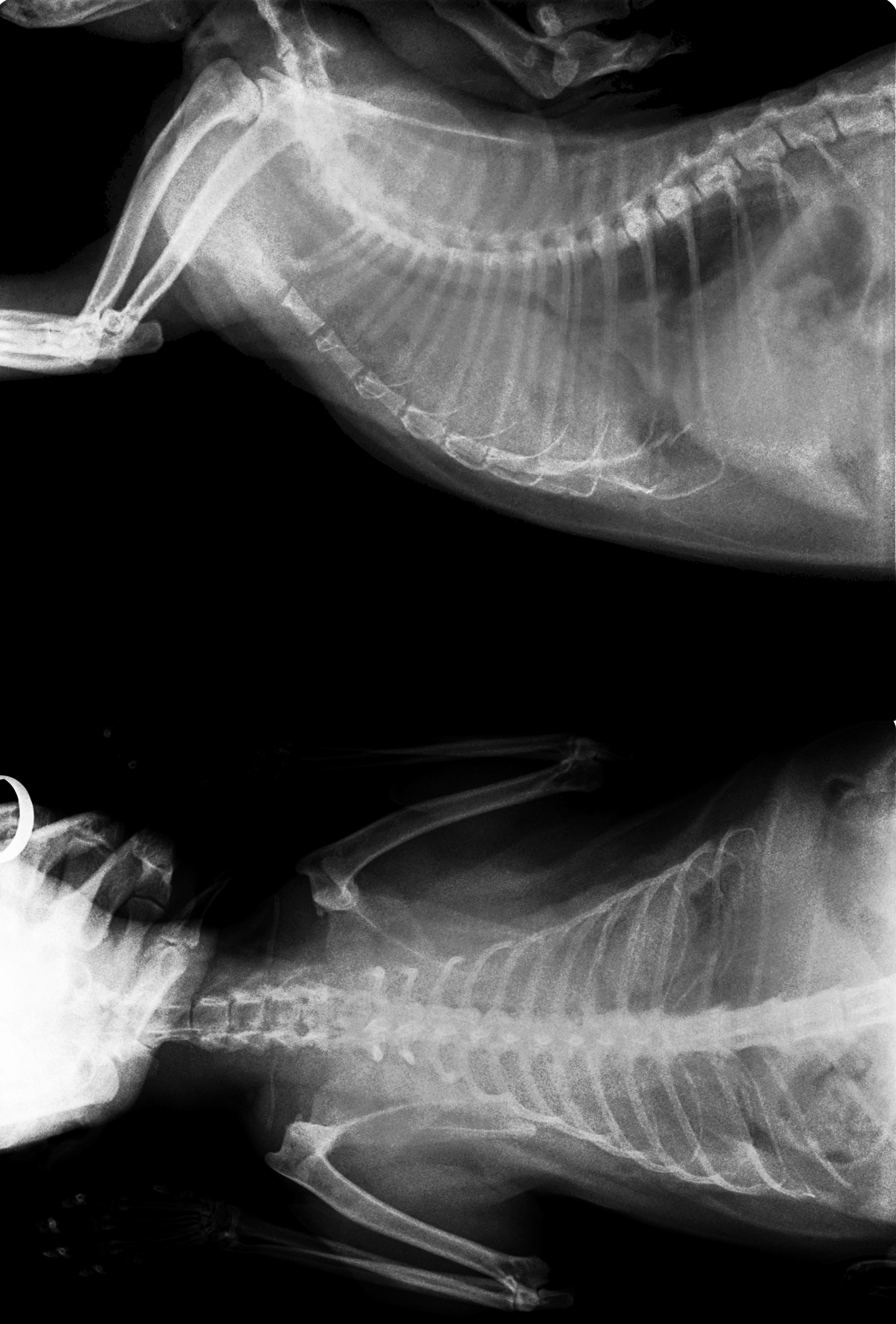
Cancer in cats is the leading cause of death among cats. It is caused by uncontrolled cell growth, and affects a wide range of cell types and organs in the body. Feline cancer initially manifests as a lump or bump on any part of the body. It rapidly grows in the affected cell, attaches itself to the tissue under the skin in that area, and, depending on the tumour, it can spread to other parts of the body. Although cancer accounts for approximately 32% of deaths in cats over ten years old, it can be successfully treated if diagnosed early. While the causes of cancer in cats are unknown, feline leukaemia virus is suspected to be a prime contributor. Other factors suspected to increase rates of feline cancer include toxins from the environment, passive smoking, excessive grooming, or licking parts of the body that have been in contact with an environmental toxin. Cancer can be detected at an early stage by observing certain signs and symptoms. Common diagnostic methods include ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lump
Lump may refer to: * "Lump" (song), a 1995 song by The Presidents of the United States of America * ''Lump'' (compilation album), a 2000 best-of album by The Presidents of the United States of America * Lump (dog), a dog who inspired Pablo Picasso * '' The Lump'', a 1991 animated short film * Lump hammer, a sledgehammer * Lump, a thermo-spatial unit in a lumped capacitance model of a thermal system * Swelling (medical) * Globus pharyngeus, a "lump in one's throat" * Clay lump, a mudbrick * Lump of coal, a threat to misbehaving children ( instead of presents at Christmas); or a bringer of warmth for the New Year * Lump, the Ober of Hearts in Schafkopf language * Protusion on a tool surface, also known as gall * LUMP, a musical collaboration of Laura Marling and Tunng member Mike Lindsay * The practice of combining sets of individuals into one classification See also * Lump sum A lump sum is a single payment of money, as opposed to a series of payments made over time (suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system, a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample Cell (biology), cells or Biological tissue, tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then Histopathology, fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauliflower Ear
Cauliflower ear is an irreversible condition that occurs when the Auricle (anatomy), external portion of the ear is hit and develops a Thrombus, blood clot or other collection of fluid under the perichondrium. This separates the cartilage from the overlying perichondrium that supplies its nutrients, causing it to die and resulting in the formation of fibrous tissue in the overlying skin. As a result, the outer ear becomes permanently swollen and deformed, resembling a cauliflower, hence the name. The condition is common in wrestling, boxing, and kickboxing, in martial arts such as Brazilian jiu-jitsu, judo, sumo, and mixed martial arts, and in full-contact sports such as rugby union. Presentation People presenting with possible auricular hematoma often have additional injuries (for example, head/neck lacerations) due to the frequently traumatic causes of auricular hematoma. The ear itself is often tense, fluctuant, and tender with throbbing pain. However, because of potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feline Hyperthyroidism
Feline hyperthyroidism is an endocrine disorder in which the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone. Hyperthyroidism is the most common endocrinopathy of cats. The complete pathogenesis is not fully understood. Background In 1979 the first clinical report of a cat with hyperthyroidism was reported. More studies and greater awareness would follow and today hyperthyroidism is a common condition in small animal practice. Whether that is due to increased prevalence or better testing is not entirely agreed upon. A study in 1987 transplanted thyroid tissue from affected cats into nude mice. The mice were administered levothyroxine, which suppresses thyroid-stimulating hormone. The thyroid cells remained in the hyperthyroid state. This study helped provide evidence for thyroid dysfunction as the cause rather than thyroid stimulation. Causes The majority of cases of hyperthyroidism in cats are the result of benign tumours. The most commonly identified abnormalities of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the auricle to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter. Structure The human ear canal is divided into two parts. The elastic cartilage part forms the outer third of the canal; its anterior and lower wall are cartilaginous, whereas its superior and back wall are fibrous. The cartilage is the continuation of the cartilage framework of auricle. The cartilaginous portion of the ear canal contains small hairs and specialized sweat glands, called apocrine glands, which produce cerumen ( ear wax). The bony part forms the inner two thirds. The bony part is much shorter in children and is only a ring (''annulus tympanicus'') in the newborn. The layer of epithelium encompassing the bony portion of the ear canal is much thinner and therefore, more sensitive in comparison to the cartilaginous portion. Size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebaceous Gland
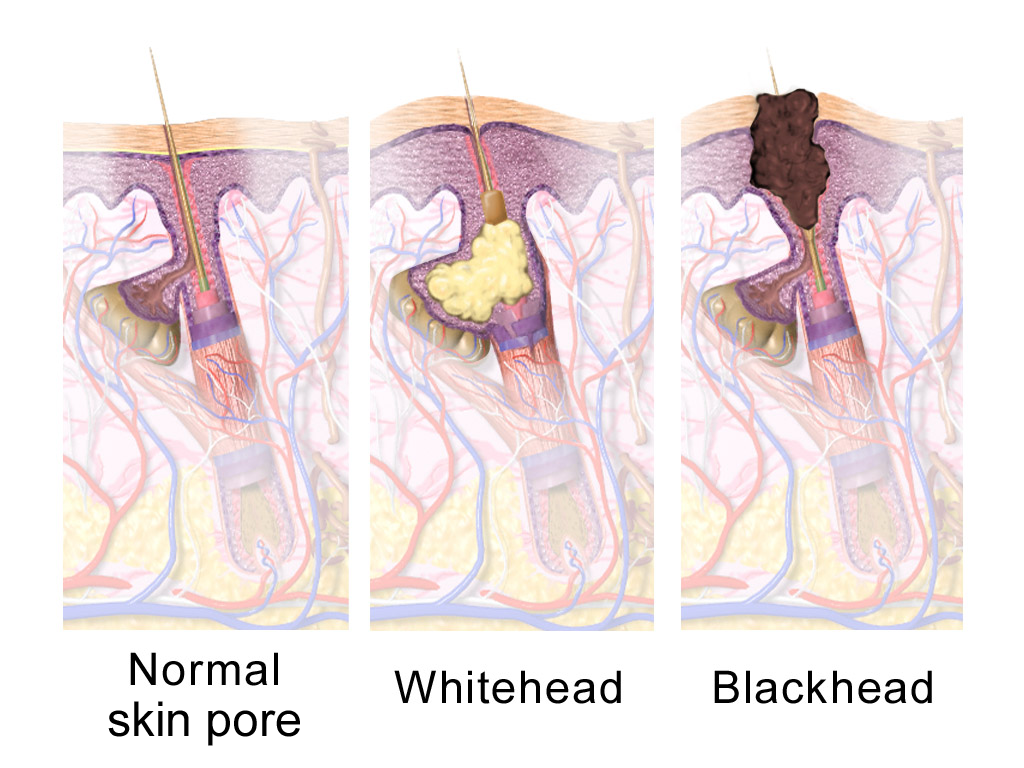
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipples, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipples. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location In humans, sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands: those connected to hair follicles and those that ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenoma
An adenoma is a benign tumor of epithelium, epithelial tissue with glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular organ (anatomy), organs, including the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, thyroid, prostate, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure (as can happen in familial polyposis coli). Although adenomas are benign, they should be treated as pre-cancerous. Over time adenomas may malignant transformation, transform to become malignancy, malignant, at which point they are called adenocarcinomas. Most adenomas do not transform. However, even though benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures (mass effect (medicine), mass effect) and by producing large amounts of hormones in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner (causing paraneoplastic syndromes). Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematemesis
Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood. It can be confused with hemoptysis (coughing up blood) or epistaxis (nosebleed), which are more common. The source is generally the upper gastrointestinal tract, typically above the suspensory muscle of duodenum. It may be caused by ulcers, tumors of the stomach or esophagus, varices, prolonged and vigorous retching, gastroenteritis, ingested blood (from bleeding in the mouth, nose, or throat), or certain drugs. Hematemesis is treated as a medical emergency, with treatments based on the amount of blood loss. Investigations include endoscopy. Any blood loss may be corrected with intravenous fluids and blood transfusions. Patients may need to avoid taking anything by mouth. Definition Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood. This is usually vomit that contains bright red blood. Coffee ground vomiting is similar to hematemesis, but is distinct in not involving bright red blood. Hematemesis must be differentiated from hemoptysis (coughing u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siamese Cat
The Siamese cat (; แมวสยาม, Maeo Sayam; แมววิเชียรมาศ, Maeo Wichien Maat) is one of the first distinctly recognised breeds of Asian cat. It derives from the Wichianmat landrace. The Siamese cat is one of several varieties of cats native to Thailand (known as Siam before 1939). The original Siamese became one of the most popular breeds in Europe and North America in the 19th century. Siamese cats have a distinctive colourpoint coat, resulting from a temperature-sensitive type of albinism. Distinct features like blue almond-shaped eyes, a triangular head shape, large ears, an elongated, slender, and muscular body, and various forms of point colouration characterise the modern-style Siamese. The modern-style Siamese's point-colouration resembles the "old-style" foundation stock. The "old-style" Siamese have a round head and body. They have been re-established by multiple registries as the Thai cat. Siamese and Thai cats are selectively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domestic Short-haired Cat
A moggy is any cat which has not been intentionally bred. Moggies lack a consistent appearance unlike purebred cats that are Selective breeding, selectively bred for appearance conforming to a Breed standard, standard. In contexts where cats need to be registered—such as in veterinary practices or shelters—moggies may be called domestic short-haired (DSH) or domestic long-haired (DLH) cats, depending on coat length (and less common designations may include "domestic medium-haired (DMH)" or "domestic semi-long-haired"). The vast majority of cats worldwide lack any pedigree ancestry. History Cat fancying is relatively new and over 85% of cat breeds have come into existence since the 1930s. Demography In the United States, domestic short-haired cats make up 95% of the cat population. In the UK 89–92% of cats are of non-pedigree lineage. Domestic short-haired In the cat fancy, and among veterinarians and Animal control officer, animal control agencies, domestic short-hai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lick Granuloma
A lick granuloma, also known as acral lick dermatitis, is a skin disorder found most commonly in dogs, but also in cats. In dogs, it results typically from the dog's urge to lick the lower portion of one of their legs. The lesion can initially be red, swollen, irritated, and bleeding, similar to a hot spot (wet eczema). The animal's incessant licking of the lesion eventually results in a thickened, firm, oval plaque, which is the granuloma. A major cause of lick granuloma appears to be psychological, related to stress, anxiety, separation anxiety, boredom, or compulsiveness. Lick granulomas are especially seen in active dogs left alone for long periods of time. One theory about the cause of lick granulomas is that excessive licking causes endorphin release, which reduces pain and makes the animal feel comfort temporarily. Other triggers include itchy skin, painful conditions caused by trauma to the skin, arthritis, neuralgia, and peripheral neuropathy. A bacterial or fung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |