|
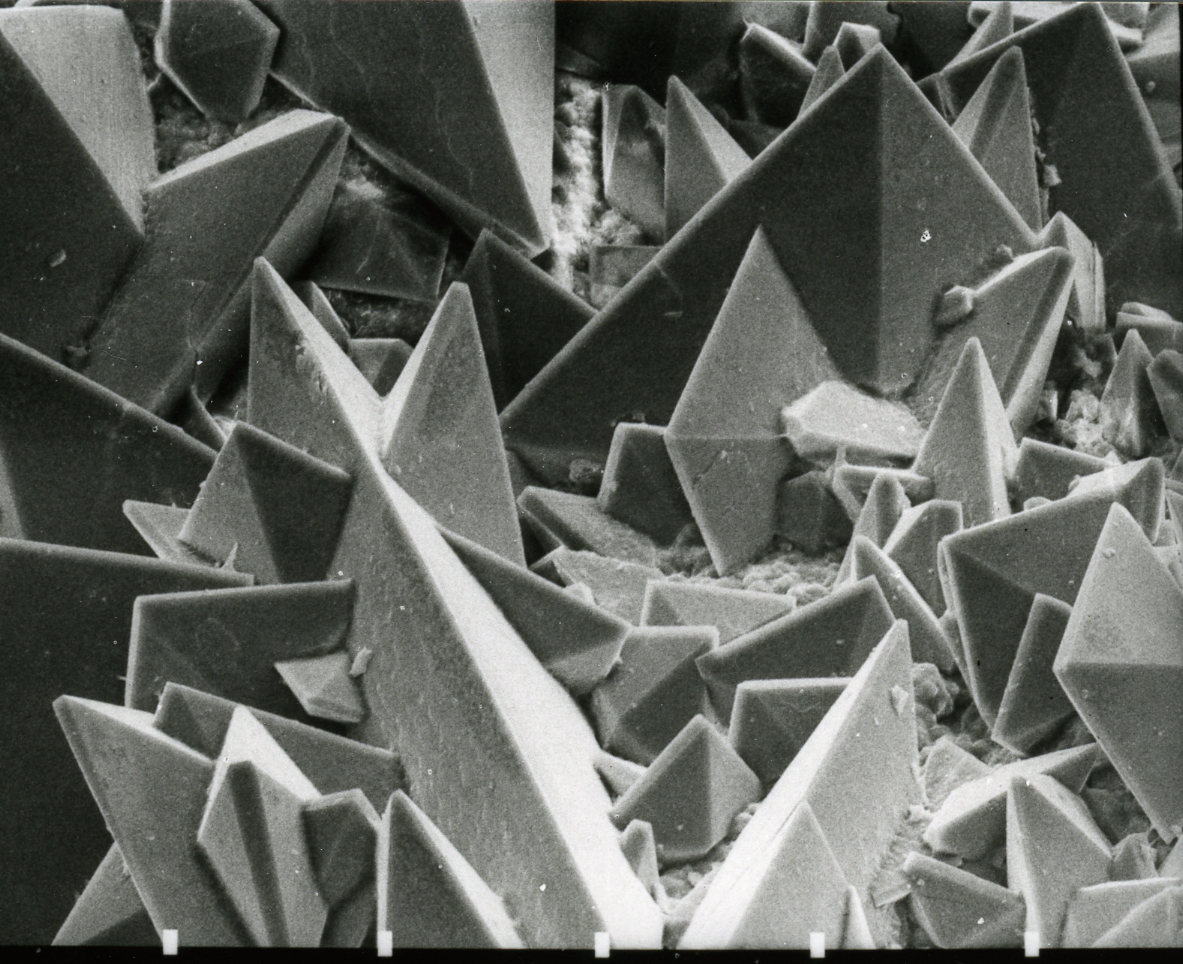
Caesium Oxalate
Caesium oxalate (standard IUPAC spelling) dicesium oxalate, or cesium oxalate (American spelling) is the oxalate of caesium. Caesium oxalate has the chemical formula of Cs2C2O4. Preparation Caesium oxalate can be prepared by passing carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide over caesium carbonate at 380 °C: :Cs2CO3 + CO + CO2 → Cs2C2O4 + CO2 Other alkali carbonates do not undergo transformation to oxalate. Caesium carbonate can react with oxalic acid in aqueous solution to give caesium oxalate. :Cs2CO3 + H2C2O4•2H2O → Cs2C2O4•H2O + CO2 + H2O Chemical Reactions Caesium oxalate can be reduced back into caesium carbonate and carbon dioxide by thermal decomposition. :Cs2C2O4 → Cs2CO3 + CO Double salts Compounds that contain caesium and another element in addition to the oxalate anion are double salts. The oxalate may form a complex with a metal that can make a salt with caesium. Examples include: Mixed anion compounds containing caesium, oxalate and another ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalate
Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate) is an anion with the formula C2O42−. This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (Na2C2O4), and several esters such as dimethyl oxalate (C2O4(CH3)2). It is a conjugate base of oxalic acid. At neutral pH in aqueous solution, oxalic acid converts completely to oxalate. Relationship to oxalic acid The dissociation of protons from oxalic acid proceeds in a stepwise manner; as for other polyprotic acids, loss of a single proton results in the monovalent hydrogenoxalate anion . A salt with this anion is sometimes called an acid oxalate, monobasic oxalate, or hydrogen oxalate. The equilibrium constant ( ''K''a) for loss of the first proton is (p''K''a = 1.27). The loss of the second proton, which yields the oxalate ion, has an equilibrium constant of (p''K''a = 4.28). These values imply, in solutions with neutral pH, no oxalic acid and only tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesium
Caesium ( IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. It is pyrophoric and reacts with water even at . It is the least electronegative element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite. The element has 40 known isotopes, making it, along with barium and mercury, one of the elements with the most isotopes. Caesium-137, a fission product, is extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactors. The German chemist Robert Bunsen and physicist Gustav Kirchhoff discovered caesium in 1860 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy. The first small-scale applications fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds, when insufficient oxygen or heat is present to produce carbon dioxide. There are also numerous environmental and biological sources that generate and emit a significant amount of carbon monoxide. It is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Upon emission into the atmosphere, carbon monoxide affects several processes that contribute to climate change. Carbon monoxide has important biological roles across phylog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesium Carbonate
Caesium carbonate or cesium carbonate is a white crystalline solid compound. Caesium carbonate has a high solubility in polar solvents such as water, alcohol and DMF. Its solubility is higher in organic solvents compared to other carbonates like potassium and sodium carbonates, although it remains quite insoluble in other organic solvents such as toluene, p-xylene, and chlorobenzene. This compound is used in organic synthesis as a base. It also appears to have applications in energy conversion. Preparation Caesium carbonate can be prepared by thermal decomposition of caesium oxalate. Upon heating, caesium oxalate is converted to caesium carbonate with emission of carbon monoxide. :Cs2C2O4 → Cs2CO3 + CO It can also be synthesized by reacting caesium hydroxide with carbon dioxide. :2 CsOH + CO2 → Cs2CO3 + H2O Chemical reactions Caesium carbonate is very important for the ''N''-alkylation of compounds such as sulfonamides, amines, β-lactams, indoles, heterocyclic compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalic Acid
Oxalic acid is an organic acid with the systematic name ethanedioic acid and formula . It is the simplest dicarboxylic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that forms a colorless solution in water. Its name comes from the fact that early investigators isolated oxalic acid from flowering plants of the genus '' Oxalis'', commonly known as wood-sorrels. It occurs naturally in many foods. Excessive ingestion of oxalic acid or prolonged skin contact can be dangerous. Oxalic acid has much greater acid strength than acetic acid. It is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate (), is a chelating agent for metal cations. Typically, oxalic acid occurs as the dihydrate with the formula . History The preparation of salts of oxalic acid (crab acid) from plants had been known, at least since 1745, when the Dutch botanist and physician Herman Boerhaave isolated a salt from wood sorrel. By 1773, François Pierre Savary of Fribourg, Switzerland had isolated oxalic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Anion Compounds
Mixed anion compounds, heteroanionic materials or mixed anion materials are chemical compounds containing cations and more than one kind of anion. The compounds contain a single phase, rather than just a mixture. Use in materials science By having more than one anion, many more compounds can be made, and properties tuned to desirable values. In terms of optics, properties include laser damage threshold, refractive index, birefringence, absorption particularly in the ultraviolet or near infrared, non-linearity. Mechanical properties can include ability to grow a large crystal, ability to form a thin layer, strength, or brittleness. Thermal properties can include melting point, thermal stability, phase transition temperatures, Thermal expansion coefficient. For electrical properties, electric conductivity, band gap, superconducting transition temperature piezoelectricity, pyroelectricity, ferromagnetism, dielectric constant, charge-density wave transition can be adjusted. Product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesium Compounds
Caesium (IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. It is pyrophoric and reacts with water even at . It is the least electronegative element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite. The element has 40 known isotopes, making it, along with barium and mercury, one of the elements with the most isotopes. Caesium-137, a fission product, is extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactors. The German chemist Robert Bunsen and physicist Gustav Kirchhoff discovered caesium in 1860 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy. The first small-scale applications for caesium wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |