|
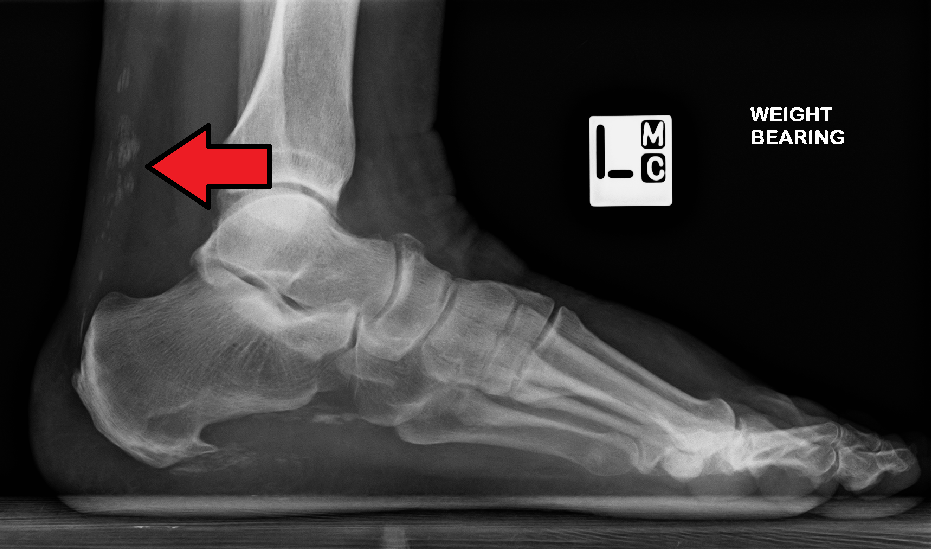
Calcinosis Kidney
Calcinosis is the formation of calcium deposits in any soft tissue. It is a rare condition that has many different causes. These range from infection and injury to systemic diseases like kidney failure. Types Dystrophic calcification The most common type of calcinosis is dystrophic calcification. This type of calcification can occur as a response to any soft tissue damage, including that involved in implantation of medical devices. Metastatic calcification Metastatic calcification involves a systemic calcium excess imbalance, which can be caused by hypercalcemia, kidney failure, milk-alkali syndrome, lack or excess of other minerals, or other causes. Tumoral calcinosis The cause of the rare condition of tumoral calcinosis is not entirely understood. It is generally characterized by large, globular calcifications near joints. See also * Calcification * Calcinosis cutis * Dermatomyositis * Fahr's syndrome * Hyperphosphatemia * Primrose syndrome * Scleroderma Scleroderma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eternal Leaders Of North Korea
The eternal leaders of North Korea are titles accorded to deceased leaders of North Korea. The phrase was used in a line of the preamble to the Constitution, as amended on 30 June 2016, and in subsequent revisions. It reads (in the original version): History of the title Presidency of North Korea before 1994 The post of "President of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea" was established in the Constitution of North Korea in 1972. Until then, Kim Il Sung held the posts of premier and general secretary of the Workers' Party of Korea. In 1972, the presidency was established, and Kim Il Sung was elected to the position by the Supreme People's Assembly, the North Korean legislature, on 28 December 1972. Kim served as president until 1994 when he died, and the position was left vacant and his son and successor Kim Jong Il was not given the title. "Eternal President" The preamble of the Constitution of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea as amended on 5 September 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
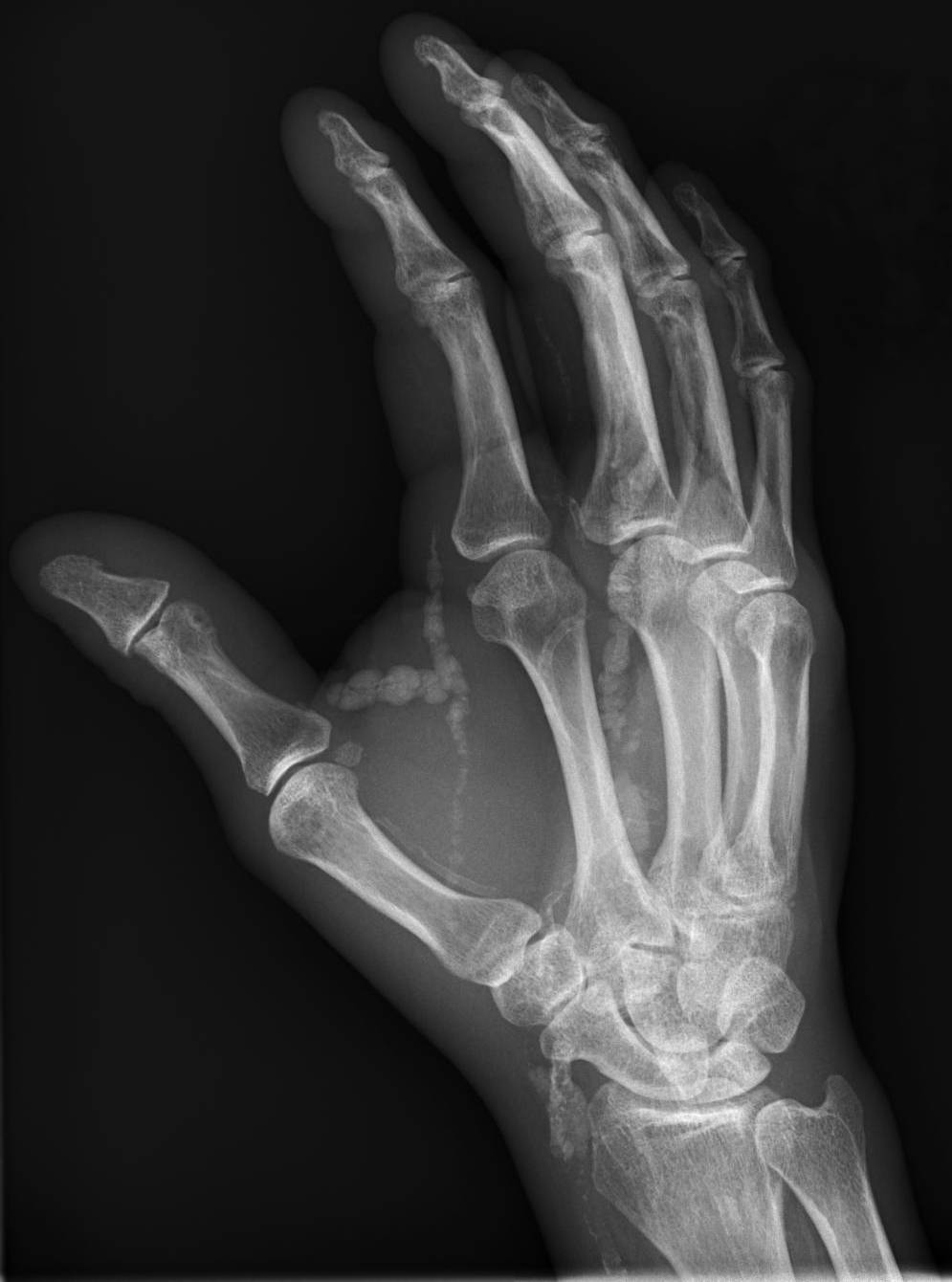
Tumoral Calcinosis
Tumoral calcinosis is a rare condition in which there is calcium deposition in the soft tissue in periarticular location, around joints, outside the joint capsule. They are frequently (0.5–3%) seen in patients undergoing renal dialysis. Clinically also known as hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis (HFTC), is often caused by genetic mutations in genes that regulate phosphate physiology in the body (leading to too much phosphate (hyperphosphatemia)). Best described genes that harbour mutations in humans are FGF-23, Klotho (biology), Klotho (KL), or GALNT3. A zebrafish animal model with reduced GALNT3 expression also showed HFTC-like phenotype, indicating an evolutionary conserved mechanism that is involved in developing tumoral calcinosis. Clinical features The name indicates calcinosis (calcium deposition) which resembles tumor (like a new growth). They are not true neoplasms – they don't have dividing Cell (biology), cells. They are just deposition of inorganic calci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptoms And Signs
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition. Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showing on a medical scan. A symptom is something out of the ordinary that is experienced by an individual such as feeling feverish, a headache or other pains in the body, which occur as the body's immune system fights off an infection. Signs and symptoms Signs A medical sign is an objective observable indication of a disease, injury, or medical condition that may be detected during a physical examination. These signs may be visible, such as a rash or bruise, or otherwise detectable such as by using a stethoscope or taking blood pressure. Medical signs, along with symptoms, help in forming a diagnosis. Some examples of signs are nail clubbing of either the fingernails or to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure. One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud's syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small, dilated blood vessels. The cause is unknown, but it may be due to an abnormal immune response. Risk factors include family history, certain genetic factors, and exposure to silica. The underlying mechanism involves the abnormal growth of connective tissue, which is believed to be the result of the immune system attacking healthy tissues. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, supported by a skin biopsy or blood tests. While no cure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primrose Syndrome
Primrose syndrome is a rare, slowly progressive genetic disorder that can vary symptomatically between individual cases, but is generally characterised by ossification of the external ears, learning difficulties, and facial abnormalities. It was first described in 1982 in Scotland's Royal National Larbert Institution by Dr D.A.A. Primrose. Primrose syndrome appears to occur spontaneously, regardless of family history. The cause is currently unknown and there are no known treatments. Signs and symptoms The common symptoms in all reported cases of Primrose syndrome include ossified pinnae, learning disabilities or intellectual disability, hearing problems, movement disorders (ataxia, paralysis, and parkinsonism among others—likely due, in part, to calcification of the basal ganglia), a torus palatinus (a neoplasm on the mouth's hard palate), muscle atrophy, and distorted facial features. Other symptoms usually occur, different in each case, but it is unknown whether or not these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperphosphatemia
Hyperphosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is an elevated level of phosphate in the blood. Most people have no symptoms while others develop calcium deposits in the soft tissue. The disorder is often accompanied by low calcium blood levels, which can result in muscle spasms. Causes include kidney failure, pseudohypoparathyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, diabetic ketoacidosis, tumor lysis syndrome, and rhabdomyolysis. Diagnosis is generally based on a blood phosphate level exceeding 1.46 mmol/L (4.5 mg/dL). Levels may appear falsely elevated with high blood lipid levels, high blood protein levels, or high blood bilirubin levels. Treatment may include a phosphate low diet and antacids like calcium carbonate that bind phosphate. Occasionally, intravenous normal saline or kidney dialysis may be used. How commonly it occurs is unclear. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms include ectopic calcification, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fahr's Syndrome
Primary familial brain calcification Initial Posting: April 18, 2004; Last Update: August 24, 2017. (PFBC), also known as familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (FIBGC) and Fahr's disease, is a rare, genetically dominant or recessive, inherited neurological disorder characterized by abnormal deposits of calcium in areas of the brain that control movement. Through the use of CT scans, calcifications are seen primarily in the basal ganglia and in other areas such as the cerebral cortex. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of this disease include deterioration of motor functions and speech, seizures, and other involuntary movement. Other symptoms are headaches, dementia, and vision impairment. Characteristics of Parkinson's Disease are also similar to PFBC. The disease usually manifests itself in the third to fifth decade of life but may appear in childhood or later in life.Sobrido MJ, Hopfer S, Geschwind DH (2007)Familial idiopathic basal ganglia calcification" In: Pagon RA, Bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a Chronic condition, long-term inflammatory disorder, inflammatory Autoimmune disease, autoimmune disorder which affects the skin and the muscles. Its symptoms are generally a skin rash and worsening muscle weakness over time. These may occur suddenly or develop over months. Other symptoms may include weight loss, fever, lung inflammation, or light sensitivity. Complications may include calcinosis, calcium deposits in muscles or skin. Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune disorder featuring both humoral and T-cell autoimmune processes. Dermatomyositis may develop as a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with several forms of malignancy. It is known to be associated with several viruses, especially coxsackievirus, but no definitive causal link has been found. Dermatomyositis is considered a type of inflammatory myopathy. Diagnosis is typically based on some combination of symptoms, blood tests, electromyography, and muscle biopsy, muscle biopsies. Eighty percen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcinosis Cutis
Calcinosis cutis is an uncommon condition marked by calcium buildup in the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Calcinosis cutis can range in intensity from little nodules in one area of the body to huge, crippling lesions affecting a vast portion of the body. Five kinds of the condition are typically distinguished: calciphylaxis, idiopathic calcification, iatrogenic calcification, dystrophic calcification, and metastatic calcification. Tumors, inflammation, varicose veins, infections, connective tissue disease, hyperphosphatemia, and hypercalcemia can all lead to calcinosis. Systemic sclerosis is linked to calcineuris cutis. Calcinosis is seen in Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis, also known as CREST syndrome (the "C" in CREST). Signs and symptoms Lesions might be more severe and widespread, or they can develop gradually and show no symptoms. The nodules may cause pain and hinder function in addition to having a variety of sizes and shapes. The underlying condition determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Materials'' 12, 476-478 (2013). causing it to harden. Calcifications may be classified on whether there is mineral balance or not, and the location of the calcification. Calcification may also refer to the processes of normal mineral deposition in biological systems, such as the formation of stromatolites or mollusc shells (see Biomineralization). Signs and symptoms Calcification can manifest itself in many ways in the body depending on the location. In the pulpal structure of a tooth, calcification often presents asymptomatically, and is diagnosed as an incidental finding during radiographic interpretation. Individual teeth with calcified pulp will typically respond negatively to vitality testing; teeth with calcified pulp often lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk-alkali Syndrome
Milk-alkali syndrome (MAS), also referred to as calcium-alkali syndrome, is the third most common cause of elevated blood calcium levels ( hypercalcemia). Milk-alkali syndrome is characterized by hypercalcemia, metabolic alkalosis, and acute kidney injury. Milk-alkali syndrome can be caused by the excessive intake of calcium and absorbable alkali. Sources of calcium and alkali include dietary supplements taken for the prevention of osteoporosis or hyperparathyroidism and antacids taken for peptic ulcer disease. Common acute symptoms of milk-alkali syndrome include nausea and vomiting, dry mouth, confusion, lethargy, and distaste for milk. If left untreated, milk-alkali syndrome may lead to kidney failure or even death. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of milk-alkali syndrome can develop after only a few days and up to several months following the initial ingestion of absorbable calcium and alkali. However, the severity of signs and symptoms of milk-alkali syndrome i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kim Il Sung
Kim Il Sung (born Kim Song Ju; 15 April 1912 – 8 July 1994) was a North Korean politician and the founder of North Korea, which he led as its first Supreme Leader (North Korean title), supreme leader from North Korea#Founding, its establishment in 1948 until Death and state funeral of Kim Il Sung, his death in 1994. Afterwards, he was succeeded by his son Kim Jong Il and was declared Eternal leaders of North Korea, Eternal President. He held the posts of the Premier of North Korea, Premier from 1948 to 1972 and President of North Korea, President from 1972 to 1994. He was General Secretary of the Workers' Party of Korea, the leader of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK) from 1949 to 1994 (titled as chairman from 1949 to 1966 and as general secretary after 1966). Coming to power after the end of Korea under Japanese rule, Japanese rule over Korea in 1945 following Japan's surrender in World War II, he authorized Operation Pokpung, the invasion of First Republic of Korea, South K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |