|
Calcium Signaling Pathway
Calcium signaling is the use of calcium ions (Ca2+) to communicate and drive intracellular processes often as a step in signal transduction. Ca2+ is important for a wide variety of cellular signaling pathways. Once Ca2+ enters the cytosol of the cytoplasm it exerts allosteric regulatory effects on many enzymes and proteins. Ca2+ signaling can activate certain ion channels for short term changes (like changes to electrochemical gradients) in the cell. For longer-term changes (like changes in gene transcription), Ca2+ can act as a second messenger through indirect signal transduction pathways, such as in G protein-coupled receptor pathways. Calcium Concentration Regulation The resting concentration of Ca2+ in the cytoplasm is normally maintained around 100 nM. This is 20,000- to 100,000-fold lower than typical extracellular concentration. To maintain this low concentration, Ca2+ is naturally buffered by different organelles and proteins within the cell. To change Ca2+ levels in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Space
Extracellular space refers to the part of a multicellular organism outside the cells, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid. This is distinguished from intracellular space, which is inside the cells. The composition of the extracellular space includes metabolites, ions, proteins, and many other substances that might affect cellular function. For example, neurotransmitters "jump" from cell to cell to facilitate the transmission of an electric current in the nervous system. Hormones also act by travelling the extracellular space towards cell receptors. In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular (or sometimes extracellular space) means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid (see extracellular matrix). The term is used in contrast to intracellular (inside the cell). According to the Gene Ontology, the extracellular space is a cellular component def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase C
In cell biology, protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades. In biochemistry, the PKC family consists of fifteen isozymes in humans. They are divided into three subfamilies, based on their second messenger requirements: conventional (or classical), novel, and atypical. Conventional (c)PKCs contain the isoforms α, βI, βII, and γ. These require Ca2+, DAG, and a phospholipid such as phosphatidylserine for activation. Novel (n)PKCs include the δ, ε, η, and θ isoforms, and require DAG, but do not require Ca2+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. Diglycerides are natural components of food fats, though minor in comparison to triglycerides. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
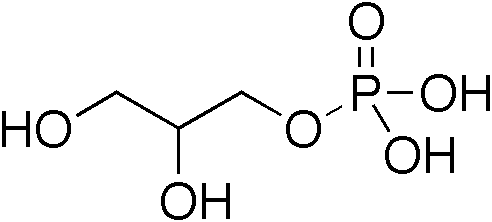
Inositol Trisphosphate
Inositol trisphosphate or inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate abbreviated InsP3 or Ins3P or IP3 is an inositol phosphate signaling molecule. It is made by hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), a phospholipid that is located in the plasma membrane, by phospholipase C (PLC). Together with diacylglycerol (DAG), IP3 is a second messenger molecule used in signal transduction in biological cells. While DAG stays inside the membrane, IP3 is soluble and diffuses through the cell, where it binds to its receptor, which is a calcium channel located in the endoplasmic reticulum. When IP3 binds its receptor, calcium is released into the cytosol, thereby activating various calcium regulated intracellular signals. Properties Chemical formula and molecular weight IP3 is an organic molecule with a molecular mass of 420.10 g/mol. Its empirical formula is C6H15O15P3. It is composed of an inositol ring with three phosphate groups bound at the 1, 4, and 5 carbon positions, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PIP2
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)''P''2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)''P''2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms PIP2 domain, lipid clusters that sort proteins. PIP2 is formed primarily by the type I phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinases from Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate, PI(4)P. In metazoans, PIP2 can also be formed by type II phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate 4-kinases from Phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, PI(5)P. The fatty acids of PIP2 are variable in different species and tissues, but the most common fatty acids are stearic acid, stearic in position 1 and arachidonic in 2. Signaling pathways PIP2 is a part of many cellular signaling pathways, including PI(4,5)P2 Cycle, PIP2 cycle, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, PI3K signalling, and PI5P metabolism. Recently, it has been found in the Cell nucleu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high-affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinase proteins. Receptor tyrosine kinases have been shown not only to be key regulators of normal cellular processes but also to have a critical role in the development and progression of many types of cancer. Mutations in receptor tyrosine kinases lead to activation of a series of signalling cascades which have numerous effects on protein expression. The receptors are generally activated by dimerization and substrate presentation. Receptor tyrosine kinases are part of the larger family of protein tyrosine kinases, encompassing the receptor tyrosine kinase proteins which contain a transmembrane domain, as well as the non-receptor tyrosine kinases which do not possess transmembrane domains. History The first RTKs to be discovered were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Surface Receptor
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral membrane proteins that allow communication between the cell and the extracellular space. The extracellular molecules may be hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines, growth factors, cell adhesion molecules, or nutrients; they react with the receptor to induce changes in the metabolism and activity of a cell. In the process of signal transduction, ligand binding affects a cascading chemical change through the cell membrane. Structure and mechanism Many membrane receptors are transmembrane proteins. There are various kinds, including glycoproteins and lipoproteins. Hundreds of different receptors are known and many more have yet to be studied. Transmembrane receptors are typically classified based on their tertiary (three-dimens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase C
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role in eukaryotic cell physiology, in particular signal transduction pathways. Phospholipase C's role in signal transduction is its cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacyl glycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), which serve as second messengers. Activators of each PLC vary, but typically include heterotrimeric G protein subunits, protein tyrosine kinases, small G proteins, Ca2+, and phospholipids. There are thirteen kinds of mammalian phospholipase C that are classified into six isotypes (β, γ, δ, ε, ζ, η) according to structure. Each PLC has unique and overlapping controls over expression and subcellular distribution. However, PLC is not limited to mammals, and is present in bacteria a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLC Role In IP3-DAG Pathway
PLC or plc may refer to: * Public limited company, a type of public company Education * Platoon Leaders Class, of the US Marine Corps Officer Candidates School * Post Leaving Certificate, a qualification in Ireland * Presbyterian Ladies' College (other), several schools in Australia * Professional learning community, for collaborative learning Medicine * Perlecan, a protein in humans * Peptide loading complex, an intracellular membrane protein matrix * Peter Lougheed Centre, a hospital in Calgary, Alberta, Canada * Phospholipase C, a class of membrane-associated enzymes * Pityriasis lichenoides chronica, a skin condition * Posterolateral corner, a region of the human knee Politics * Colombian Liberal Party () * Conservative Party (Spain) () * Constitutionalist Liberal Party (), in Nicaragua * Liberal Party of Canada () * Palestinian Legislative Council, of the Palestinian Authority * Pennsylvania Leadership Conference, in the US * Provisional Legislative Counci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |