|
Callaïs
Callaïs is the generic name for ancient green-blue precious stones used for making pendants and beads by western European cultures of the later Neolithic and early Bronze Age. The term includes turquoise and variscite but not jade. "Callaïs" was described by Pliny the Elder as being paler than lapis lazuli. Callaïs objects have been found in Neolithic tombs from the mid- 5th millennium BC in the Carnac region of western France. Callaïs deposits are thought to have been widely distributed throughout the Iberian peninsula, and transported from Andalusia, Castile, and Catalonia to Brittany, Normandy, and the Paris Basin The Paris Basin () is one of the major geological regions of France. It developed since the Triassic over remnant uplands of the Variscan orogeny (Hercynian orogeny). The sedimentary basin, no longer a single drainage basin, is a large sag in .... References Anthropology Gemstones Jewellery making Lithics {{gemology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turquoise
Turquoise is an opaque, blue-to-green mineral that is a hydrous phosphate of copper and aluminium, with the chemical formula . It is rare and valuable in finer grades and has been prized as a gemstone for millennia due to its hue. The robin egg blue or sky blue color of the Persian turquoise mined near the modern city of Nishapur, Iran, has been used as a guiding reference for evaluating turquoise quality. Like most other opaque gems, turquoise has been devalued by the introduction of treatments, imitations, and synthetics into the market. Names The word ''turquoise'' dates to the 17th century and is derived from the Old French ''turquois'' meaning "Turkish" because the mineral was first brought to Europe through the Ottoman Empire.Turquoise . minerals.usgs.gov However, according to [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andalusia
Andalusia ( , ; , ) is the southernmost autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Peninsular Spain, located in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, in southwestern Europe. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognized as a nationalities and regions of Spain, historical nationality and a national reality. The territory is divided into eight provinces of Spain, provinces: Province of Almería, Almería, Province of Cádiz, Cádiz, Province of Córdoba (Spain), Córdoba, Province of Granada, Granada, Province of Huelva, Huelva, Province of Jaén (Spain), Jaén, Province of Málaga, Málaga, and Province of Seville, Seville. Its capital city is Seville, while the seat of High Court of Justice of Andalusia, its High Court of Justice is the city of Granada. Andalusia is immediately south of the autonomous communities of Extremadura and Castilla-La Mancha; west of the autonomous community of Region of Mur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemstones
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. Certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to steadily increase to a value of $4.46billion by 2033. A gem expert is a gemo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behaviour, while cultural anthropology studies cultural meaning, including norms and values. The term sociocultural anthropology is commonly used today. Linguistic anthropology studies how language influences social life. Biological anthropology, Biological (or physical) anthropology studies the biology and evolution of Human evolution, humans and their close primate relatives. Archaeology, often referred to as the "anthropology of the past," explores human activity by examining physical remains. In North America and Asia, it is generally regarded as a branch of anthropology, whereas in Europe, it is considered either an independent discipline or classified under related fields like history and palaeontology. Etymology The abstract noun ''wikt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
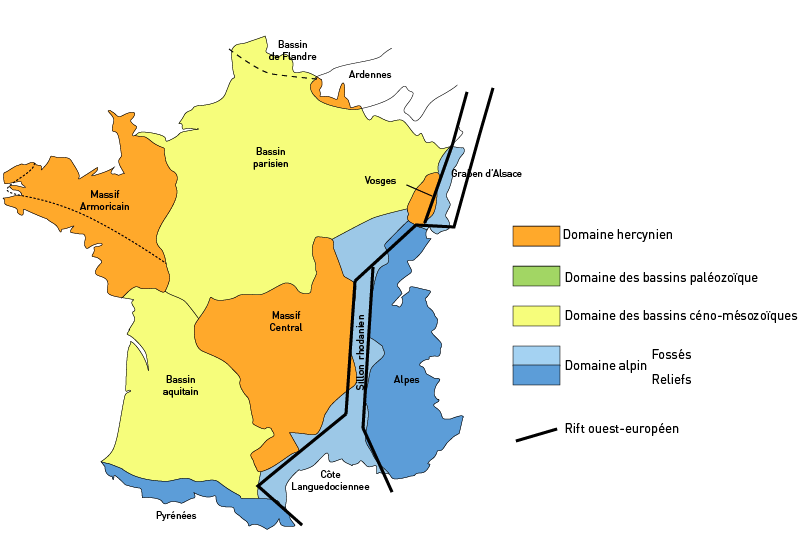
Paris Basin
The Paris Basin () is one of the major geological regions of France. It developed since the Triassic over remnant uplands of the Variscan orogeny (Hercynian orogeny). The sedimentary basin, no longer a single drainage basin, is a large sag in the craton, bordered by the Armorican Massif to the west, the Ardennes-Brabant axis to the north, the Massif des Vosges to the east, and the Massif Central to the south.Duval, B.C., 1992, Villeperdue Field, In Giant Oil and Gas Fields of the Decade, 1978-1988, AAPG Memoir 54, Halbouty, M.T., editor, Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Extent The region usually regarded as the Paris Basin is rather smaller than the area formed by the geological structure. The former occupies the centre of the northern half of the country, excluding Eastern France. The latter extends from the hills just south of Calais to Poitiers and from Caen to the brink of the middle Rhine Valley, east of Saarbrücken. Geography The landscape i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy. Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular Normandy (mostly the British Channel Islands). It covers . Its population in 2017 was 3,499,280. The inhabitants of Normandy are known as Normans; the region is the historic homeland of the Norman language. Large settlements include Rouen, Caen, Le Havre and Cherbourg-en-Cotentin, Cherbourg. The cultural region of Normandy is roughly similar to the historical Duchy of Normandy, which includes small areas now part of the departments of Mayenne and Sarthe. The Channel Islands (French: ''Îles Anglo-Normandes'') are also historically part of Normandy; they cover and comprise two bailiwicks: Bailiwick of Guernsey, Guernsey and Jersey, which are British Crown Dependencies. Normandy's name comes from the settlement of the territory by Vikings ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duchy of Brittany, duchy before being Union of Brittany and France, united with the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a provinces of France, province governed as a separate nation under the crown. Brittany is the traditional homeland of the Breton people and is one of the six Celtic nations, retaining Culture of Brittany, a distinct cultural identity that reflects History of Brittany, its history. Brittany has also been referred to as Little Britain (as opposed to Great Britain, with which it shares an etymology). It is bordered by the English Channel to the north, Normandy to the northeast, eastern Pays de la Loire to the southeast, the Bay of Biscay to the south, and the Celtic Sea and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its land area is 34,023 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situated on the northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, to the south of the Pyrenees mountain range. Catalonia is administratively divided into four Provinces of Spain, provinces or eight Vegueries of Catalonia, ''vegueries'' (regions), which are in turn divided into 43 Comarques of Catalonia, ''comarques''. The capital and largest city, Barcelona, is the second-most populous Municipalities in Spain, municipality in Spain and the fifth-most populous List of metropolitan areas in Europe, urban area in the European Union. > > > ''Catalonia'' theoretically derived. During the Middle Ages, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine chroniclers claimed that ''Catalania'' derives from the local medley of Goths with Alans, initially constituting a ''Goth-Alania''. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castile (historical Region)
Castile or Castille (; ) is a territory of imprecise limits located in Spain. The use of the concept of Castile relies on the assimilation (via a metonymy) of a 19th-century determinism, determinist geographical notion, that of Castile as Spain's ("tableland core", connected to the Meseta Central) with a long-gone historical entity of diachronically variable territorial extension (the Kingdom of Castile). The proposals advocating for a particular semantic codification/closure of the concept (a ''dialogical'' construct) are connected to Essentialism#In historiography, essentialist arguments relying on the Reification (fallacy), reification of something that does not exist beyond the social action of those Social constructivism, building Castile not only by Castilian nationalism, identifying with it as a homeland of any kind, but also Alterity, ''in opposition'' to it. A hot topic concerning the concept of Castile is its relation with Spain, insofar intellectuals, politicians, writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnac
Carnac (; , ) is a commune beside the Gulf of Morbihan on the south coast of Brittany in the Morbihan department in north-western France. Its inhabitants are called ''Carnacois'' in French. Carnac is renowned for the Carnac stones – one of the most extensive Neolithic menhir collections in the world – as well as its beaches, which are popular with tourists. Located on a narrow peninsula halfway between the medieval town Vannes and the seaside resort Quiberon, Carnac is split into two centres: ''Carnac-Ville'' and ''Carnac-Plage'' (the beachfront). In total there are five beaches, including ''la Grande Plage'', and further to the east, ''Plage Men Dû'' and ''Beaumer''. Map Standing stones Carnac is famous as the site of more than 10,000 Neolithic standing stones, also known as menhirs. The stones were hewn from local rock and erected by the pre-Celtic people of Brittany. Local tradition claims that the reason they stand in such perfectly straight lines is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between these types is an empirical observation. Their interpretation in terms of ethnic or political groups is based on archaeologists' understanding. However, this is often subject to long-unresolved debates. The concept of the archaeological culture is fundamental to culture-historical archaeology. Concept Different cultural groups have material culture items that differ both functionally and aesthetically due to varying cultural and social practices. This notion is observably true on the broadest scales. For example, the equipment associated with the brewing of tea varies greatly across the world. Social relations to material culture often include notions of identity and status. Advocates of culture-historical archaeology use the notion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |