|
Calenberg Loess Börde
The Calenberg is a hill in central Germany in the Leine depression near Pattensen in the municipality of Schulenburg. It lies 13 km west of the city of Hildesheim in south Lower Saxony on the edge of the Central Uplands. It is made from a chalk marl slab (''Kalkmergelbank''), has a height of and was formed almost 100 million years ago at the beginning of the Upper Cretaceous series in Cenomanian stage. The Calenberg became historically important as a result of the fort, stronghold and castle built as the main residence of the House of Hanover. Etymology The syllables ''Kal'', ''Kalen-'', ''Calen-'' in the word ''Calenberg'' are derived from the word ''kal'' in the Middle High German and Middle Low German languages and mean ''kahl'' i.e. "bare", "stripped", "unwooded". Name formations using ''Kal'', ''Kalen'' or ''Calen'' could refer to its geological base (''rock, stone''). The syllable ''-berg'' goes back to the Old High German word ''berg'', to the Middle High German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
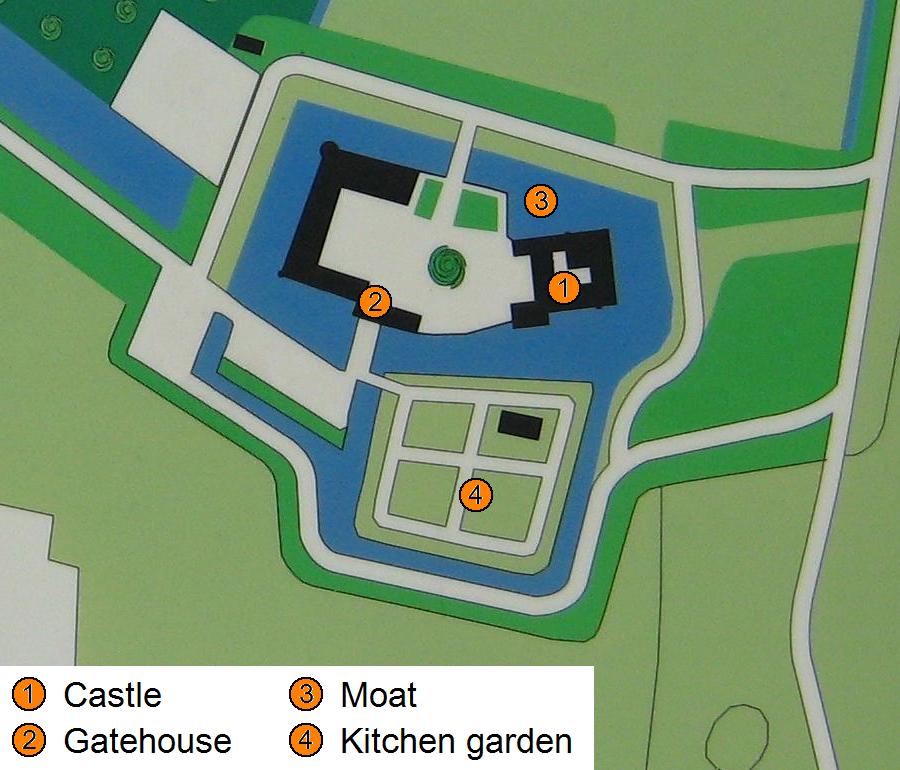
Calenberg Castle
Calenberg Castle (, later called and ; ruins known as ) was a medieval lowland castle in central Germany, near Schulenburg in the borough of Pattensen, west of the city of Hildesheim. It was built as a water castle in 1292 by the House of Welf, Welf duke, Otto II of Lüneburg, Otto the Strict, in der Leine (river), Leine river meadows between two branches of the Leine river on the southern part of the chalk marl hill of the Calenberg. At the start of the 16th century it was converted into a fort (''Feste''). In the 15th century, ''Fort Calenberg'' gave its name to the Welf Principality of Calenberg. Following the Thirty Years' War it lost its military importance and was slighting, slighted. Today it is a ruin with underground vaults that are surrounded by high ramparts. Etymology The word ''Feste'' or ''Veste'' ("fort") stems, like the words ''Festung'' ("fortress") and ''Befestigung'' ("fortification") from the adjective ''fest'' ("strong", "firm" or "immovable"). The adjec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Castle
A water castle, sometimes water-castle, is a castle which incorporates a natural or artificial body of water into its defences.Forde-Johnston (1979), p. 163. It can be entirely surrounded by water-filled moats (moated castle) or natural waterbodies such as island castles in a river or offshore. The term comes from European castle studies, mainly German ''Burgenkunde''. Some interpretations of the category emphasise that the use of water extends beyond a defensive purpose.Plowman (2005), p. 44. When stately homes were built in such a location, or a Wasserburg was later rebuilt as a residential manor, the German term becomes Wasserschloss, lit. "water palace/manor". Description Forde-Johnston describes such a site as "a castle in which water plays a prominent part in the defences." Apart from hindering attackers, an abundant supply of water was also an advantage during a siege. Topographically, such structures are a type of low-lying castle. Such a castle usually had only one e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto II Of Lüneburg
Otto is a masculine German given name and a surname. It originates as an Old High German short form (variants ''Audo'', '' Odo'', '' Udo'') of Germanic names beginning in ''aud-'', an element meaning "wealth, prosperity". The name is recorded from the 7th century ( Odo, son of Uro, courtier of Sigebert III). It was the name of three 10th-century German kings, the first of whom was Otto I the Great, the first Holy Roman Emperor, founder of the Ottonian dynasty. The Gothic form of the prefix was ''auda-'' (as in e.g. '' Audaþius''), the Anglo-Saxon form was ''ead-'' (as in e.g. '' Eadmund''), and the Old Norse form was '' auð-''. Due to Otto von Bismarck, the given name ''Otto'' was strongly associated with the German Empire in the later 19th century. It was comparatively frequently given in the United States (presumably in German American families) during the 1880s to 1890s, remaining in the top 100 most popular masculine given names in the US throughout 1880–1898, but its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Welf
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meuse-Moselle area was closely related to the imperial family of the Carolingians. Origins The (Younger) House of Welf is the older branch of the House of Este, a dynasty whose earliest known members lived in Veneto and Lombardy in the late 9th/early 10th century, sometimes called Welf-Este. The first member was Welf I, Duke of Bavaria, also known as Welf IV. He inherited the property of the Elder House of Welf when his maternal uncle Welf, Duke of Carinthia, Welf III, Duke of Carinthia and Verona, the last male Welf of the Elder House, died in 1055. Welf IV was the son of Welf III's sister Kunigunde of Altdorf and her husband Albert Azzo II, Margrave of Milan. In 1070, Welf IV became Duke of Bavaria. Welf II, Duke of Bavaria married Countess Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowland Castle
The term lowland castle or plains castle () describes a type of castle that is situated on a lowland, plain or valley floor, as opposed to one built on higher ground such as a hill spur. The classification is extensively used in Germany where about 34 percent of all castles are of the lowland type.Krahe, pp. 21-23 (2002) Because lowland castles do not have the defensive advantage of a site on higher ground, sites are chosen that are easy to defend, taking advantage, for example, of rivers, islands in lakes or marshes. Where such natural obstacles do not exist, artificially similar obstacles take on added significance. These include water-filled or dry moats, ramparts, palisades and curtain walls. In order to increase the height of the castle above the surrounding terrain, artificial earth mounds may be built (such as mottes), and fortified towers also fulfil this purpose. Castles of the Early Middle Ages (including Slavic and Saxon castles) often had a narrow, deep ditch a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallanlagen Von Alt Calenberg
The Wallanlagen (lit., "Wall Park") is a park area in Frankfurt, Germany, which forms a five-kilometre-long green belt around the city centre. The parklands run along the course of the former city walls, which were built from the 14th century and which were torn down in the early 19th century. The former course of the city wall was landscaped as a park between 1804 and 1812. The Wallanlagen parklands are commonly divided into seven areas, which are usually named after the former city gate A city gate is a gate which is, or was, set within a city wall. It is a type of fortified gateway. Uses City gates were traditionally built to provide a point of controlled access to and departure from a walled city for people, vehicles, goods ...s. They are the ''Untermainanlage'', the ''Gallusanlage'', the ''Taunusanlage'', the ''Bockenheimer Anlage'', the ''Eschenheimer Anlage'', the ''Friedberger Anlage'' and the ''Obermainanlage''.Benno Reifenberg: Der Anlagenring. In: ''Das Einzigarti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxony State Museum
The Lower Saxon State Museum Hanover (, or simply ) is the state museum of Lower Saxony in Hanover, Germany. Situated adjacent to the New Town Hall, the museum comprises the state gallery (), featuring paintings and sculptures from the Middle Ages to the 20th century, and departments of archaeology, natural history and ethnology. The museum includes a vivarium with fish, amphibians, reptiles and arthropods. History Originally the Museum of Art and Science () inaugurated in 1856 in the presence of George V of Hanover based in the present-day Hanover Arthouse (), it was later renamed Museum of the Province of Hanover, or simply Provincial Museum. The museum soon ran out of space for its art collections, prompting the construction of the current building, designed by Hubert Stier in a Neo-Renaissance style, on the edge of the Maschpark in 1902. The building's relief frieze, titled "Key Moments in the Evolution of Humanity" (), was created by the Hanoverian artist Georg Herting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumuli
A tumulus (: tumuli) is a mound of Soil, earth and Rock (geology), stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, mounds, howes, or in Siberia and Central Asia as ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built for various purposes, may also originally have been a tumulus. Tumuli are often categorised according to their external apparent shape. In this respect, a long barrow is a long tumulus, usually constructed on top of several burials, such as passage graves. A round barrow is a round tumulus, also commonly constructed on top of burials. The internal structure and architecture of both long and round barrows have a broad range; the categorization only refers to the external apparent shape. The method of may involve a dolmen, a cist, a mortuary enclosure, a mortuary house, or a chamber tomb. Examples of barrows include Duggleby Howe and Maeshowe. Etymology The word ''tumulus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inoceramid
The Inoceramidae are an extinct family (biology), family of bivalves ("clams") in the Class Mollusca. Fossils of inoceramids are found in marine sediments of Permian to latest Cretaceous in age. Inoceramids tended to live in upper bathyal and neritic environments. Many species of inoceramid are found all over the world, demonstrating the wide distribution of their preferred ecosystems, and possibly long-lived planktotrophic larvae.Lower Turonian Euramerican Inoceramidae: A morphologic, taxonomic, and biostratigraphic overview A report from the first Workshop on Early Turonian Inoceramids (Oct. 5-8, 1992) in Hamburg, Germany; organized by Heinz Hilbrecht and Peter J. Harries Despite their wide distribution, the pace of evolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |