|
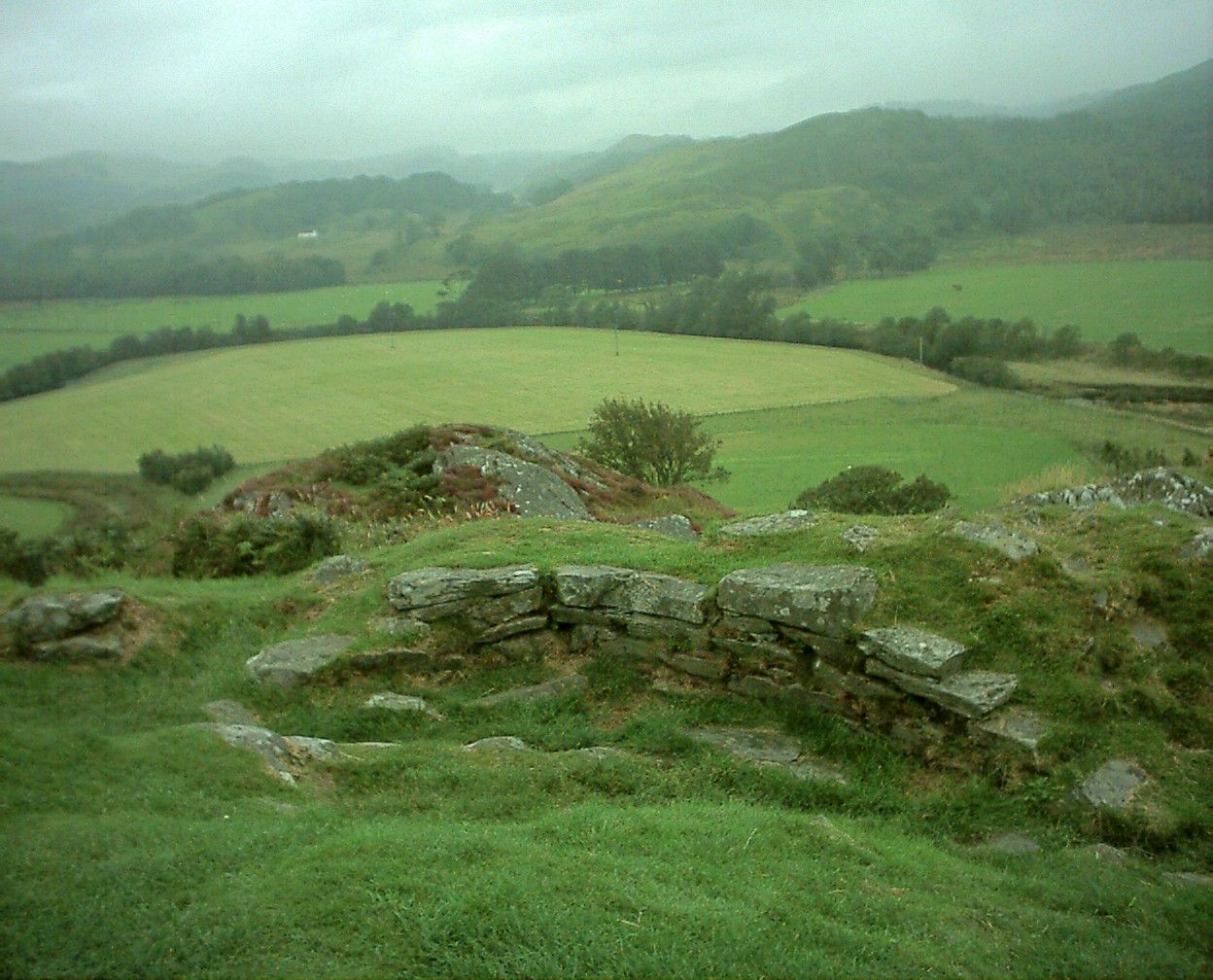
Cadson Bury
Cadson Bury is an Iron Age hillfort about south-west of Callington, in Cornwall, England. It is owned by the National Trust,Cadsonbury Camp, Cadsonbury National Trust Heritage Records Online. Retrieved 16 November 2017. and it is . Description The fort is sited in a commanding position on a steep hill, called Cadson Bury Down, above the River Lynher. It is , pro ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callington, Cornwall
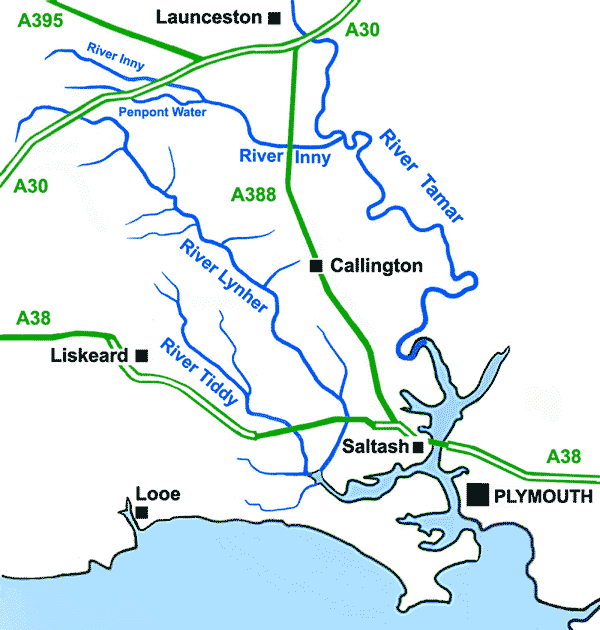
Callington () is a civil parish and town in east Cornwall, England, United Kingdom about north of Saltash and south of Launceston. Callington parish had a population of 4,783 in 2001, according to the 2001 census. This had increased to 5,786 in the 2011 census. Geography The town is situated in east Cornwall between Dartmoor to the east and Bodmin Moor to the west. A former agricultural market town, it lies at the intersection of the south–north A388 Saltash to Launceston road and the east–west A390 Tavistock to Liskeard road. Kit Hill is a mile north-east of the town and rises to with views of Dartmoor, Bodmin Moor and the River Tamar. The hamlets of Bowling Green, Kelly Bray, Frogwell and Downgate are in the parish. Railway station Callington railway station was the terminus of a branch line from Bere Alston, the junction with the Southern Railway's Tavistock to Plymouth line. The railway line beyond Gunnislake to the Callington terminus was closed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
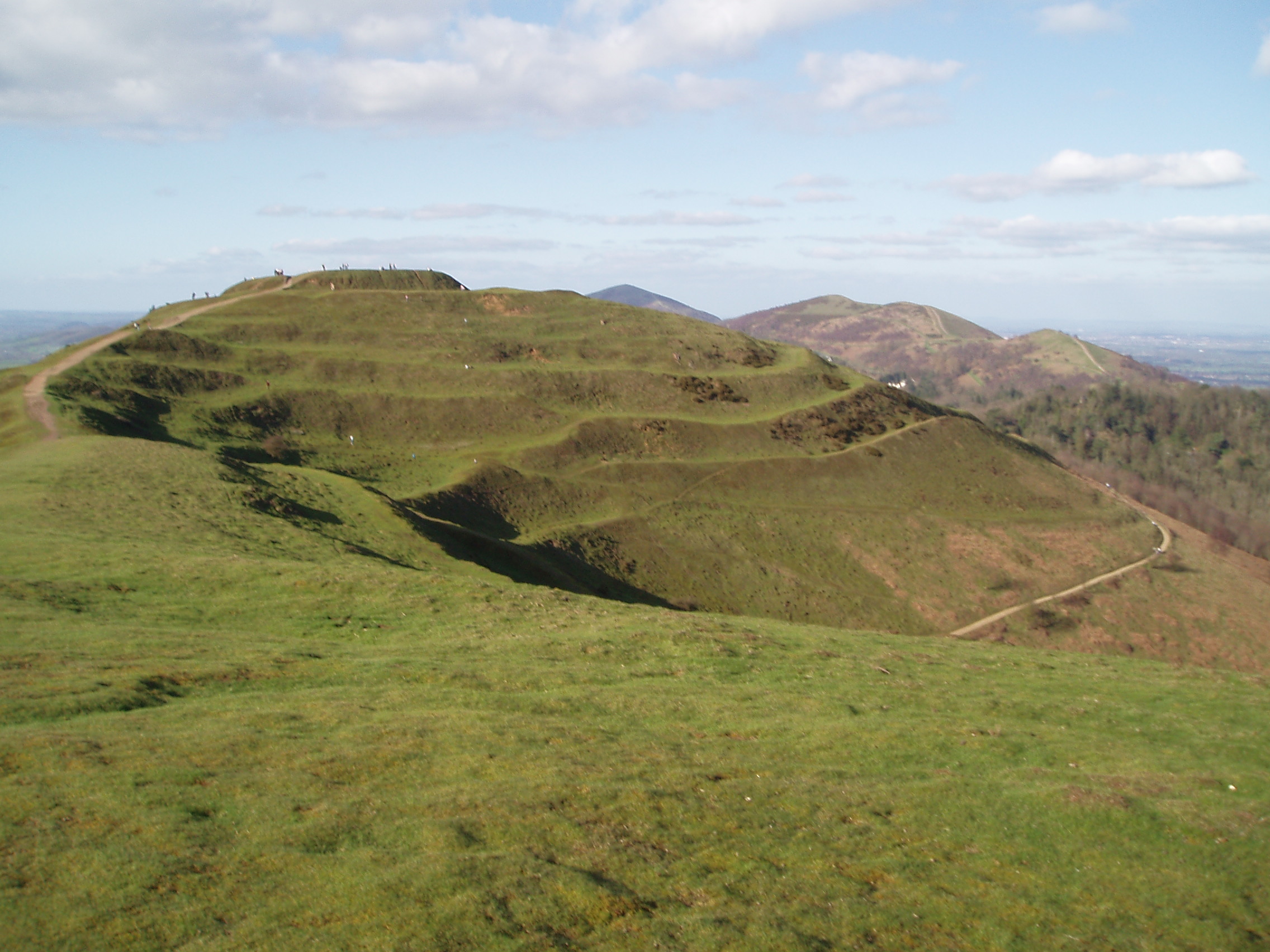
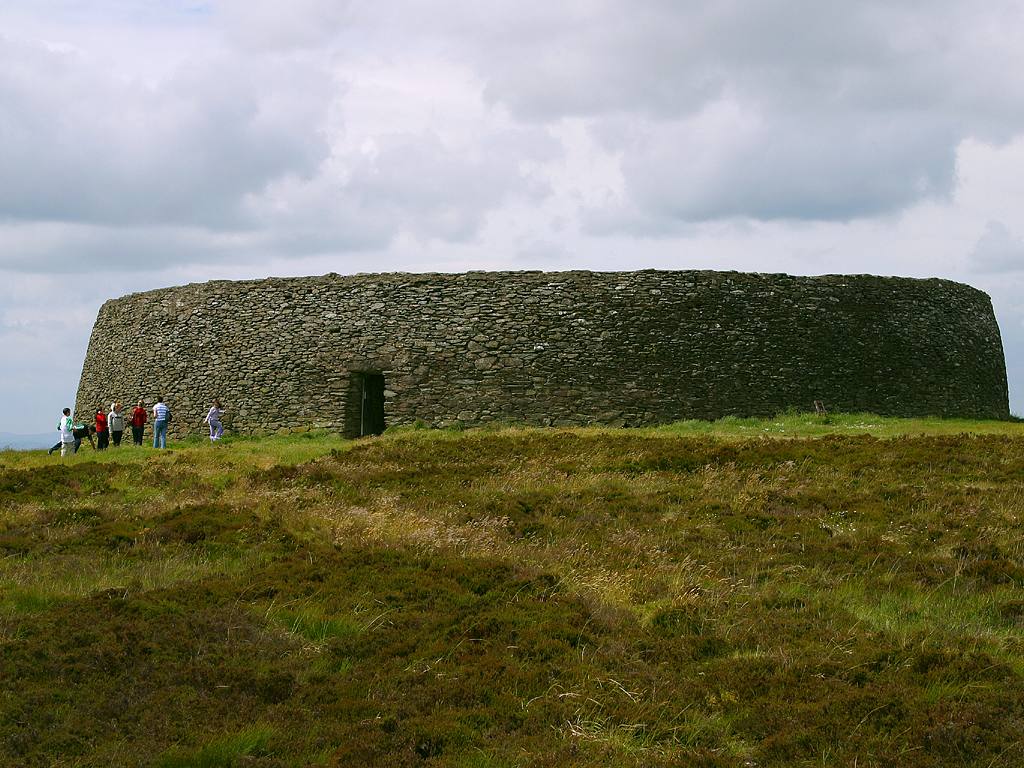
Hillfort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roman Empire, Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of Earthworks (Archaeology), earthworks or stone Rampart (fortification), ramparts, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. If enemies were approaching, the inhabitants would spot them from a distance. Prehistoric Europe saw a growing population. It has been estimated that in about 5000 BC during the Neolithic between 2 million and 5 million lived in Europe; in the Late Iron Age it had an estimated population of around 15 to 30 million. Outside Greece and Italy, which were more densely populated, the vast majority of settlements in the Iron Age were small, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Iron Age
The British Iron Age is a conventional name used in the archaeology of Great Britain, referring to the prehistoric and protohistoric phases of the Iron Age culture of the main island and the smaller islands, typically excluding prehistoric Ireland, which had an Iron Age Ireland, independent Iron Age culture of its own. The Iron Age is not an archaeological horizon of common artefacts but is rather a locally-diverse cultural phase. The British Iron Age followed the Bronze Age Britain, British Bronze Age and lasted in theory from the first significant use of iron for tools and weapons in Britain to the Romano-British culture, Romanisation of the southern half of the island. The Romanised culture is termed Roman Britain and is considered to supplant the British Iron Age. The tribes living in Britain during this time are often popularly considered to be part of a broadly-Celts, Celtic culture, but in recent years, that has been disputed. At a minimum, "Celtic" is a linguistic ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillfort
A hillfort is a type of fortification, fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late Bronze Age Europe, European Bronze Age and Iron Age Europe, Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roman Empire, Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of Earthworks (Archaeology), earthworks or stone Rampart (fortification), ramparts, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. If enemies were approaching, the inhabitants would spot them from a distance. Prehistoric Europe saw a growing population. It has been estimated that in about 5000 BC during the Neolithic between 2 million and 5 million lived in Europe; in the Late Iron Age it had an estimated population of around 15 to 30 million. Outside Greece and Italy, which were more densely populated, the vast majority of settlements in the Iron Age were small, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, Devon to the east, and the English Channel to the south. The largest urban area is the Redruth and Camborne conurbation. The county is predominantly rural, with an area of and population of 568,210. After the Redruth-Camborne conurbation, the largest settlements are Falmouth, Cornwall, Falmouth, Penzance, Newquay, St Austell, and Truro. For Local government in England, local government purposes most of Cornwall is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, with the Isles of Scilly governed by a Council of the Isles of Scilly, unique local authority. The Cornish nationalism, Cornish nationalist movement disputes the constitutional status of Cornwall and seeks greater autonomy within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is the weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Trust
The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the permanent preservation for the benefit of the Nation of lands and tenements (including buildings) of beauty or historic interest". It has since been given statutory powers, starting with the National Trust Act 1907. Historically, the Trust acquired land by gift and sometimes by public subscription and appeal, but after World War II the loss of country houses resulted in many such properties being acquired either by gift from the former owners or through the National Land Fund. One of the largest landowners in the United Kingdom, the Trust owns almost of land and of coast. Its properties include more than 500 historic houses, castles, archaeological and industrial monuments, gardens, parks, and nature reserves. Most properties are open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Monument
In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change. The various pieces of legislation that legally protect heritage assets from damage, visual disturbance, and destruction are grouped under the term "Designation (heritage assets), designation". The protection provided to scheduled monuments is given under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979, which is a different law from that used for listed buildings (which fall within the town and country planning system). A heritage asset is a part of the historic environment that is valued because of its historic, archaeological, architectural or artistic interest. Only some of these are judged to be important enough to have extra legal protection through designation. There are about 20,000 scheduled monuments in England representing about 37,000 heritage assets. Of the tens of thousands of scheduled monuments in the UK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Lynher
The River Lynher () (or St Germans River downstream from its confluence with the Tiddy) flows through east Cornwall, England, and enters the River Tamar at the Hamoaze, which in turn flows into Plymouth Sound. Navigation The normal tidal limit is a weir upstream of Notter Bridge. St Germans is a historic fishing village situated on the River Tiddy just upstream of its confluence with the Lynher. The Quay Sailing Club are based at St Germans Quay. The Queen's Harbour Master for Plymouth is responsible for managing navigation on the tidal Lynher and its tributaries (up to the normal tidal limits). Geography The river is about 21 miles (34 km long), rising at a height of about 920 feet (280m) on Bodmin Moor and flowing into the Tamar Estuary near Plymouth. It has four main tributaries, the largest of which is the River Tiddy. The smaller tributaries include Deans Brook, Withey Brook, Marke Valley and Darleyford streams and Kelly Brook. Ecology The Lynher and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Univallate
A hillfort is a type of fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late European Bronze Age and Iron Age. Some were used in the post- Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of earthworks or stone ramparts, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. If enemies were approaching, the inhabitants would spot them from a distance. Prehistoric Europe saw a growing population. It has been estimated that in about 5000 BC during the Neolithic between 2 million and 5 million lived in Europe; in the Late Iron Age it had an estimated population of around 15 to 30 million. Outside Greece and Italy, which were more densely populated, the vast majority of settlements in the Iron Age were small, with perhaps no more than 50 inhabitants. Hillforts were the exception, and were the home of up to 1,000 p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillforts In Britain
Hillforts in Britain refers to the various hillforts within the island of Great Britain. Although the earliest such constructs fitting this description come from the Neolithic British Isles, with a few also dating to later Bronze Age Britain, British hillforts were primarily constructed during the British Iron Age. Some of these were apparently abandoned in the southern areas that were a part of Roman Britain, although at the same time, those areas of northern Britain that remained free from Roman occupation saw an increase in their construction. Some hillforts were reused in the Early Middle Ages, and in some rarer cases, into the later medieval period as well. By the early modern period, these had essentially all been abandoned, with many being excavated by archaeology, archaeologists in the nineteenth century onward. There are around 3,300 structures that can be classed as hillforts or similar "defended enclosures" within Britain. Most of these are clustered in certain regions: s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill Forts In Cornwall
There are over 80 hillforts in Cornwall dating from the Iron Age, Ancient Rome, Roman and post-Roman periods, with most showing evidence of occupation and re-occupation by the Cornish people, Cornish Cornovii (Cornish), Cornovii tribe. Two of the most impressive, at opposite ends of Cornwall, are Chûn Castle, near Penzance and Warbstow Bury in North East Cornwall. Others can be found at Caer Bran, Castle an Dinas, St. Columb Major, Castle An Dinas (Goss Moor), Castle an Dinas (Penzance), Castle Canyke, Kelly Rounds, Cadson Bury, Resugga Castle, Helsbury near Michaelstow, St Dennis, Cornwall, St Dennis, Gear fort, Lescudjack Hillfort, Prideaux Castle, and Castle Dore. Promontory forts or cliff top forts were also common in the Iron Age and examples of these are at Trevelgue Head, Trevelgue near Newquay, Maen Castle near Sennen, St Michael's at Rame Head, Dodman Point (near Gorran Haven), Treryn Dinas (site of Logan Rock), Trereen Dinas (Gurnard's Head) and The Rumps (near St Minv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |